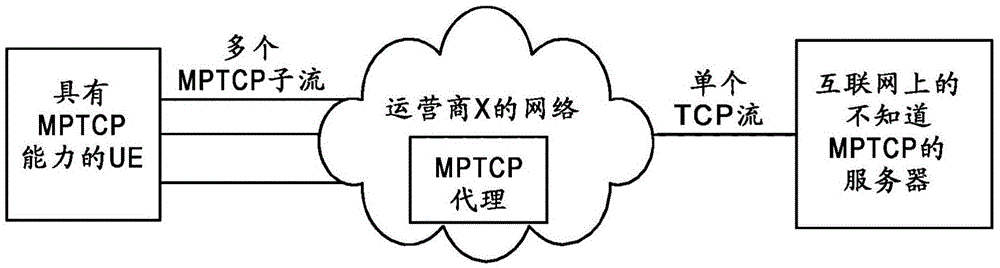
MPTCP scheduling
A technology of scheduler and dispatching station, applied in connection management, wireless communication, transmission system, etc., to achieve the effect of optimizing total throughput and/or cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0068] Example 1 - External information from RATs (3GPPRAN and Wi-Fi)
[0069] like Figure 10 As illustrated in , the RAT can provide input / feedback to the MPTCP proxy 5, and the scheduler 61 in the MPTCP proxy can use this information to take system-level optimized scheduling decisions. In this figure, an MPTCP capable peer 2 is connected with an MPTCP proxy 5 via two subflows 8 (subflow 8a on cellular RAN3, and subflow 8b on Wi-Fi 4). A single flow / subflow 9 connects the proxy 5 to the Internet 6 and the first peer 7 ( Figure 5 )connect. The paths for external information input from the respective RANs 3 and 4 are given as dashed lines in the figure. The figure also shows the Policy Charging and Rules Function (PCRF) 101 and its interface Gx with the MPTCP proxy 5 .
[0070] The MPTCP Proxy 5 is in this example located in a Packet Data Network (PDN) Gateway (P-GW) in the 3GPP network. Peer 2 at the edge of a RAT cell (like a 3GPP RAT cell for LTE or a Wi-Fi cell) ma...
example 2
[0073] Example 2 - External information about available paths to peers is present in the P-GW
[0074] If the MPTCP proxy 5 has information about available paths / subflows 8 to MPTCP capable peers 2, the scheduler 61 can use this information to Evenly distribute peers 2.
[0075] Consider a scenario where all peers 2 in a particular LTE cell are getting very low bandwidth (say 1 Mbps) and some of these peers 2 have both LTE and Wi-Fi Access / substream 8 of both. The P-GW in the 3GPP network knows that Peer 2 has more than one access. So, the scheduler 61 in the MPTCP proxy 5 located in the P-GW can use this information and set Wi-Fi as the preferred subroutine to such a peer 2 which is both LTE capable and Wi-Fi capable. Stream 8. Also, if some peers 2 have a lot of bandwidth over Wi-Fi, the scheduler can stop using LTE for such peers 2 so that other peers 2 that only have LTE sub-flows get better bandwidth. This type of resource sharing will improve overall system perfo...
example 3
[0076] Example 3 — Input related to routing policy
[0077] The MPTCP proxy scheduler 61 can improve overall system performance by applying operator-controlled routing policies. Such policies can be preconfigured in the scheduler, or Access Network Discovery and Selection Function (ANDSF) 111 inputs can be fed back to the MPTCP scheduler. ANDSF rules for MPTCP scheduling can be very similar to existing Intersystem Routing Policy (ISRP) rules.
[0078] This will require a new interface between MPTCP Proxy 5 and ANDSF111. This can basically be ANDSF111 with MPTCP capable peer 2 ( Figure 10-12 A copy of the existing 3GPPS14 interface between UEs). This is illustrated in Figure 11 , where this new interface is referred to as S14' (S14 apostrophe).
[0079] Instead, no new interfaces are defined. Instead, relevant information is sent from ANDSF 111 in a vendor-specific manner to PCRF 101 via proprietary interface Z2, and from PCRF 101 to P-GW via a (vendor-specific) exten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com