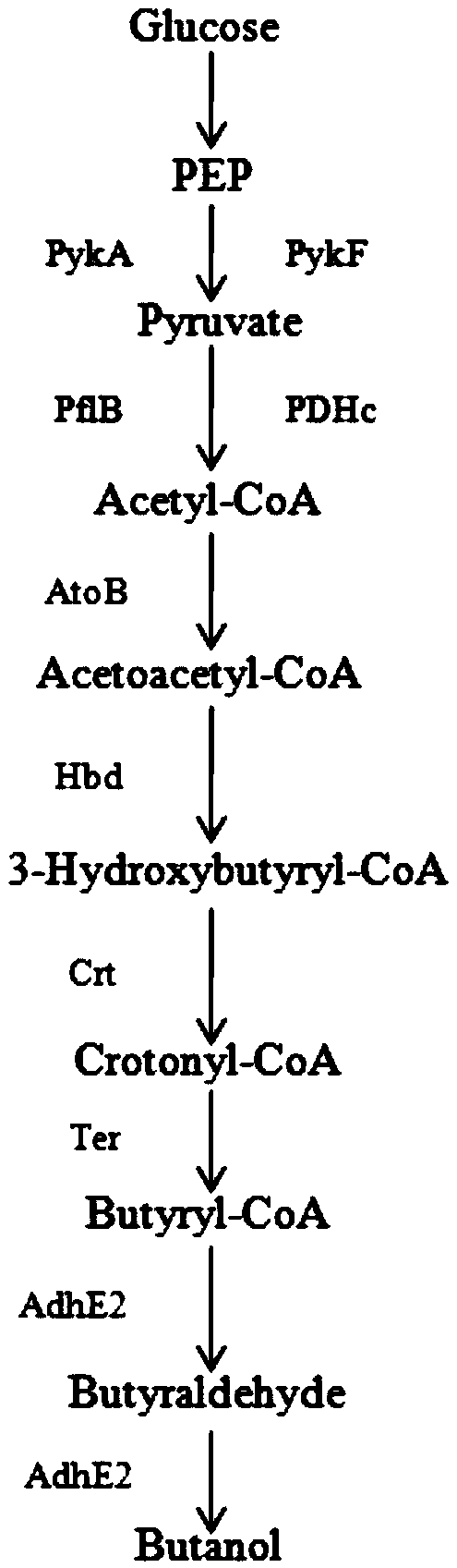
Method for improving yield of butanol produced by escherichia coli
A technology for producing butanol and Escherichia coli, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of Clostridium not showing sufficient advantages and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
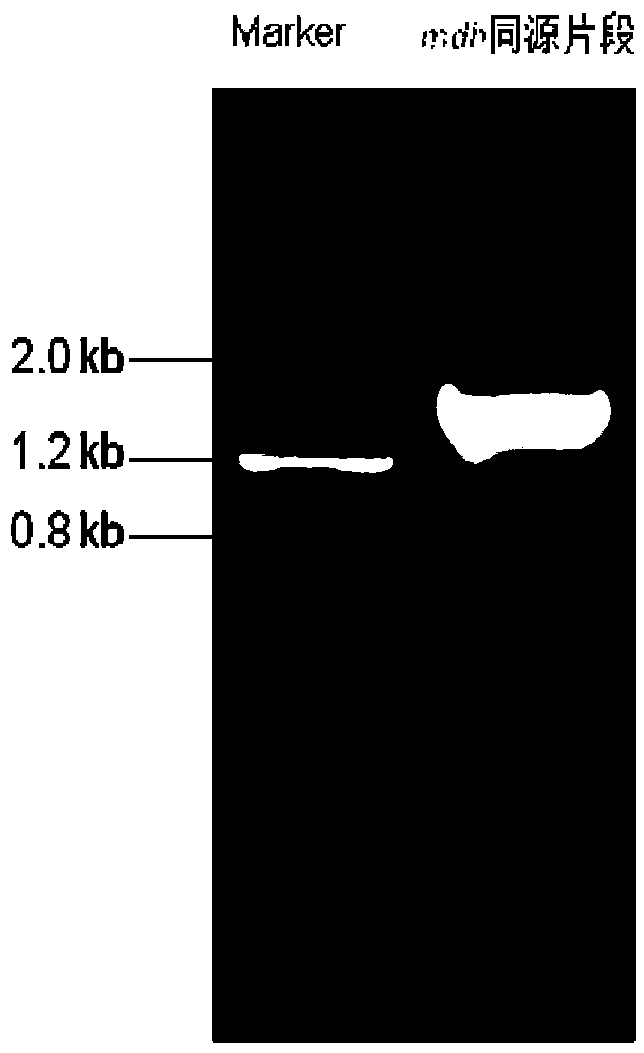
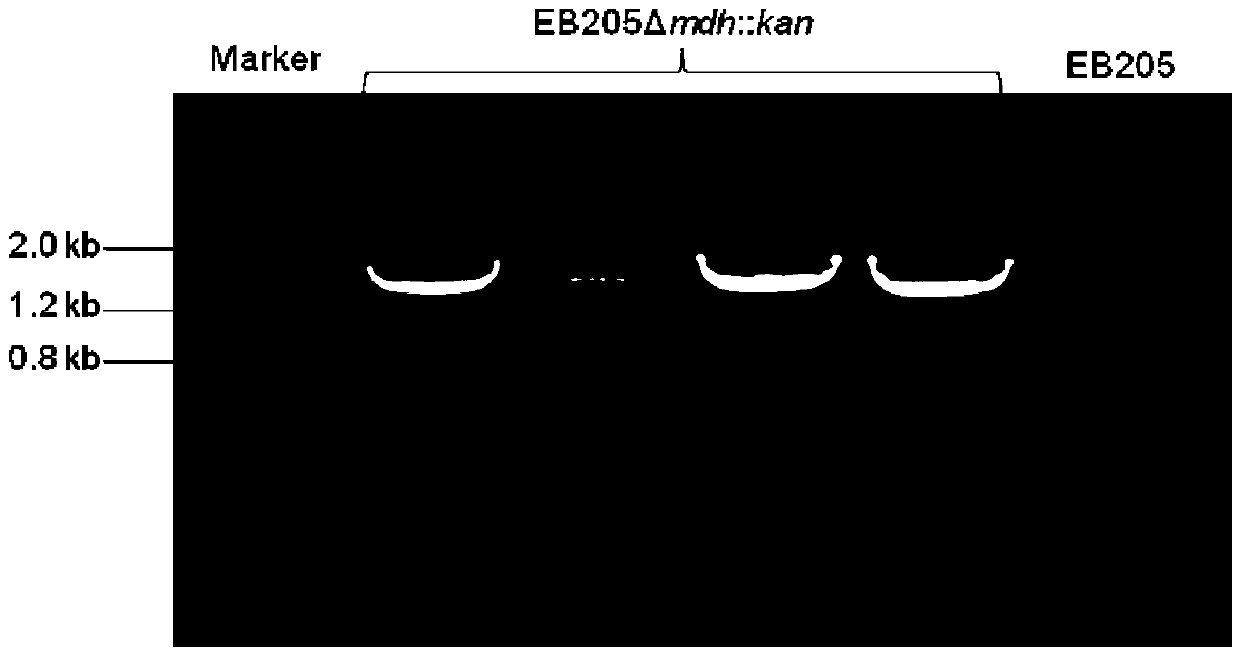
[0034] Embodiment 1, preparation of recombinant bacteria by knocking out the mdh gene in Escherichia coli EB205
[0035] The following examples use the λ-red homologous recombination system to knock out the mdh gene, involving the plasmids:
[0036] pKD4 is described in the following documents: Datsenko, Kirill A., and Barry L. Wanner. One-step in activation of chromosomal genes in Escherichiacoli K-12 using PCR products. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences 97.12 (2000): 6640-6645;
[0037] pKD46 is described in the following documents: Datsenko, Kirill A., and Barry L. Wanner. One-step in activation of chromosomal genes in Escherichiacoli K-12 using PCR products. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences 97.12 (2000): 6640-6645;
[0038] The nucleotide sequence of the mdh gene is sequence 1 in the sequence listing, and the amino acid sequence of the protein malate dehydrogenase encoded by it is sequence 3 in the sequence listing.
[0039] 1. Preparation of re...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2, fermentation of recombinant bacteria EB205△mdh::kan
[0064] The recombinant bacteria EB205△mdh::kan obtained in Example 1 and the control strain EB205 were inoculated into 10ml of M9Y medium in a centrifuge tube with a capacity of 15ml with a sterilized toothpick, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C after inoculation with a toothpick. Place and ferment for 2 days to obtain a fermented liquid. Experiments were repeated three times.
[0065] The above-mentioned M9Y medium is composed of 17.1g / lNa 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O, 3.0g / lKH 2 PO 4 , 0.5g / lNaCl, 2.5g / lNH 4 Cl, 2g / l YeastExtract, 22g / lC 6 h 12 o 6 ·H 2 O, 2mM MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.1mM CaCl 2 and water composition.
[0066] The supernatant after the centrifugation of the above-mentioned fermentation broth was filtered through a filter with a pore size of 0.22 μm and then analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. The analysis used an Agilent 1260 liquid chromatograph, a diff...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com