Low-temperature cold-start fuel cell system and use method therefor
A fuel cell system and fuel cell technology, used in the field of low temperature cold start of fuel cells and fuel cells, can solve the problems of stack leakage, permanent burnout of membrane electrodes, irreversible damage of membrane electrodes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
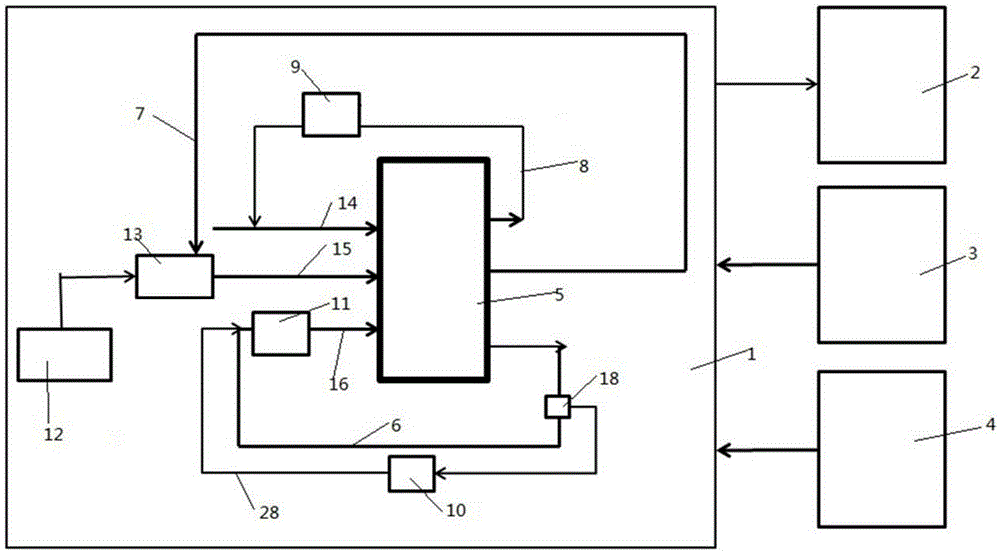
[0026] This embodiment is a comparative example. The above liquid-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell is used. After the last startup is completed, the cathode circuit 7 and the anode circuit 8 are purged with inert gas nitrogen until it contains a small amount of water. The start-up temperature is -10℃, and the normal start-up temperature is 5℃. The fuel cell adopts figure 1 Connection shown. Taking electric heating as an example, it requires 374kJ of energy to heat the stack only by heating the coolant, that is, heating the cooling inlet pipe 16 to cold start the fuel cell. If a 600W electric heater is used, regardless of energy loss and heat loss, the system needs to be heated for at least 10 minutes to reach the start-up temperature of 5°C, and then 0.1A / cm 2 When the current density is added to the electric terminal load, it reaches 25°C in about 3.5 minutes, and the fuel cell starts at -10°C, and it takes about 23.5 minutes to reach full power operating conditions....
Embodiment 2
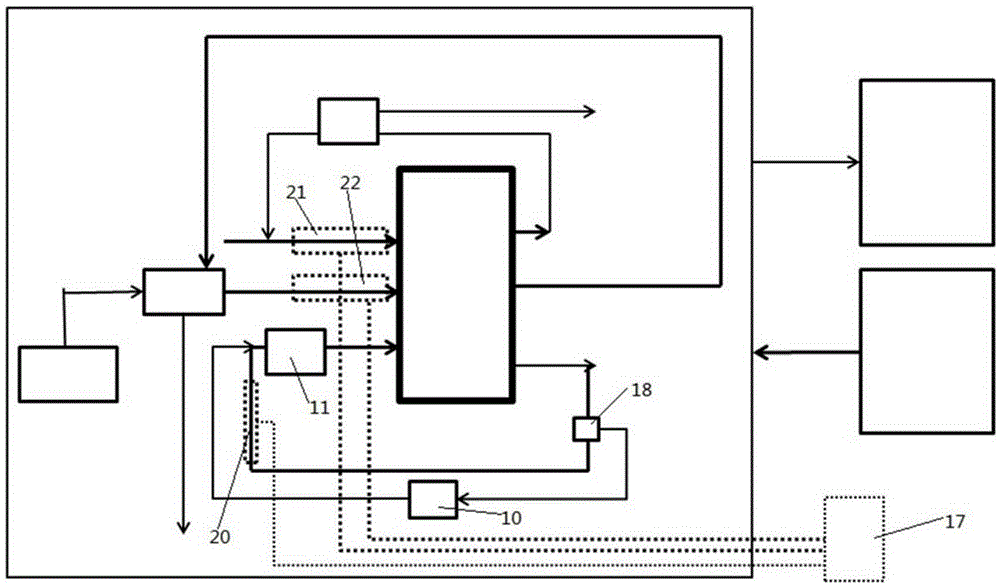
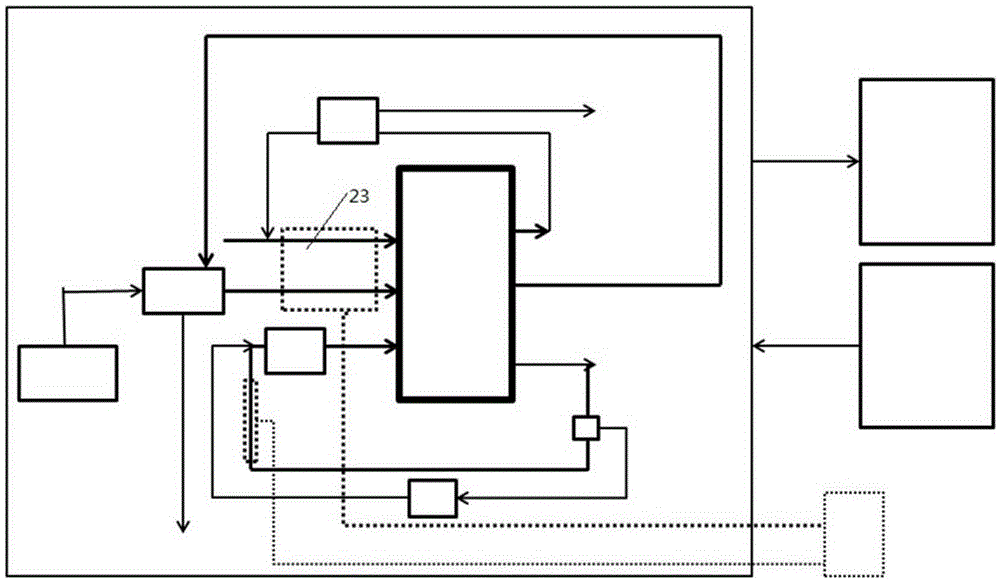
[0028] This embodiment uses the above-mentioned liquid-cooled stack, the startup temperature is -10°C, and the normal startup temperature is raised to 5°C. The fuel cell uses figure 2 Connection shown. The electric heating method is adopted to heat the stack only by heating the cathode and anode gas, that is, heating the anode inlet pipe 14 and the cathode inlet pipe 15 to cold start the fuel cell. To correspond to 0.1A / cm 2 Take the current density gas flow as an example, the anode heating power is 50W, and the cathode heating power is 250W. Considering the redundancy of heat dissipation and energy loss, the gas entering the system at -10 degrees is heated to 60 degrees C, and the two heaters are uniformly controlled. When the heated air flow is passed into the stack, the rate is 0.1A / cm 2 The current density adds the load of the electric terminal. At this time, the power generation of the stack is about 1.5kW, and the heat generation is 1.5kJ / s, the system can reach the start...
Embodiment 3
[0030] This embodiment is a preferred example. The above-mentioned liquid-cooled stack is used, the startup temperature is -10°C, and the normal startup temperature is 5°C. The fuel cell uses figure 2 Connection shown. The electric heating method is adopted to heat the stack by heating the coolant, the cathode and the anode gas, that is, the anode inlet pipe 14, the cathode inlet pipe 15, and the cooling inlet pipe 16 are heated at the same time, so as to cold start the fuel cell. To correspond to 0.1A / cm 2 Take the gas flow of current density as an example. The anode heating power is 50W, the cathode heating power is 250W, and the cooling heating power is 600W. Considering the redundancy of heat dissipation and energy loss, the gas entering the system at -10 degrees is heated to 60 degrees C while heating the coolant. , The three heaters are controlled separately. When the heated air flow is passed into the stack, the rate is 0.1A / cm 2 The current density adds the load of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com