A functional textile fabric
A textile fabric and functional technology, which is applied in the field of functional textile fabrics, can solve problems such as low efficiency, and achieve the effect of strengthening the heating and heat storage function, enhancing the heat preservation performance, and improving the drying efficiency of clothes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
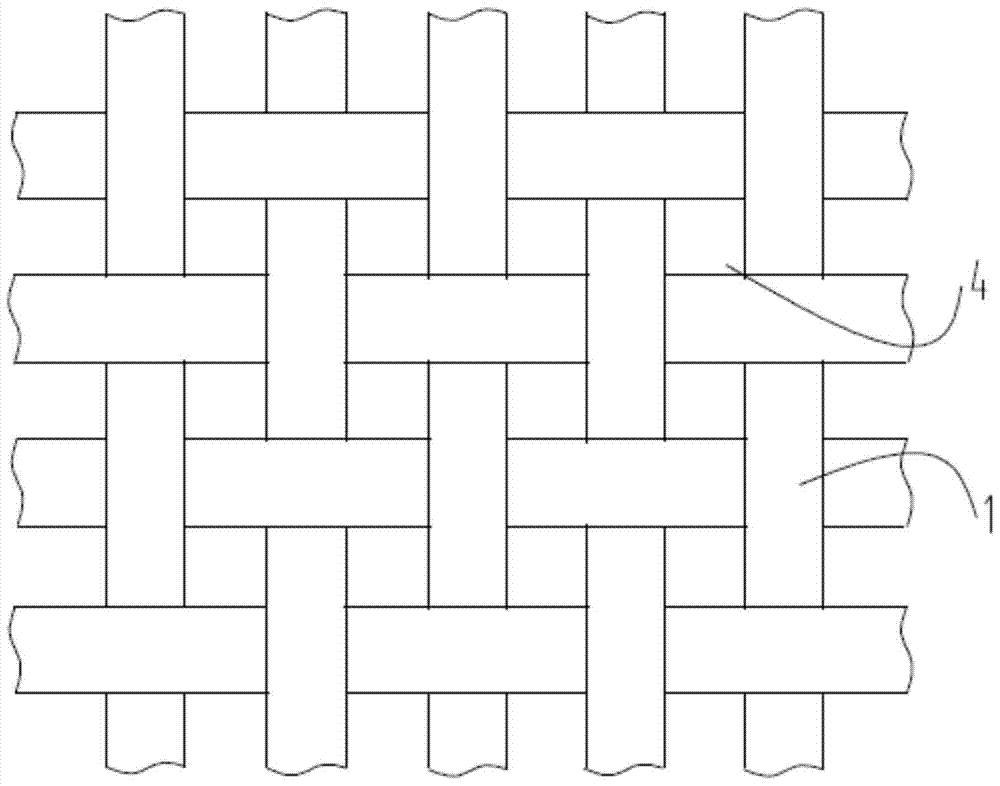
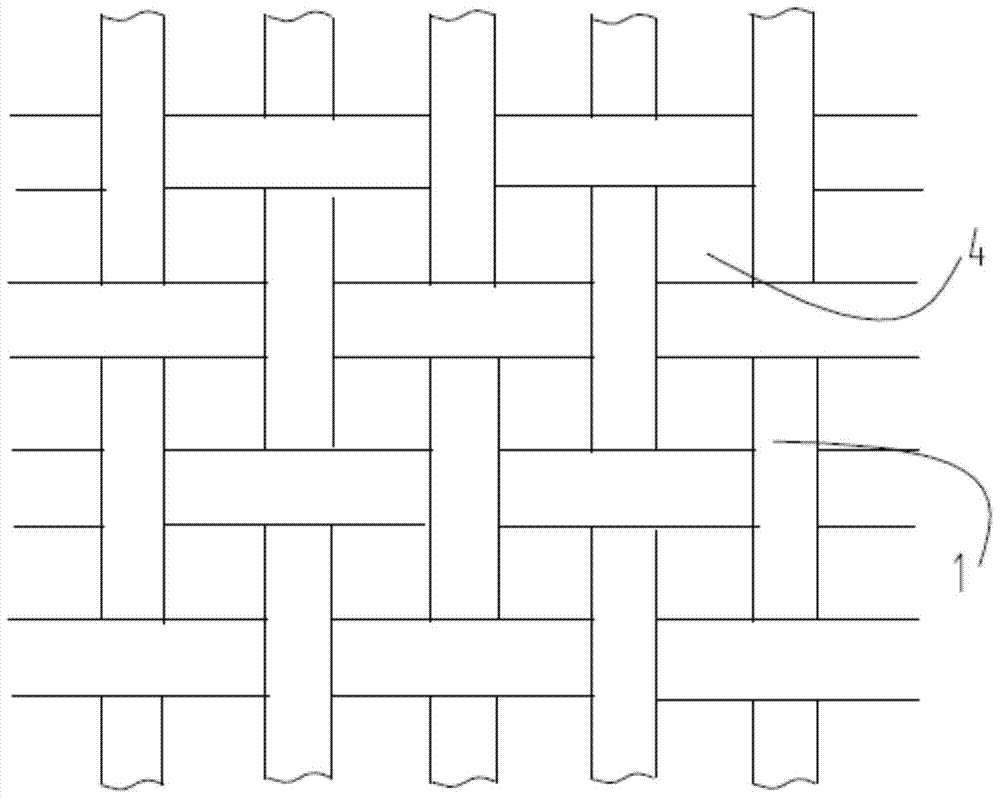
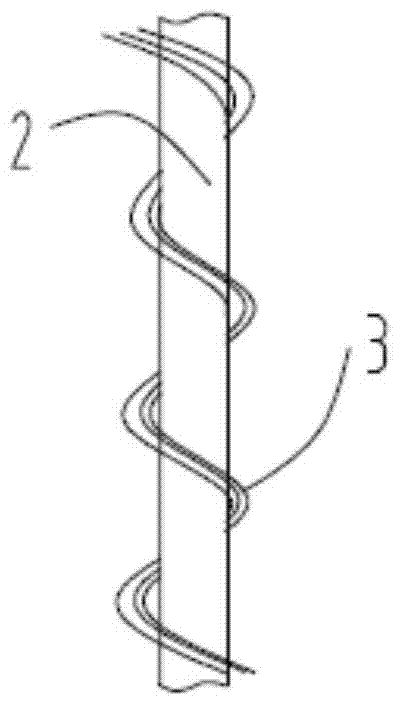
[0019] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram when the fabric is not deformed, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the fabric deformed by water, image 3 Schematic diagram of the structure of the core-spun yarn. Such as figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 As shown, what this embodiment provides is a functional textile fabric, the yarn of the functional textile fabric is a core-spun yarn 1, and the yarn core part 2 is composed of a functional fiber that is beneficial to dehumidification, and the winding part 3 is composed of a functional fiber for temperature raising and heat storage; the functional fiber for temperature raising and heat storage is composed of conventional fiber materials accounting for 99.91% by weight of the total weight of the winding part 3 and 0.09% by weight of the total weight of the winding part 3 The nano-units melt-spun; the functional fiber that is beneficial to dehumidification is a fiber that has a smaller curling rate when encountering water; t...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that: the functional fibers for heat storage and heat storage are composed of conventional fiber materials accounting for 99.95% by weight of the total weight of the winding part 3 and 0.05% by weight of the total weight of the winding part 3 The nano-units are melt-spun; the nano-units include 9000 nanometer particles, and the micro-particles include 500 weight units of zinc, 350 weight units of aluminum and 350 weight units of iron; the number of twists of the yarn core part 2 is 200T / m; the twist number of the winding part 3 is 200T / m.
Embodiment 3
[0026] The difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 is that: the functional fibers for heat storage and heat storage are composed of conventional fiber materials accounting for 99.93% by weight of the total weight of the winding part 3 and 0.07% by weight of the total weight of the winding part 3 The nano-units are melt-spun; the nano-units include 8700 nanometer particles, and the micro-particles include 400 weight units of zinc, 400 weight units of aluminum and 250 weight units of iron; the number of twists of the yarn core part 2 is 150T / m; the twist number of the winding part 3 is 150T / m.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com