Methods of identifying, isolating and using odorant and aroma receptors
An odor and receptor technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, etc., can solve problems such as incompatibility and inability to function normally
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
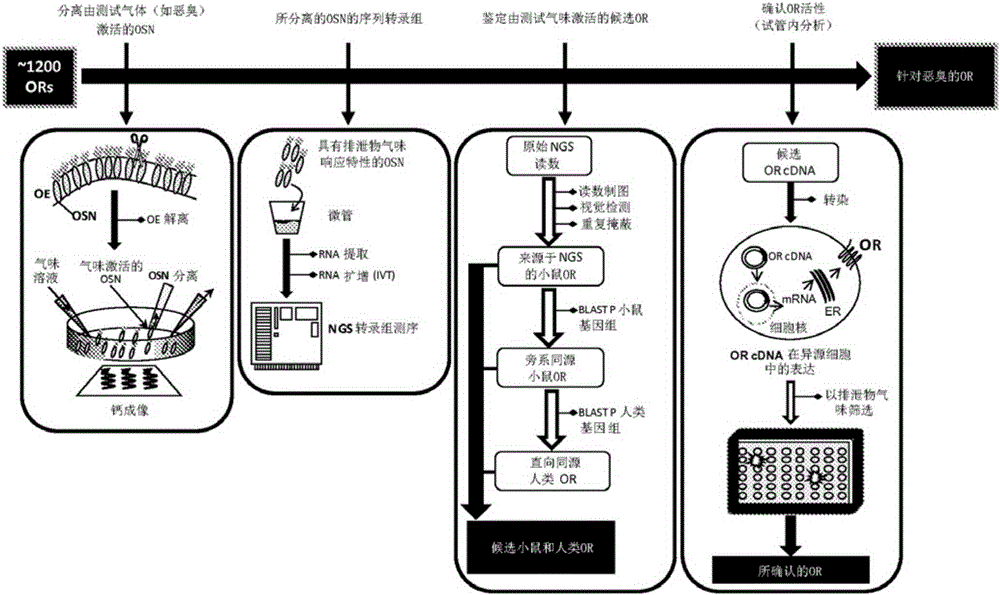
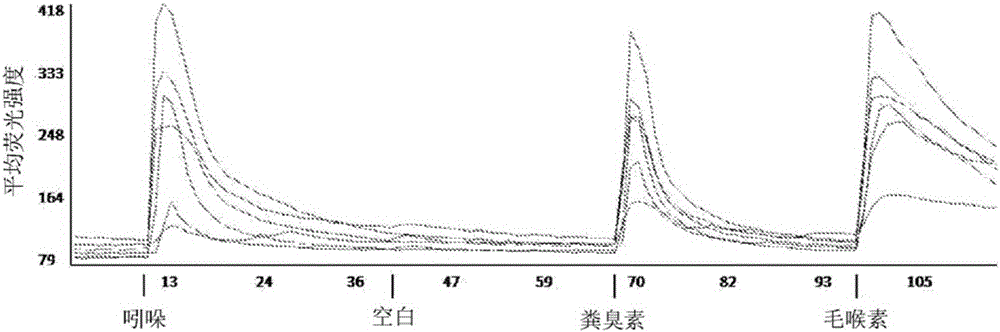
[0095] Screening of mouse olfactory sensory neurons to identify receptors that bind indole and / or skatole
[0096] The olfactory epithelium containing native olfactory nerves from mice was isolated and dissociated into single cells, then transferred to dissociation buffer for gentle mechanical and enzymatic dissociation. To optimize the dissociation method, the general procedure for preparing fresh dissociation buffer described in Araneda et al. (2004), A Pharmacological Profile of the Aldehyde Receptor Repertoire in Rat Olfactory Epithelium. Journal of Physiology: 555:743-756 was followed with the following modifications: DNase II was replaced by DNase I, Ca 2+ The concentration was raised to 5 mM and the pH was adjusted to 7.35 at 32°C. Dissociated neurons were then seeded on coverslips to allow selection of >2500 cells using fluorescence microscopy. Cells were then loaded with a calcium sensitive dye (Fura-2AM) for 30 minutes at 31°C and transferred to a microscope ready ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Isolation and amplification of mRNA from indole- and skatole-sensitive cells to generate the cDNA sequence of the "stink" gene for indole- and skatole-sensitive receptors
[0100] The activated olfactory neurons of Example 1 were isolated using glass micropipettes and then pooled into one sample for subsequent identification of odorant receptor genes expressed as mRNA in responding cells. Odor receptor gene sequences were identified from indole- and skatole-sensitive cells by placing four groups of more than five (5) olfactory neurons activated by one or more malodorous compounds ( 6, 10, 15 and 15 cells each) were isolated. Micropipettes were designed from borosilicate glass (Catalog No. B150-86-10, Sutter Instruments) and pulled using a microelectrode puller (Model P-1000, Sutter Instruments) under the following conditions: heat, ramp temperature +20°C ; Pull=0; Vel=120; Pressure=500. Pulled pipette tips were manually broken and mounted to a Newport micromanipulator...
Embodiment 3
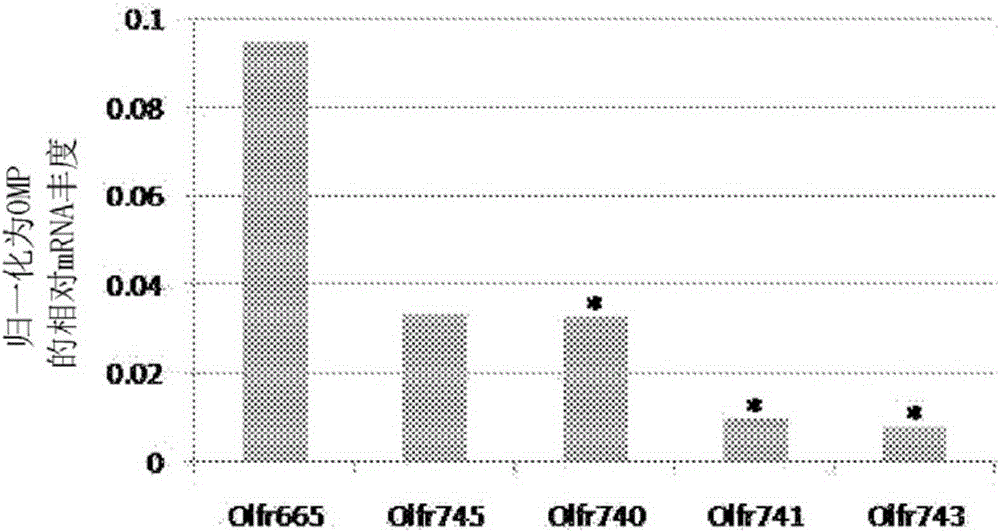
[0104] Identification of mouse and human malodour receptors
[0105] Identification of a subset of 5 mouse indole and skatole ORs out of approximately 1200 ORs in the mouse genome by coupled calcium imaging and NGS (Examples 1-2) enabled in silico additional mouse and new Rapid identification of human indole and skatole OR. As ORs with similar overall amino acid identities may display similar odor response profiles [Adipietro et al. (2012)], mouse OR sequences obtained by NGS analysis of indole / skatole-sensitive olfactory sensory neurons isolated using calcium imaging The OR list of candidate indole and skatole was expanded by querying public mouse and human genome databases. The identity of the mouse malodorous olfactory receptor was determined by comparing the NGS results to a reference genome sequence of the same species. Putative malodor receptors would be the most abundant mRNA in olfactory neuron-derived NGS samples or present in more than one independent biological re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com