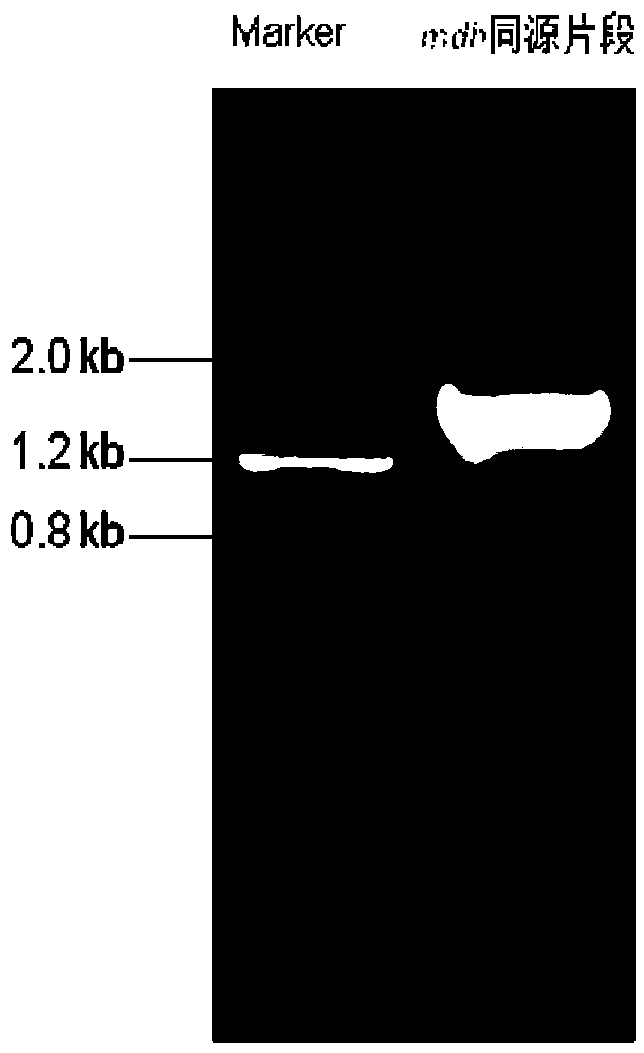
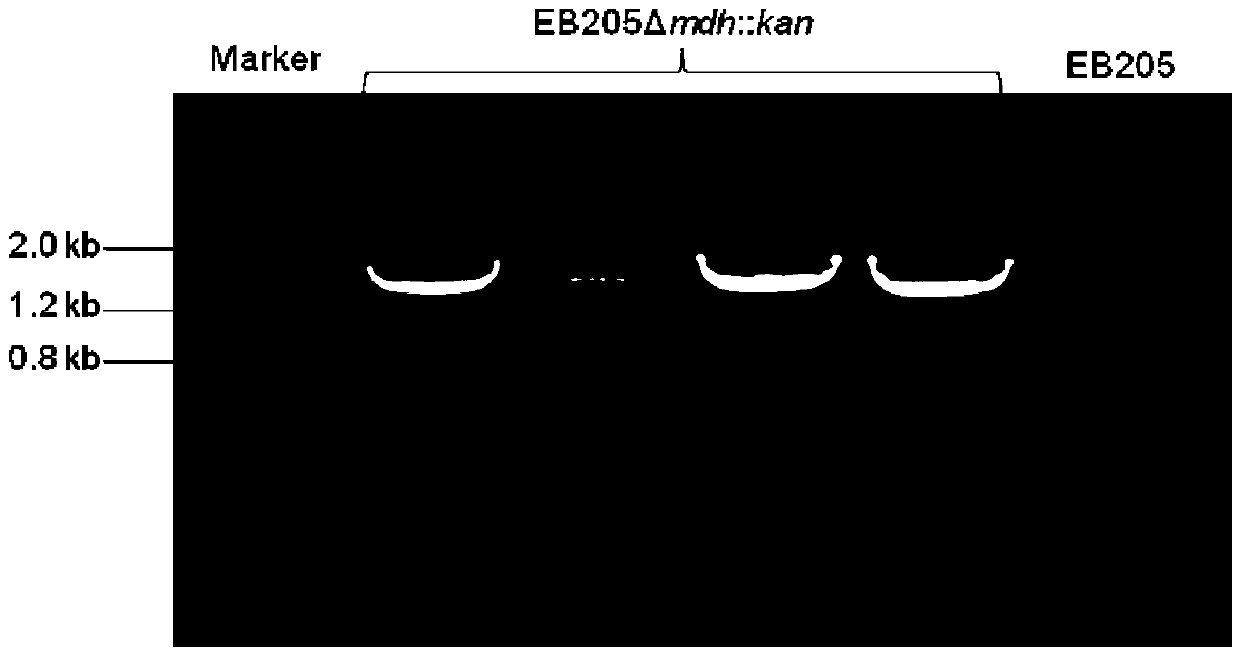
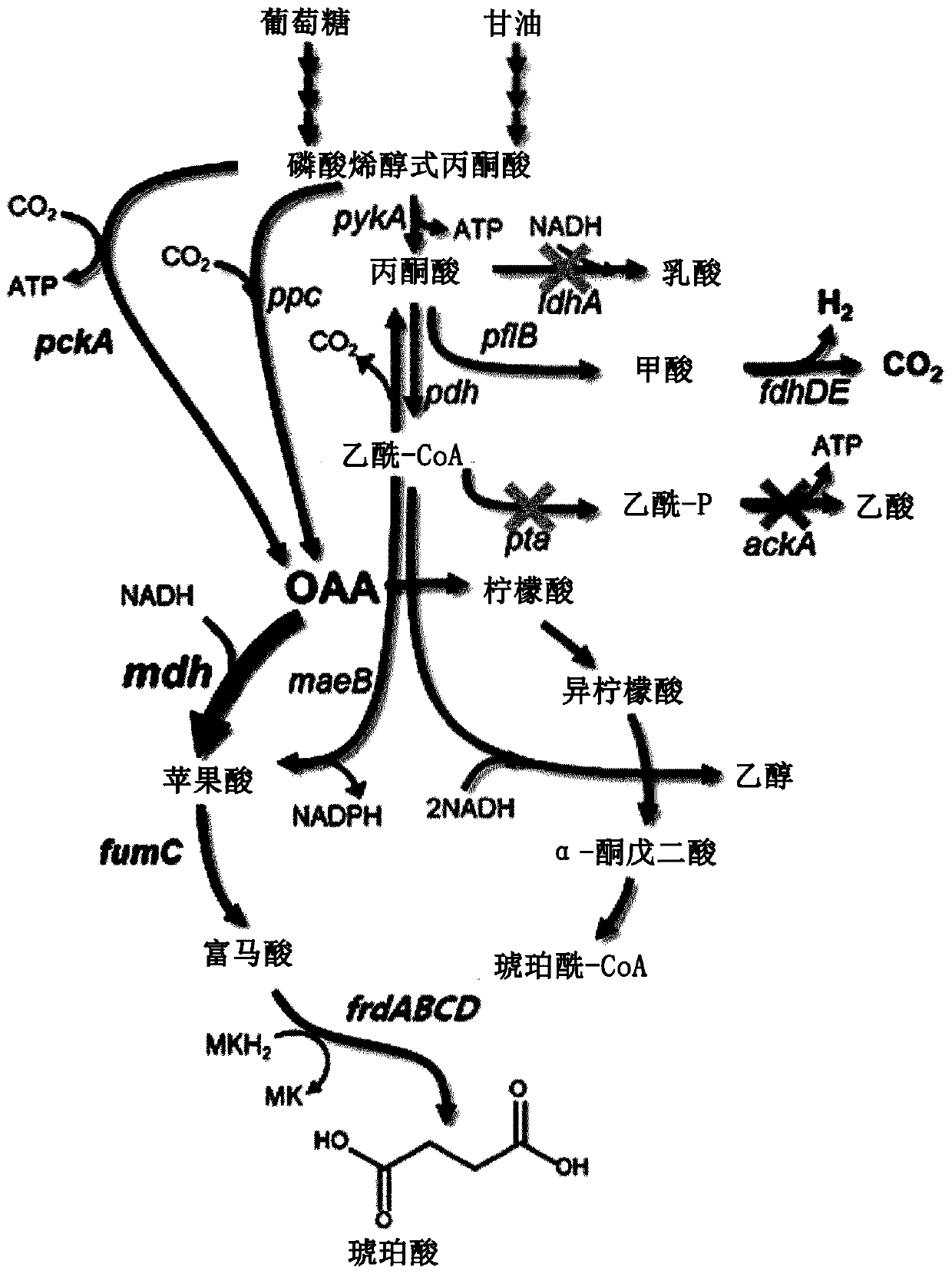
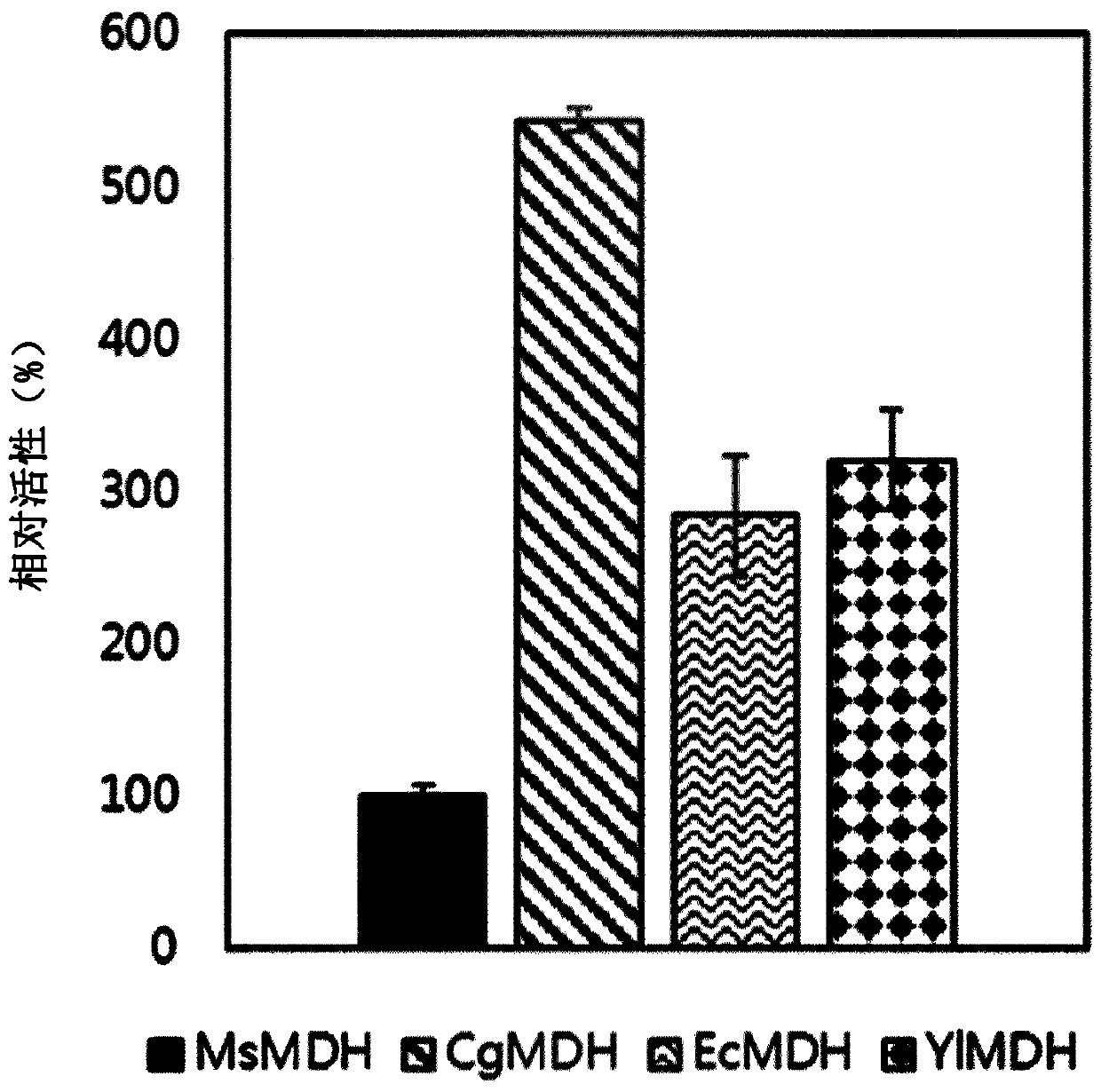
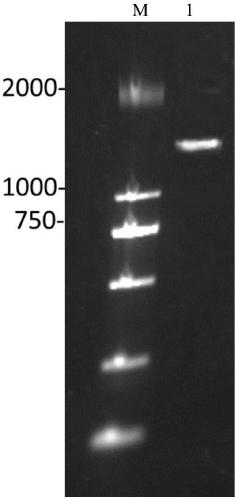
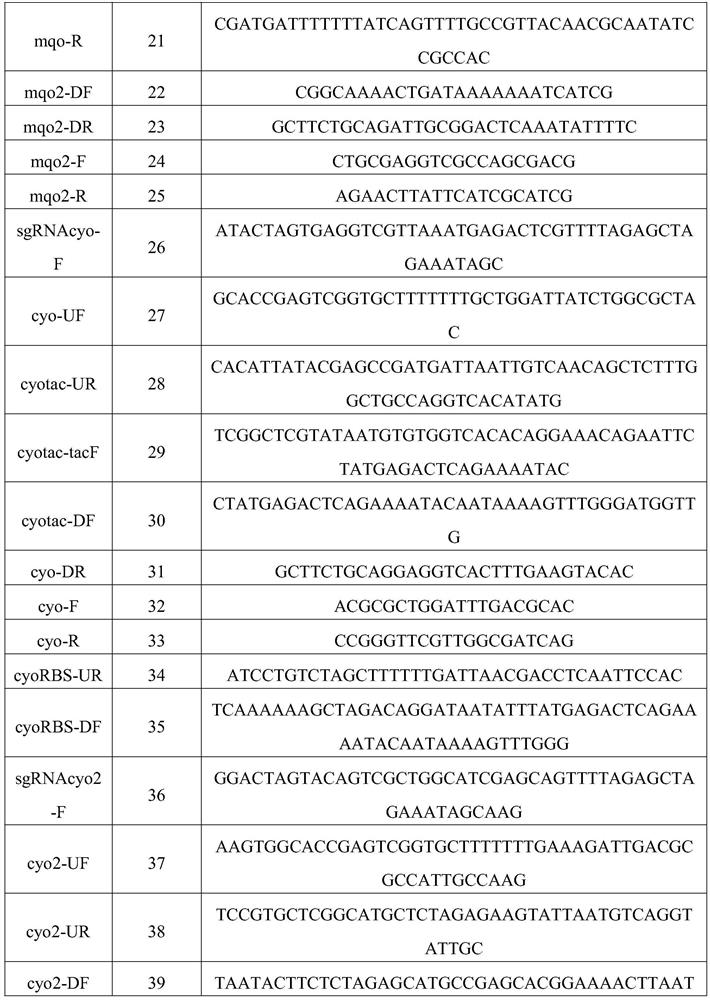
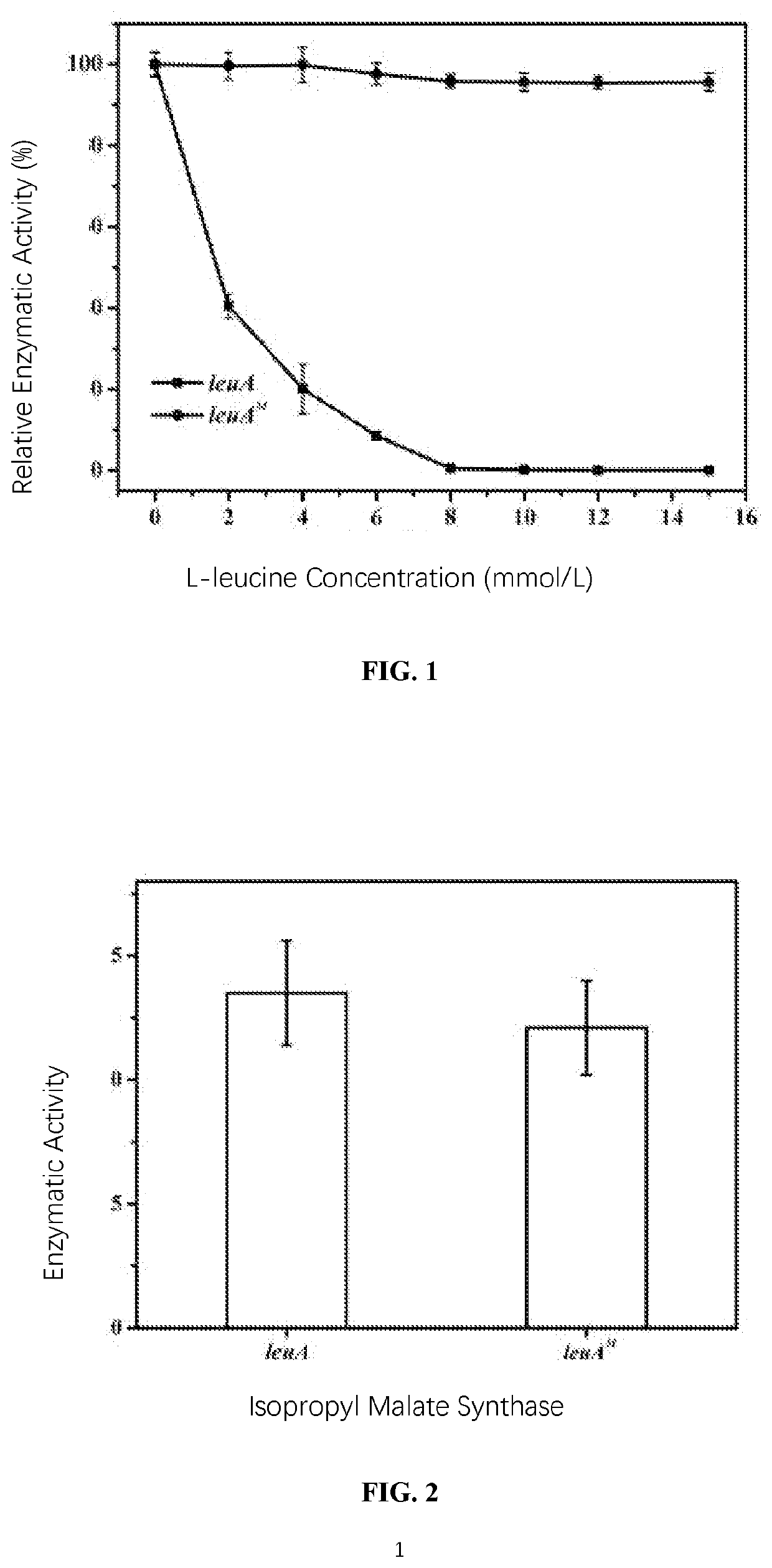
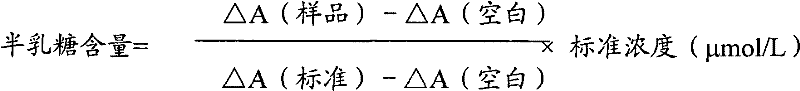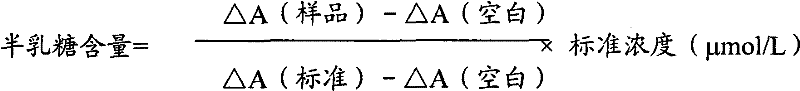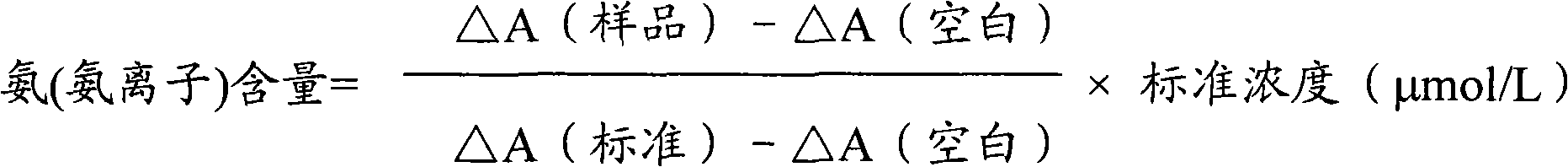Patents
Literature
41 results about "Malate quinone oxidoreductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
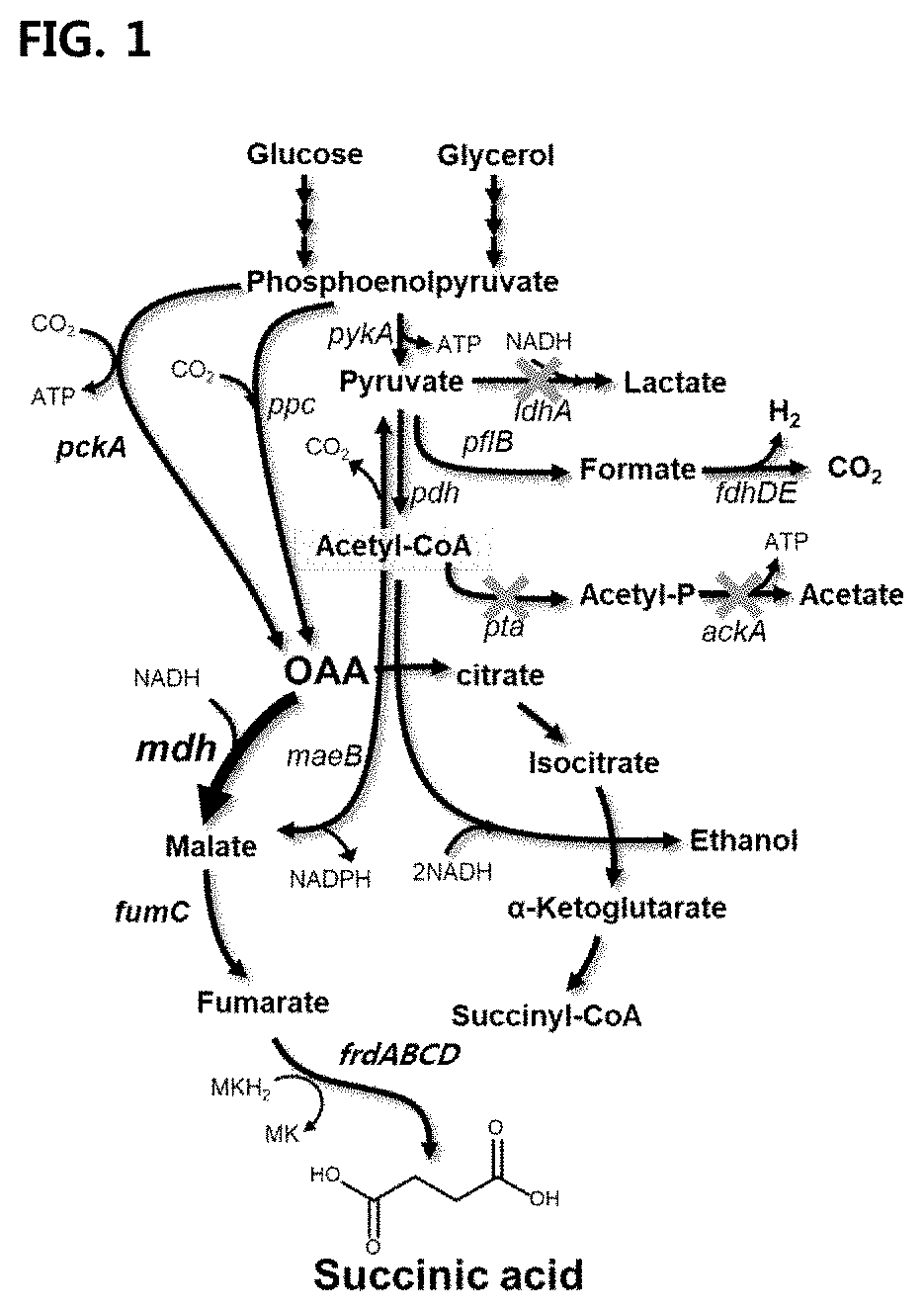
The systematic name of this enzyme class is (S)-malate:quinone oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include FAD-dependent malate-vitamin K reductase, malate-vitamin K reductase, and (S)-malate:(quinone) oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in pyruvate metabolism. It employs one cofactor, FAD.
Methods for improving malic acid production in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS20110053233A1Reduce mitochondrial importImprove the level ofFungiPeptidesHeterologousNucleotide
The present invention relates to methods of producing a C4 dicarboxylic acid, comprising: (a) cultivating a filamentous fungal host cell comprising a polynucleotide selected from the group consisting of a heterologous first polynucleotide encoding a C4 dicarboxylic acid transporter, a heterologous second polynucleotide encoding a malate dehydrogenase, and a heterologous third polynucleotide encoding a pyruvate carboxylase; wherein the filamentous fungal host cell is capable of secreting increased levels of the C4 dicarboxylic acid compared to the filamentous fungal host cell without the heterologous polynucleotide when cultivated under the same conditions; and (b) recovering the C4 dicarboxylic acid. The present invention also relates to methods for increasing C4 dicarboxylic acid production, filamentous fungal host cells and malate dehydrogenase variants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid and construction method and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineering bacterial strain for producing L-malic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. In the invention, key phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase(PEPCK) related to the L-malic acid, malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and fumarase (FumC) are transformed to obtain the gene engineering bacterial strain; a deactivation mutation is carried out on the fumCto cause the interruption of a metabolic flux at the converting position from the malic acid to the fumaric acid so as to accumulate the target product L-malic acid; before the mdh, the promoter of aninner source pepck gene is added to generate the metabolic flux biased towards the malic acid; in addition, through the inducement of monofluorine sodium acetate, the activity of the PEPCK is improved, and the product feedback inhibition is greatly reduced. The bacterial strain applied to the fermentative production of the L-malic acid so as to obviously improve the yield of L-malic acid. The invention has advantages of simple technology, obvious effect and low cost and can satisfy the demand of markets.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
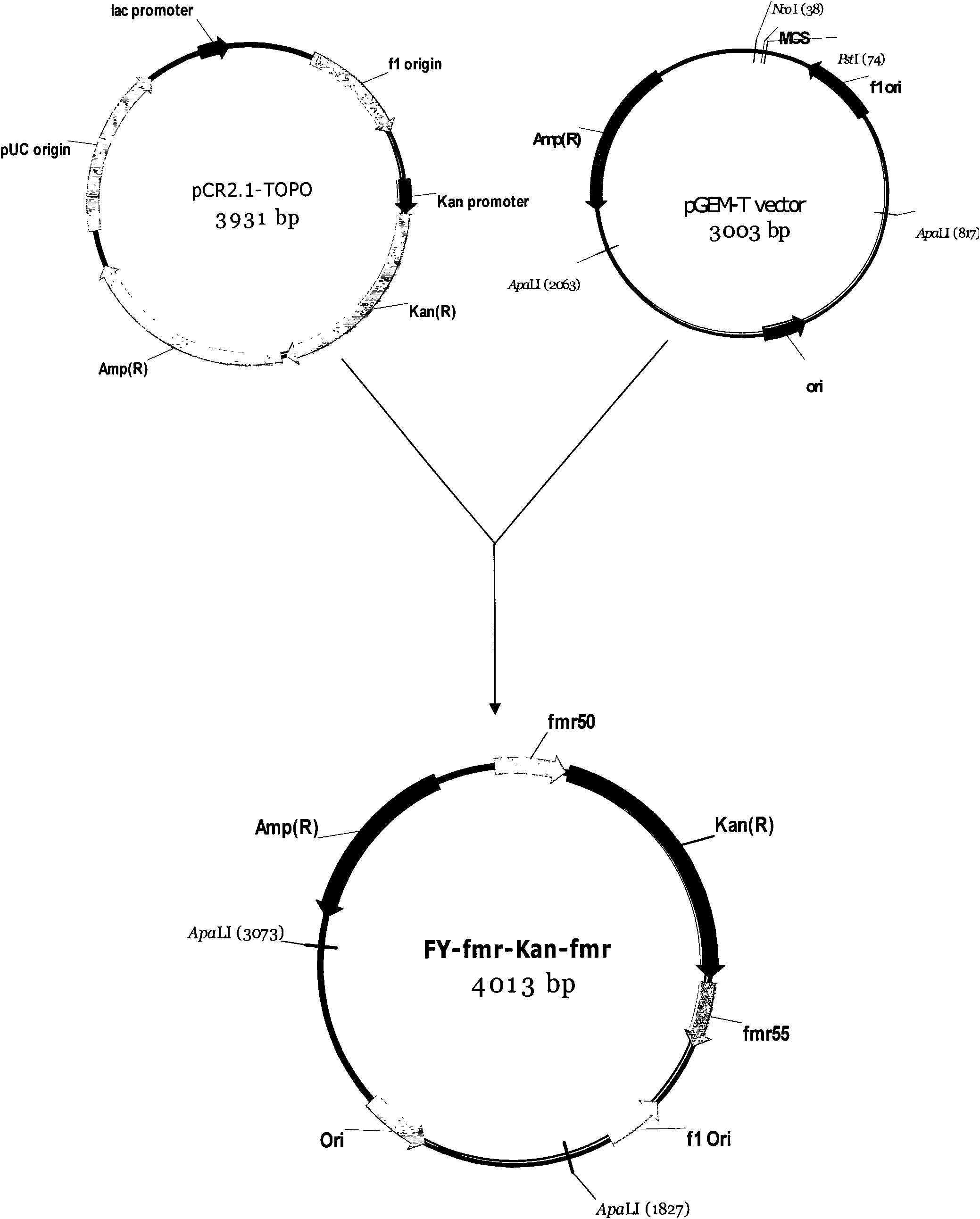
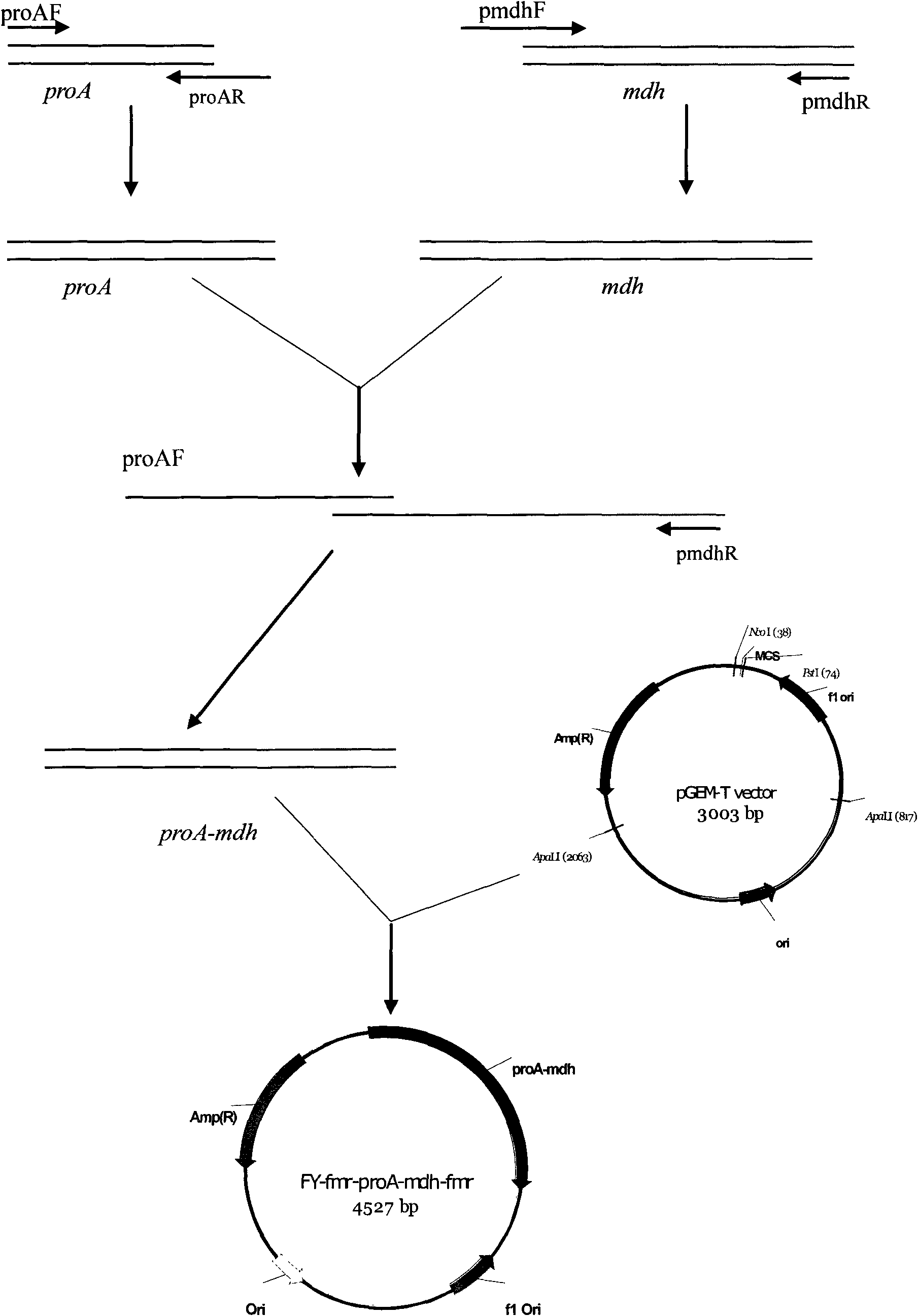
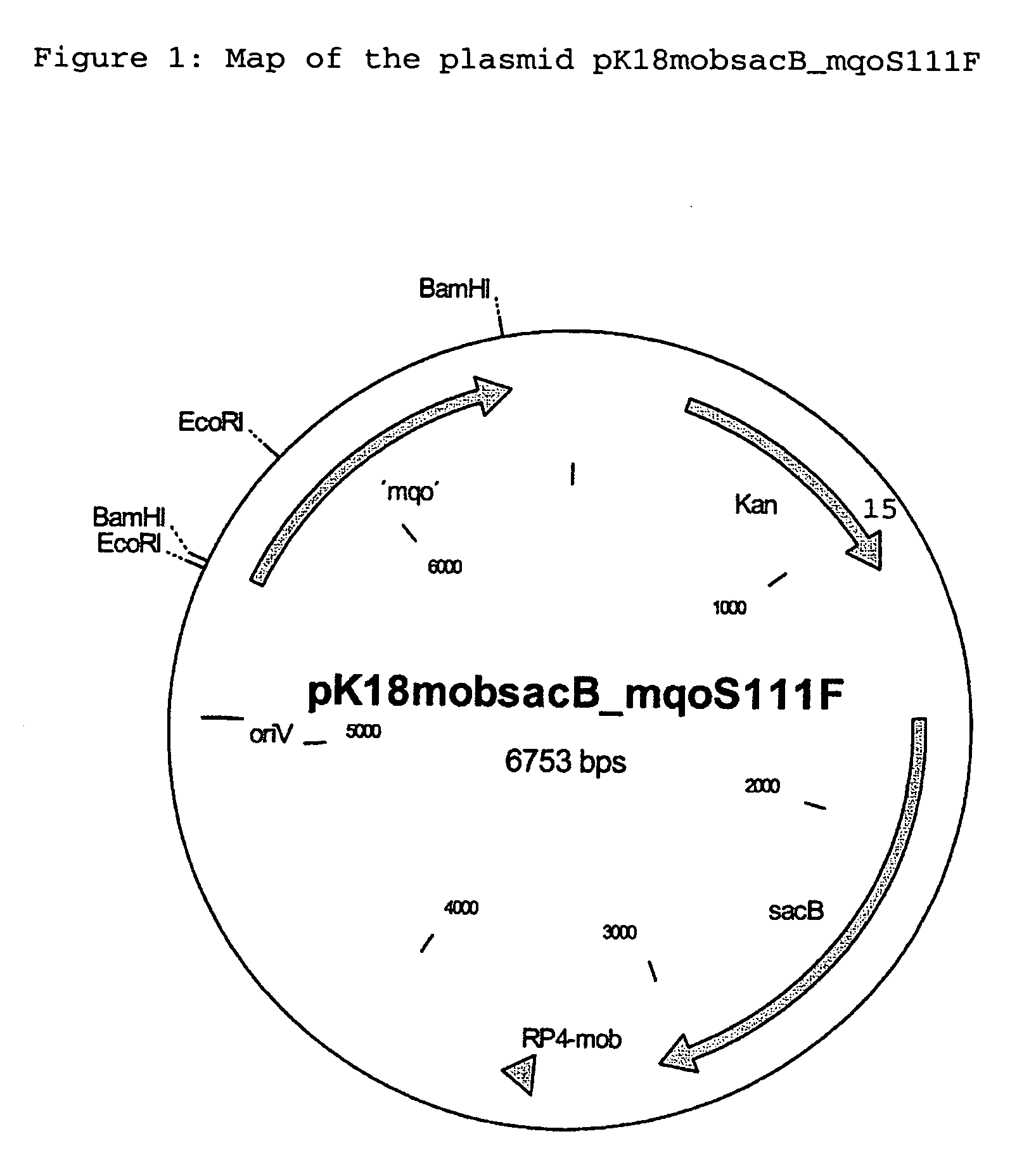
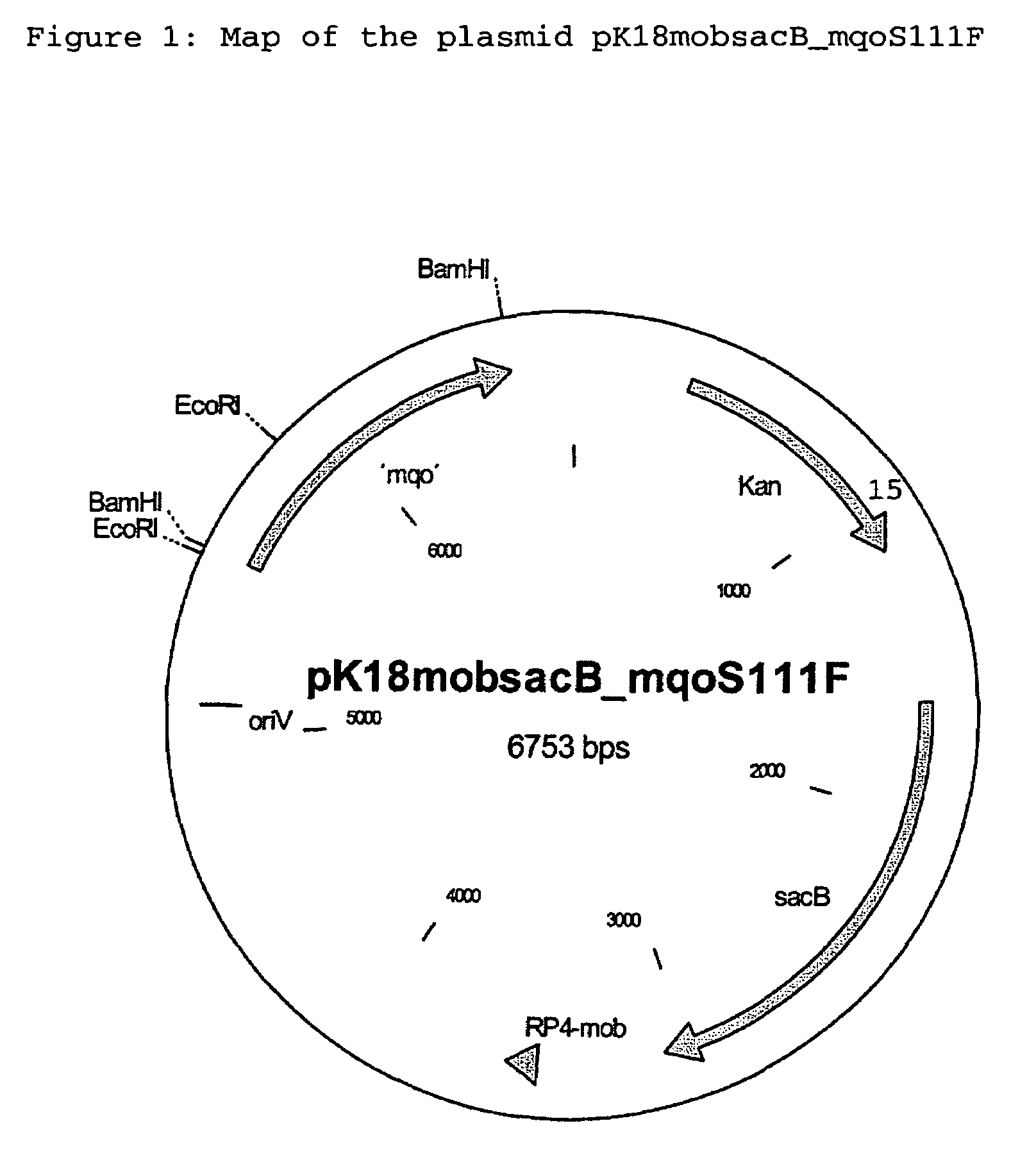
Alleles of the mqo gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the coryneform bacterium mqo gene which encodes malate quinone oxidoreductases which contain any amino acid apart from L-serine at position 111, or a comparable position, in the amino acid sequence, and to processes for fermentatively preparing amino acids, preferably L-lysine, L-tryptophan and L-proline, using bacteria which comprise these alleles.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Alleles of the mqo gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the coryneform bacterium mqo gene which encodes malate quinone oxidoreductases which contain any amino acid apart from L-serine at position 111, or a comparable position, in the amino acid sequence, and to processes for fermentatively preparing amino acids, preferably L-lysine, L-tryptophan and L-proline, using bacteria which comprise these alleles.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Dibasic organic acid producing strain and preparation and application of same
ActiveUS20180171369A1Raise the level of fermentationReduce fermentation costsMicroorganismsTransferasesGlutaric acidRhizopus
Provided are an engineered strain for synthesizing a dibasic organic acid and preparation and application of same. The engineered strain introduces or up-regulates expression of a positive regulator gene for synthesis of a dibasic organic acid, and / or down-regulates expression of a negative regulator gene for synthesis of a dibasic organic acid, as compared with the origin strain of the engineered strain, the producing capability for producing the dibasic organic acid is improved. The dibasic organic acid comprises malic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, oxaloacetic acid, glutaric acid, and adipic acid; the expression product of the positive regulator gene comprises aspartate aminotransferase, glutamic acid-aspartate transporter, C4-dicarboxylic acid transporter, pyruvate carboxylase and malate dehydrogenase, glucose transporter; the expression product of the negative regulatory gene comprises succinyl-CoA synthase, and malic acid-alpha ketoglutarate transporter, and the original strain comprises myceliophthora thermophila, thielavia terrestris, aspergillus, and rhizopus.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Hydrophilic domain protein gene
InactiveCN106117323AReduce aggregationAvoid structural changesEnzyme stabilisationBacteria peptidesCrystallographyLactate dehydrogenase
The present invention finds the protective effect of the hydrophilic domain on the enzyme in the Dhp(DR1172) protein. The present invention expresses a core protein containing a complete hydrophilic domain. The experimental results showed that the protein was repeatedly frozen and thawed in liquid nitrogen and H 2 O 2 Both can protect the activities of malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) under shock stress conditions, and both can reduce the aggregation of LDH and prevent its structure from changing to protect its activity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Malate dehyrogenases
Owner:TECHNIP ENERGIES FRANCE
Synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid
The invention discloses a synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid. The method takes allochenodeoxycholic acid as an initial raw material and includes the following steps: adding phosphate buffer, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, lactate dehydrogenase, 7-[alpha]hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and sodium pyruvate, performing reaction, and performing cooling after enzyme was inactivated through high temperature; additionally adding L-sodium malate, malate dehydrogenase and 7-[beta]hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase to react, and performing cooling to room temperature after the enzyme was inactivated through high temperature; and obtaining the 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid through filtration, washing and drying. The overall process of the method includes the oxidation and reduction steps of the allochenodeoxycholic acid and the synthesis of the 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid. The whole reaction of the method is conducted in an aqueous solution without using organic solvents; the method is simple in technology and easy to operate; and the purity of the obtained 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid can reach more than 98.5%, and the obtained 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid can be used as samples of pharmaceutical properties such as toxicology and pharmacology in pharmaceutical research institutions and can also be used as impurity reference substances during quality research of ursodeoxycholic acid.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN BAILING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Malate dehydrogenase electrode as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111896599AHigh activityPerformance is not affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanotubeCombinatorial chemistry
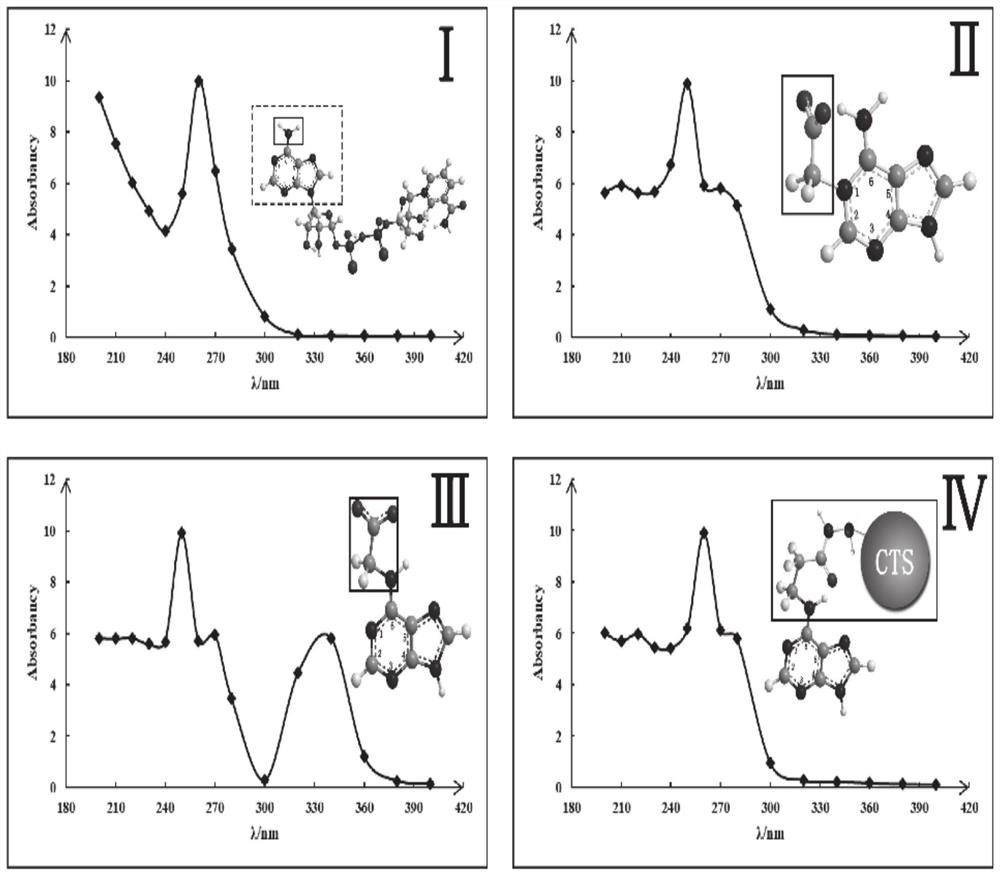
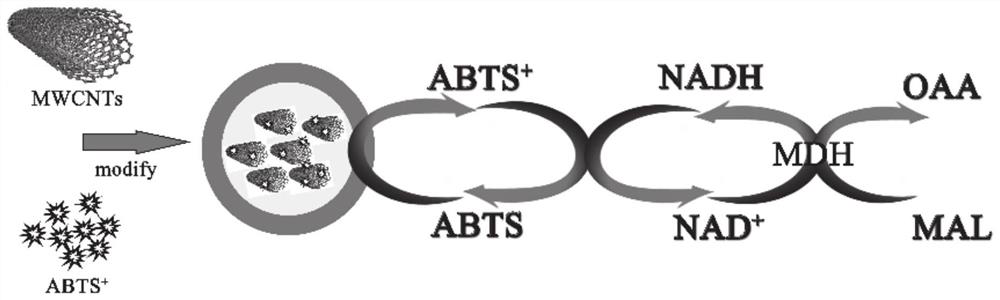
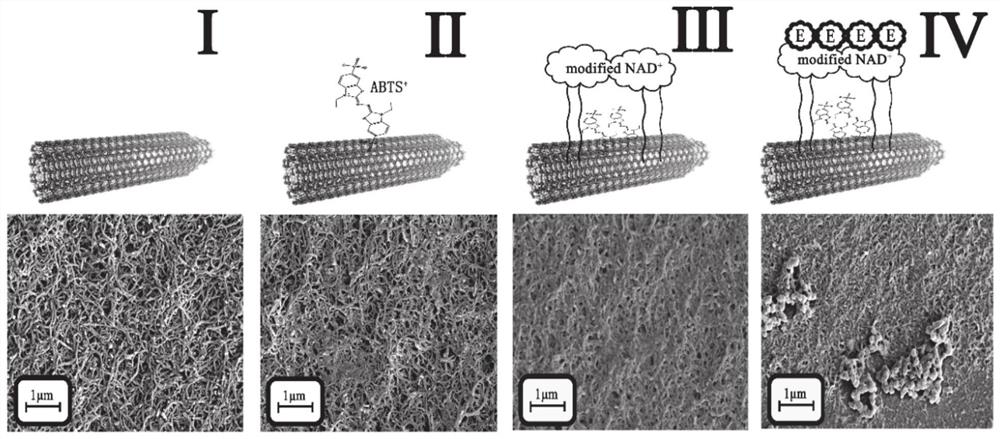
The invention provides a malate dehydrogenase electrode as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: chemically modifying a coenzyme factor smallmolecule NAD < + > non-active part through a chemical means, covalently connecting the chemically modified NAD < + > with a chitosan carrier to obtain an NAD < + >- chitosan compound, modifying a carbon nanotube on the surface of a substrate electrode, and detecting NADH by using the carbon nanotube as a substrate material; electrically depositing ABTS on the electrode, and achieving NAD <+> in-situ regeneration by using the ABTS as an electron mediator; dropwise adding an NAD < + >- chitosan compound to realize fixation of NAD < + > on the surface of the electrode; connecting dehydrogenase tothe chitosan carrier through glutaraldehyde cross-linking action to obtain a dehydrogenase electrode; the immobilization and regeneration method of NAD < + > can be combined with different types of dehydrogenases to prepare various dehydrogenase electrodes / biosensors. The method has wide practical application value in the field of biosensor preparation.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
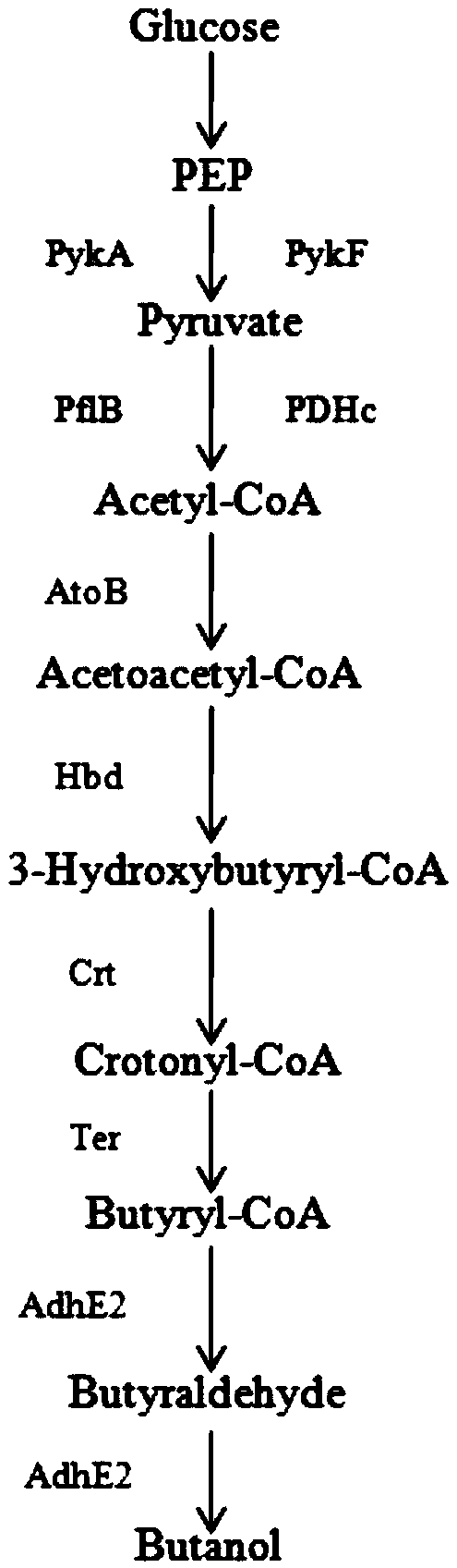
Method for improving yield of butanol produced by escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for improving yield of butanol produced by escherichia coli. According to the method for constructing recombinant bacteria, expression of a malate dehydrogenase gene (mdh) on the genome of an original strain for producing butanol is inhibited or silenced to obtain the recombinant bacteria. Experiments prove that the modified target capable of promoting escherichia coli to produce butanol is the malate dehydrogenase gene (Genbank: mdh gene (b3236) in the NC_000913.3 sequence). By a lembda-red homogenous recombinant system knockout technology, after the mdh gene of the engineering strain of escherichia coli for producing butanol is knocked out, the butanol output can be increased by 283 percent, and the yield can be increased by 89 percent.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
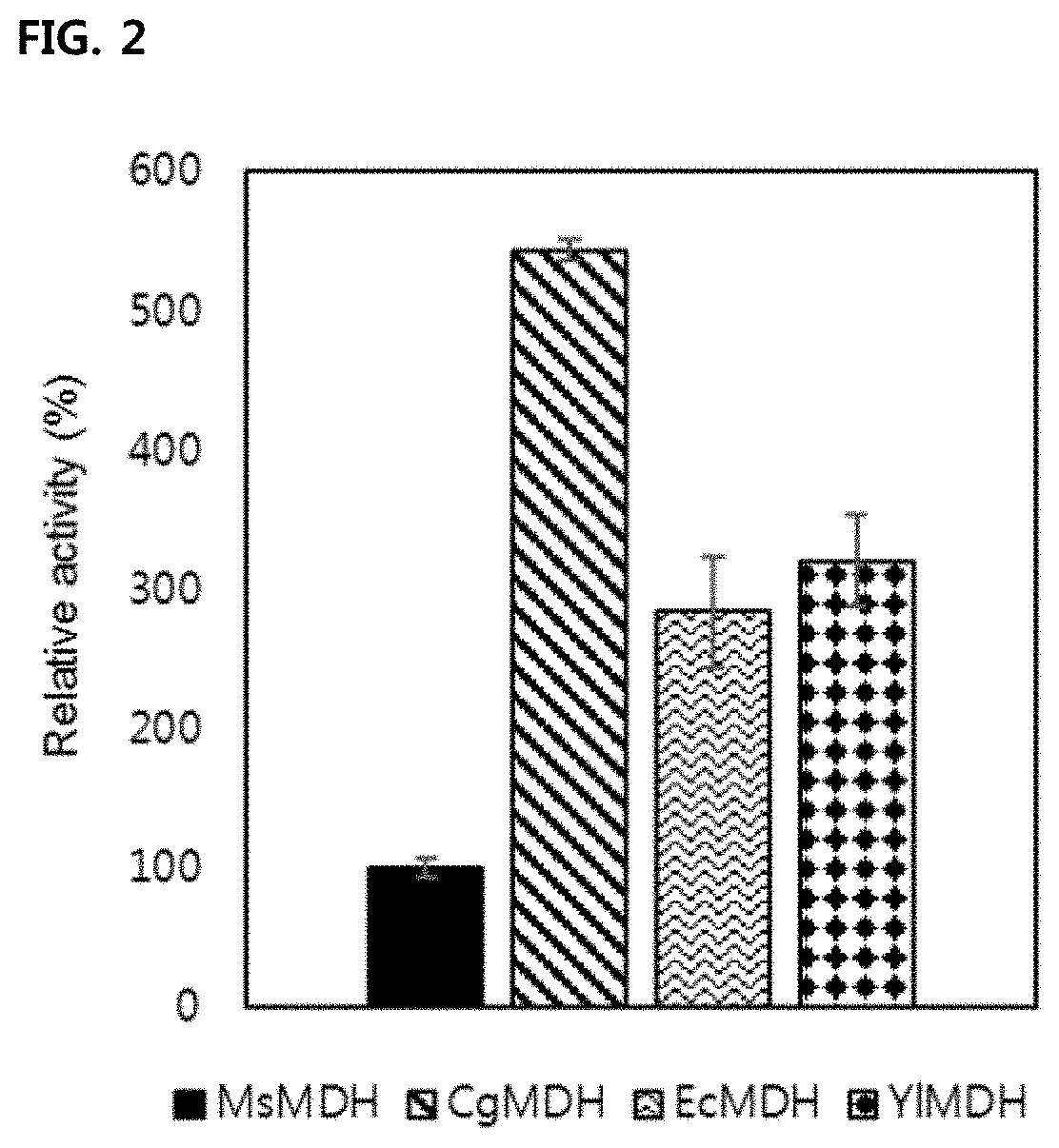
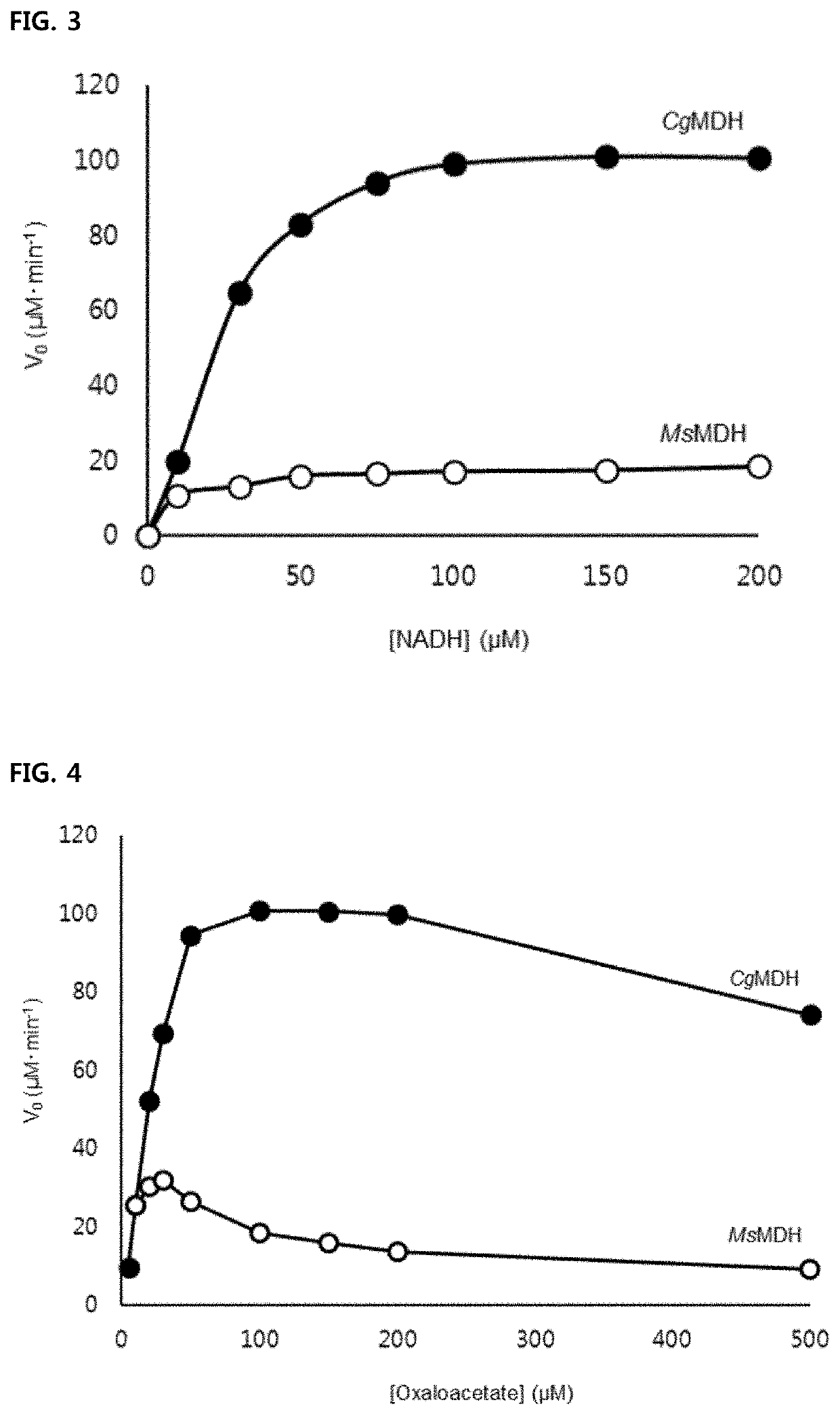
Succinic acid-producing mutant microorganism into which high activity malate dehydrogenase is introduced, and method for preparing succinic acid by using same
The present invention relates to: a succinic acid-producing mutant microorganism having improved activity of converting oxaloacetic acid to malic acid by the introduction of a gene encoding a malate dehydrogenase in which an amino acid residue interacting with a pyrophosphoric acid region of NADH through an amide functional group of a main chain is glutamine (Gln); and a method for preparing succinic acid by using same. The succinic acid-producing mutant microorganism according to the present invention has a remarkably increased activity of converting oxaloacetic acid to malic acid, and thus when the microorganism is cultured under a defined medium, high-concentration succinic acid can be produced with the highest succinic acid productivity from among that of mutant microorganisms reportedthus far. In addition, by using an advanced fermentation technology, succinic acid can be produced with higher productivity and production concentrations.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Dibasic organic acid producing strain and preparation and application of same
ActiveUS10781462B2Raise the level of fermentationLow costMicroorganismsTransferasesMyceliophthora thermophilaPyruvate synthesis
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
L-malate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
PendingCN113061593AHas the prospect of industrial development and applicationIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMalate quinone oxidoreductaseAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an L-malate dehydrogenase mutant, wherein the amino acid sequence of the L-malate dehydrogenase mutant is SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4, and compared with wild type L-malate dehydrogenase, the L-malate dehydrogenase mutant has the advantage that the enzyme activity is obviously improved. The L-malate dehydrogenase mutant can be used for producing D-malic acid and oxaloacetic acid with high optical purity through enzymatic resolution of DL-malic acid.
Owner:洛阳华荣生物技术有限公司
Marine low-temperature MDH (malate dehydrogenase) gene and recombinant expression vector thereof
InactiveCN109161555ASolve the disadvantages of residual impuritiesStrong specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and relates to a marine low-temperature MDH (malate dehydrogenase) gene and a recombinant expression vector thereof. The low-temperature MDH gene is isolated from Oceanobacillus picturae strain R-5321 and encodes low-temperature MDH, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene isshown in SEQ ID NO: 2. A marine low-temperature MDH expression vector pET-28a-MDH is successfully constructed with an RF (restriction-free) cloning method. The expression vector is electrically transferred into host cell C43 (DE3) and induced to express marine low-temperature MDH protein by IPTG. An expressed product has a marine low-temperature MDH function and can catalyze conversion of malic acid into oxaloacetic acid.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Construction of threonine production strain and method for producing threonine
PendingCN113846132AImprove conversion rateIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliThreonine
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to construction of a threonine production strain with a high conversion rate and a method for producing threonine. L-threonine yield of novel escherichia coli is higher than that of respective control strains, and the shake-flask conversion rate of strains with enhanced mqo expression activity is 24-30%, which is increased by 6-12 conversion percentages compared with original strains; the shake-flask conversion rate of strains with enhanced cyoABCDE expression activity is 26-30%, which is also increased by 8-12 conversion percentages compared with the original strains. Results of shake flasks modified by the two sites show that the production capacity of threonine can be obviously improved by enhancing the expression of malic acid:quinone oxidoreductase gene mqo or enhancing the activity of oxidase at the tail end of a respiratory chain.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
2-isopropylmalate synthetase and engineering bacteria and application thereof
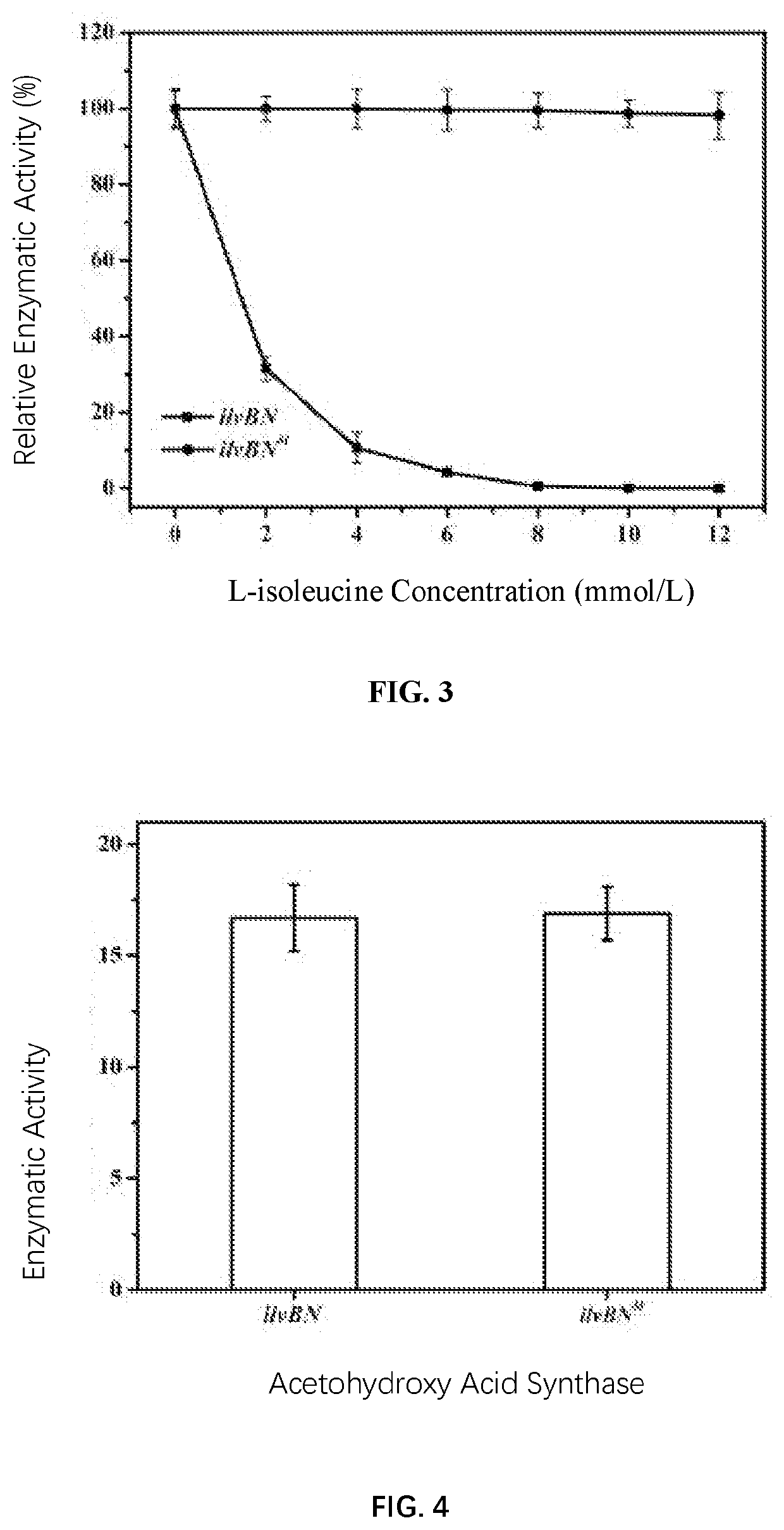
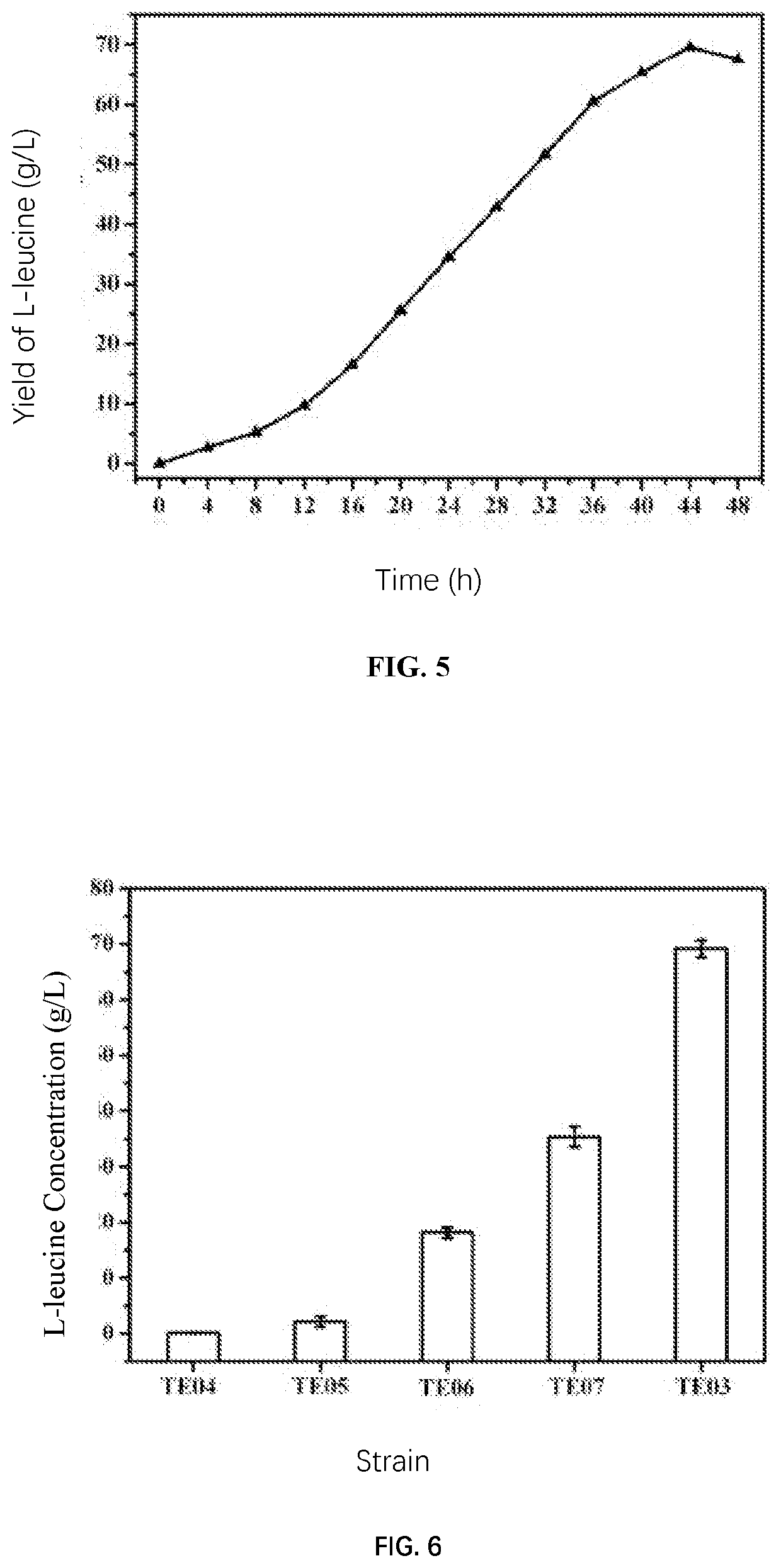
PendingUS20210189354A1Quick upgradeShort maintenance periodOxidoreductasesAcyltransferasesMalate synthaseNutritional deficiency
The invention relates to a 2-isopropyl malate synthase, a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-leucine and application thereof and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by overexpressing an isopropyl malate synthase coding gene leuAM for relieving feedback inhibition by L-leucine, an acetohydroxy acid synthase coding gene ilvBNM for relieving feedback inhibition by L-isoleucine, a 3-isopropyl malate dehydrogenase coding gene leuB and a 3-isopropyl malate dehydratase coding gene leuCD in host cells. The genetically engineered bacterium for producing the L-leucine is free from nutritional deficiency, rapid in growth, short in fermentation period, high in yield and high in conversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Creatinine content determination method and creatinine diagnosis kit
InactiveCN1766641AStrong specificityLess susceptible to interferenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseCreatinine rise
The invention relates to a method for measuring the creatinine content and a creatinine diagnosis agent box in the field of medical testing technology. The agent box comprises: buffer solution, reducing coenzyme, phosphoenolpyruvate, creatinine enzyme, atinase enzyme, urease, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, malate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. It mixes the sample and the agent with a certain volume ratio to do enzyme coupling reaction; then it dispositions the end resting material on the chemical analyzer to detect the speed of the main wavelength light absorption to measure the content of the creatinine.
Owner:王尔中
Method for detecting blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1749754AStrong specificityEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseAdenosine
The present invention belongs to the field of medical detection technology. The reagent kit for blood ammonia diagnosis includes buffering solution, adenosine triphophate, glutamic acid, pyruvic acid, phosphoenolpyruvic acid, reduced coenzyme, glutamine synthetase, pyruvate oxidase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, malate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Through mixing the sample and reagent in certain volume ratio to produce enzyme coupling reaction, and detecting in biochemical analyzer the main wavelength absorbency change speed, the blood ammonia content is measured. The present invention can obtain the measurement result in biochemical analyzer in high sensitivity, high precision and no contamination of various foreign and internal matters.
Owner:王尔中
Determination of blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778945AStrong specificityImprove test accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood ammoniaAmount of substance
The invention is about a method of measuring the content of blood ammonia, and it also concerns the reagent box of blood ammonia diagnosis. This invention belongs to the field of medical testing and measuring technology. The reagent box is consisted of buffer solution, glutamate, adenosine triphosphate, acetonic acid, reduced coenzyme, glutamyl synzyme, pyruvate oxidase, malate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Firstly, we cause an enzyme-coupled reaction through mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain proportion of volume; secondly, put the final reactant under the biochemical analyzer and test the absorbance variational situation (speed) of dominant wavelength; then we can get the content ofblood ammonia. By using this invention, we can get the necessary measuring result with high sensitiveness and fine precision through biochemical analyzer, and the result would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources. Thus, this method can be conveniently promoted and applied.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A kind of malate dehydrogenase pbmdh and its coding sequence and application
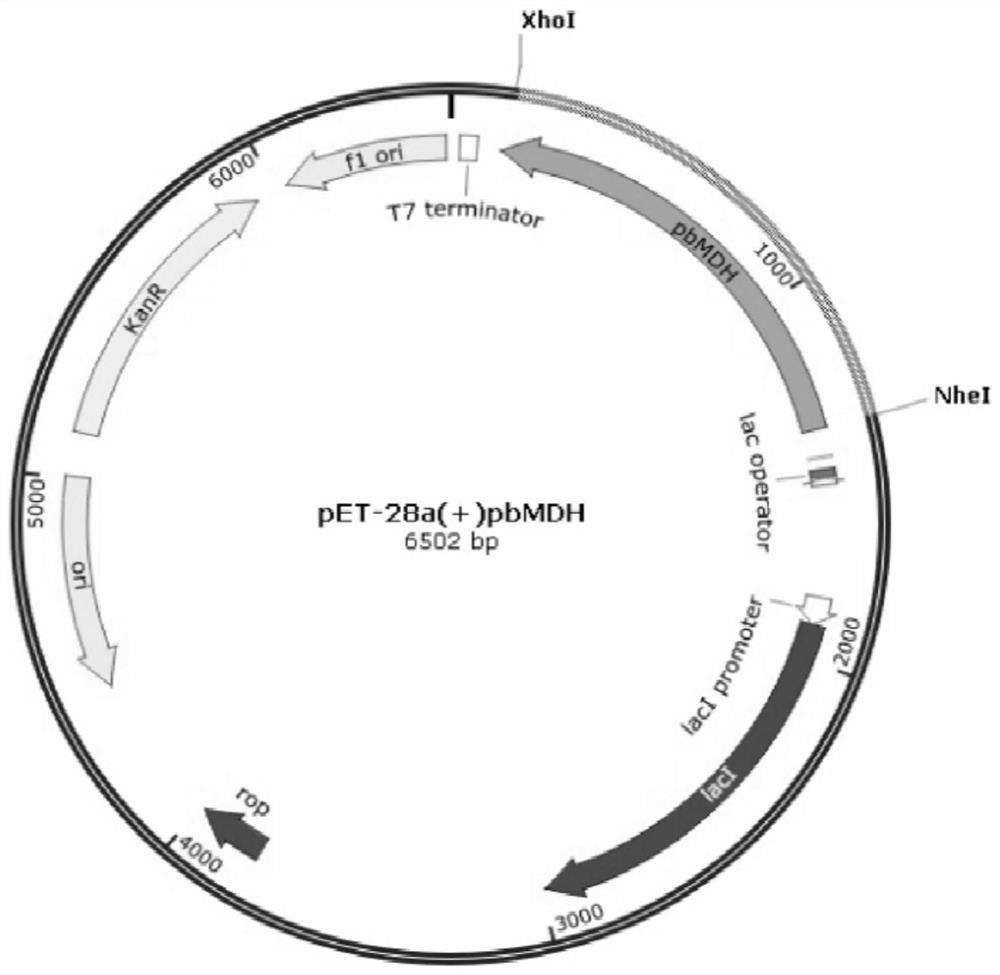
ActiveCN109337879BIncreased specific enzyme activityEfficient expressionContaminated soil reclamationOxidoreductasesNucleotideMicrobiology
The invention provides malic dehydrogenase PbMDH derived from Pseudomonas beteli, as well as a coded gene and an application of the malic dehydrogenase. Cloned plasmid with the malic dehydrogenase PbMDH nucleotide sequence can be transferred into engineering bacteria by transduction, transformation and conjugal transfer, the malic dehydrogenase PbMDH can be efficiently expressed by adjusting expression of the coded gene, and an effective way is provided for production of the malic dehydrogenase. The marine-derived malic dehydrogenase is resistant to salt and high temperature and has importantindustrial application prospects.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Glycine Determination Method and Glycine Determination Kit
InactiveCN102298022AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsGlycineGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a method for measuring glycine content using enzyme colorimetry and enzyme-linked method technology, the composition and components of reagents, the technical principle of which is based on the series of catalysis of glycine transaminase, glutamic acid decarboxylase and malate dehydrogenase After the reaction is completed, the present invention also relates to a glycine assay kit. The determination method of the invention has high sensitivity and small error, so the determination method and the kit of the invention can be widely used in food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Determination method of galactose and galactose diagnosis/measurement kit
InactiveCN102297950AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsGalactokinaseLactose
The invention relates to a method for measuring galactose content using enzyme colorimetry and enzyme-linked method technology, the composition and components of reagents, and the technical principle of its measurement is based on galactose kinase, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, malate dehydrogenase The series of catalytic reactions are completed, and the present invention also relates to a galactose diagnosis / measurement kit. The assay method of the present invention has high sensitivity and small error, so the assay method and kit of the present invention can be widely used in clinical medicine / food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Determination method of galactose and galactose diagnosis/measurement kit
InactiveCN102297976AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAcetyl-coenzyme A carboxylaseGalactokinase
The invention relates to a method for measuring galactose content using enzyme colorimetry and enzyme-linked method technology, the composition and components of reagents, and the technical principle of its measurement is based on galactose kinase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, malate dehydrogenase The series of catalytic reactions are completed, and the present invention also relates to a galactose diagnosis / measurement kit. The assay method of the present invention has high sensitivity and small error, so the assay method and kit of the present invention can be widely used in clinical medicine / food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Ammonia (ammonium ion) determination method and ammonia (ammonium ion) diagnosis/determination kit
InactiveCN102466710AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase kinaseEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to an ammonia (ammonium ion) content determination method through enzymatic colorimetry and an enzyme linked assay technology, and the composition and components of a reagent. A technical principle for determination is completed through a series of catalytic reactions of an ammonia kinase, a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase kinase, a malate dehydrogenase. The invention also relates to an ammonia (ammonium ion) diagnosis / determination kit. The determination method of the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and small error. So, the determination method and the kit of the invention can be widely applied to clinical medicine / food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A low-temperature and high-efficiency carbon dioxide kit using a cyclic enzymatic method
ActiveCN108998501BEasy to prepareLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseAdenosine
The invention relates to the field of in vitro diagnosis, in particular to a low-temperature and high-efficiency carbon dioxide kit using a cycle enzyme method. The kit is composed of NADH analog cyclic regeneration system and carbon dioxide determination reagent. The NADH analog cyclic regeneration system consists of 6-phosphate-fructose dehydrogenase 5-50U / L, hexokinase 50-500U / L, fructose 1- 5g / L, adenosine triphosphate disodium salt 0.5-2.5g / L, carbon dioxide determination reagent consists of Tris-hydrochloric acid 0.1mol / L (pH=8), stabilizer 1g / L, oxaloacetic acid 0.3g / L, composed of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase 0.1g / L, potassium phosphoenolpyruvate 0.6g / L, low temperature malate dehydrogenase 0.05g / L, Triton-100 1g / L. The carbon dioxide measuring kit of the present invention can be used at a lower temperature to detect the carbon dioxide concentration in a high-salt sample.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Mutant microorganism introduced with highly active malate dehydrogenase for producing succinic acid and method of producing succinic acid using the same
ActiveUS20210332332A1Improve productivityMaximize productivityBacteriaOxidoreductasesSuccinic acidBackbone chain
Disclosed are a mutant microorganism for producing succinic acid exhibiting improved activity of conversion of oxaloacetate to malate through the introduction of genes encoding a malate dehydrogenase, wherein an amino acid residue that interacts with a pyrophosphate moiety of NADH through an amide functional group of a main chain of malate dehydrogenase is glutamine (Gln), and a method of producing succinic acid using the same. The mutant microorganism producing succinic acid according to the present invention is capable of producing a high concentration of succinic acid at the highest productivity compared to other mutant microorganisms reported to date when the microorganism is cultured in a limited medium. In addition, the mutant microorganism is capable of producing succinic acid at higher productivity and product concentration through further advanced fermentation technology.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
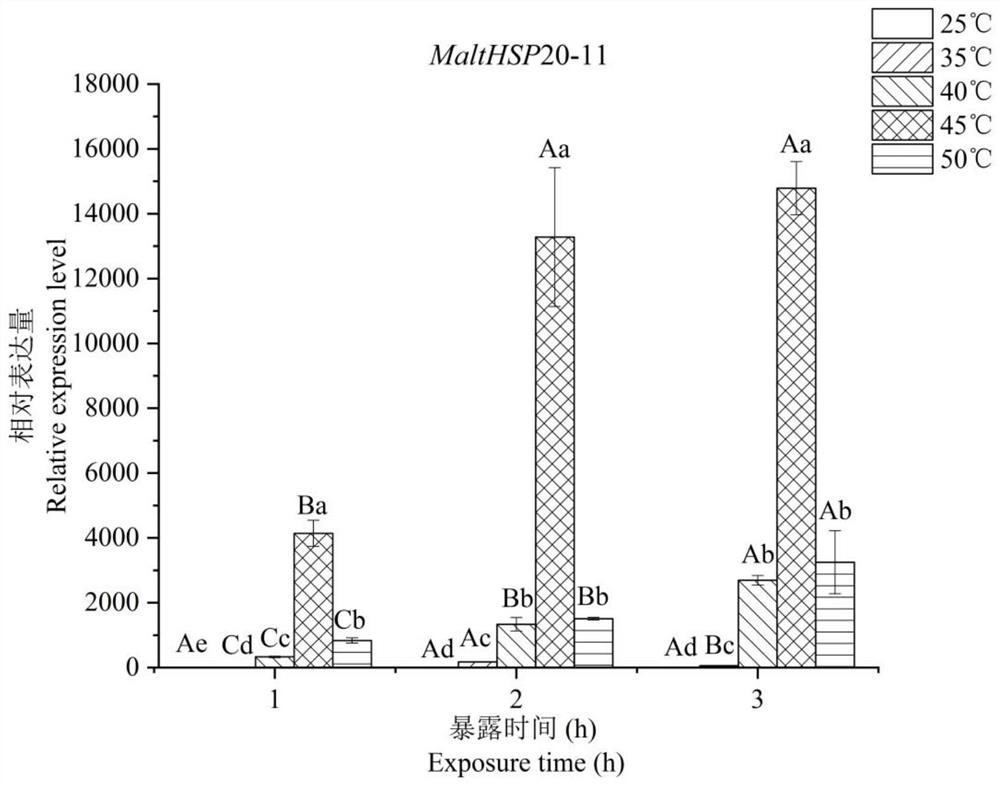
A heat shock protein malthsp20-11 of Monochamus alternatus and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN111574609BPrevent heat coagulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeat shockProkaryotic expression
The invention discloses a heat shock protein MaltHSP20‑11 of Monochamus alternatus and its coding gene and application, belonging to the field of heat shock proteins. The full length of the heat shock protein HSP20 gene of Monochamus alternatus provided by the invention is 531 bp, encoding 176 amino acids. The expression characteristics of this gene under heat stress conditions were obtained by fluorescence quantitative method, and high temperature can obviously induce the up-regulation of this gene, indicating that this protein plays an important role in the resistance of Monochamus alternata larvae to high temperature stress. Finally, a prokaryotic expression vector was constructed, and the purified heat shock protein MaltHSP20‑11 of Monochamus alternata was successfully obtained through in vitro expression. to you + The heat shock protein MaltHSP20 of Monochamus alternatus purified by resin column was verified for molecular chaperone activity, which showed that the protein could effectively protect the heat coagulation of malate dehydrogenase. Therefore, this application has extremely high application value, and also provides a molecular basis for the research on the heat resistance of Monochamus alternatus.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
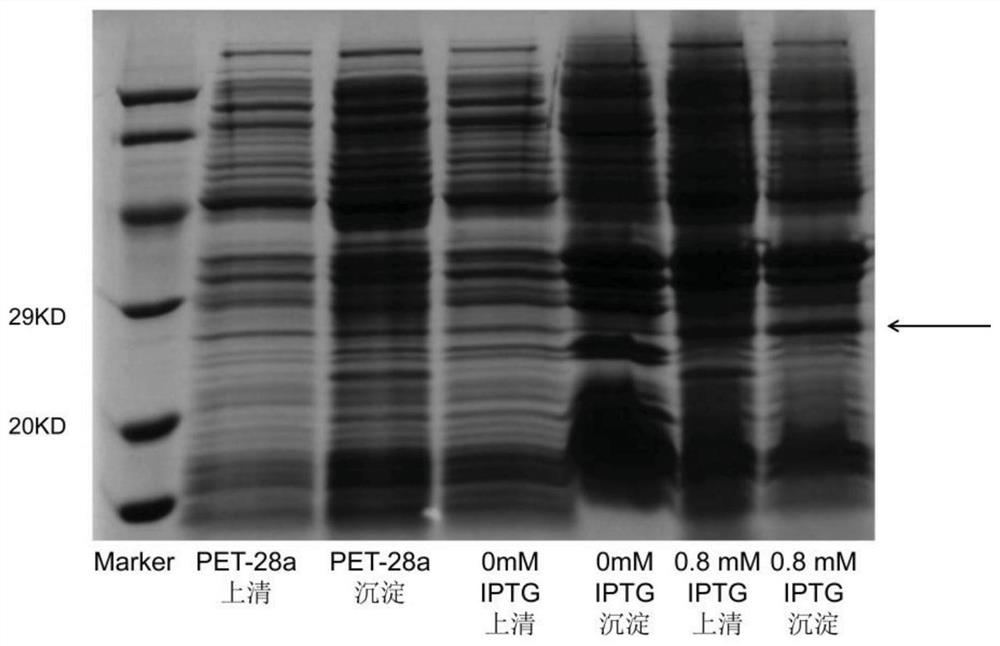
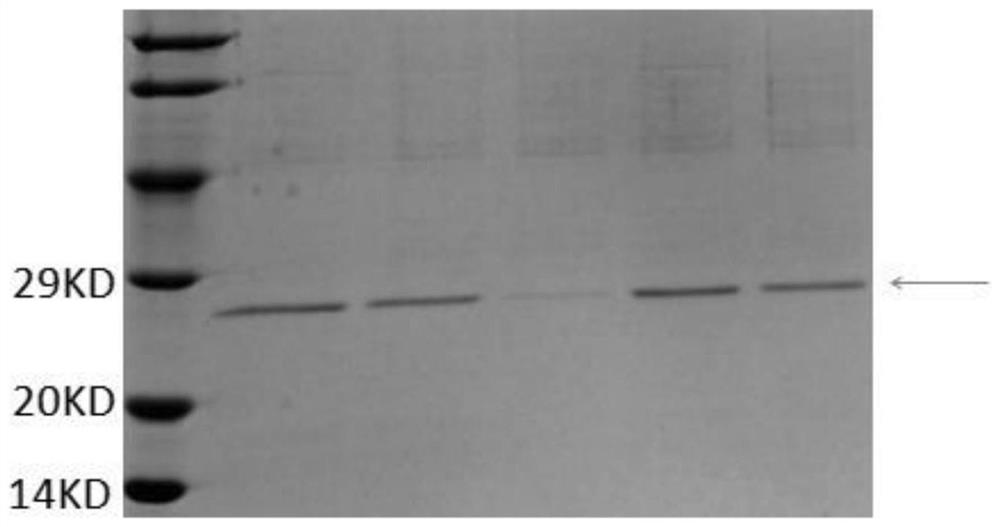
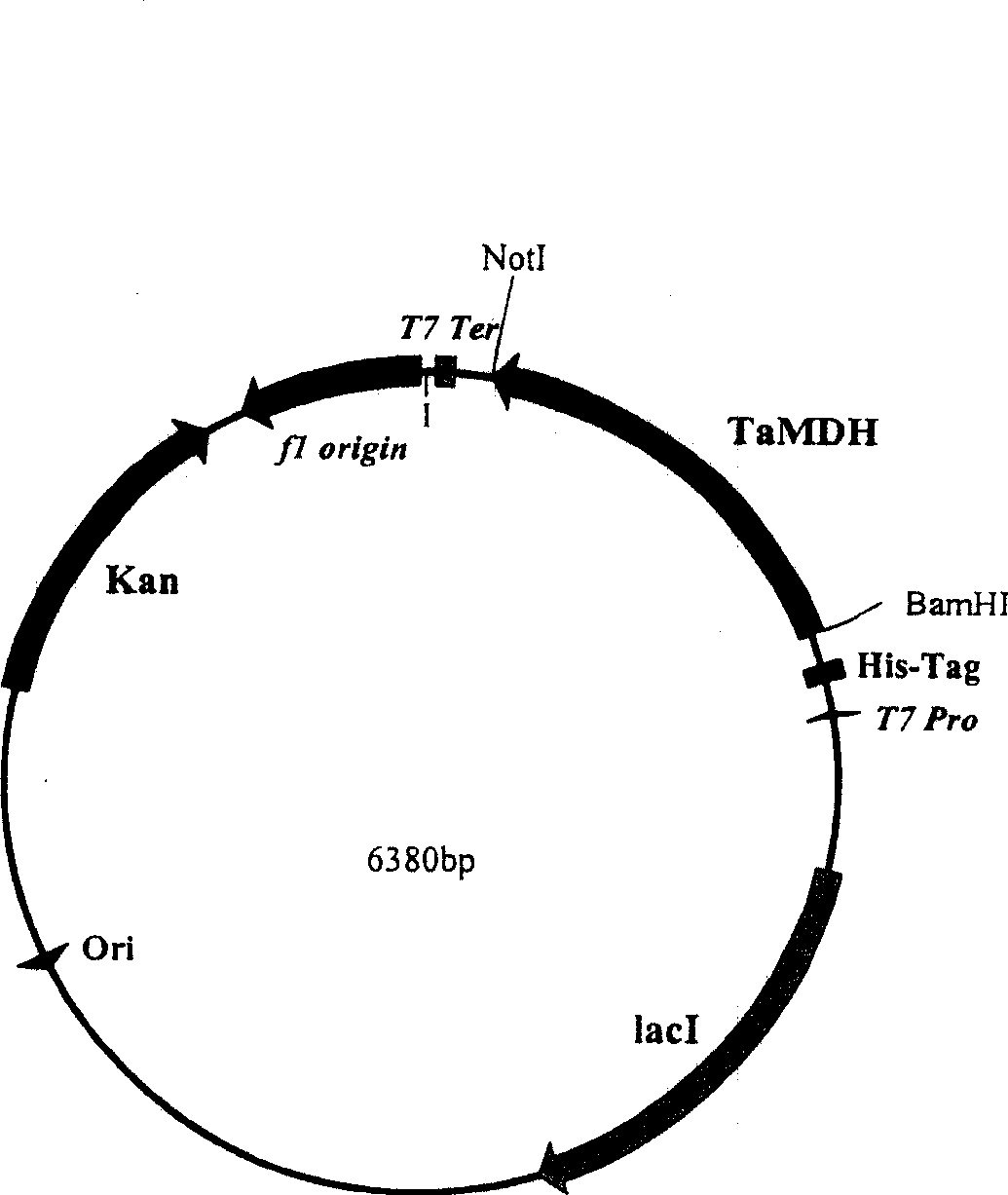
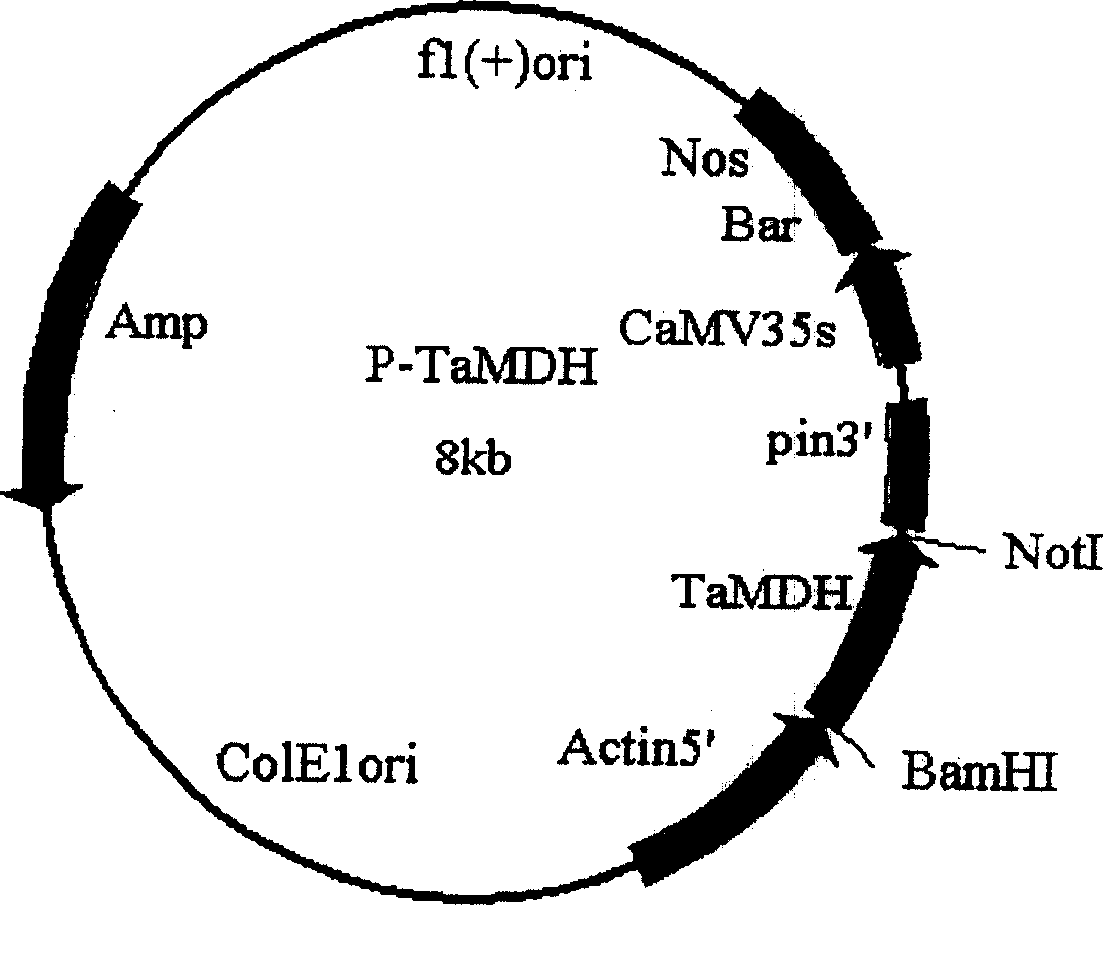
Malic dehydrogenase related to high photosynthetic capacity and resisting reversal of wheat, coded genes and method for breeding plants of resisting reversal
InactiveCN100506990CHigh light efficiencyImprove stress resistanceOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyMalate quinone oxidoreductase
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
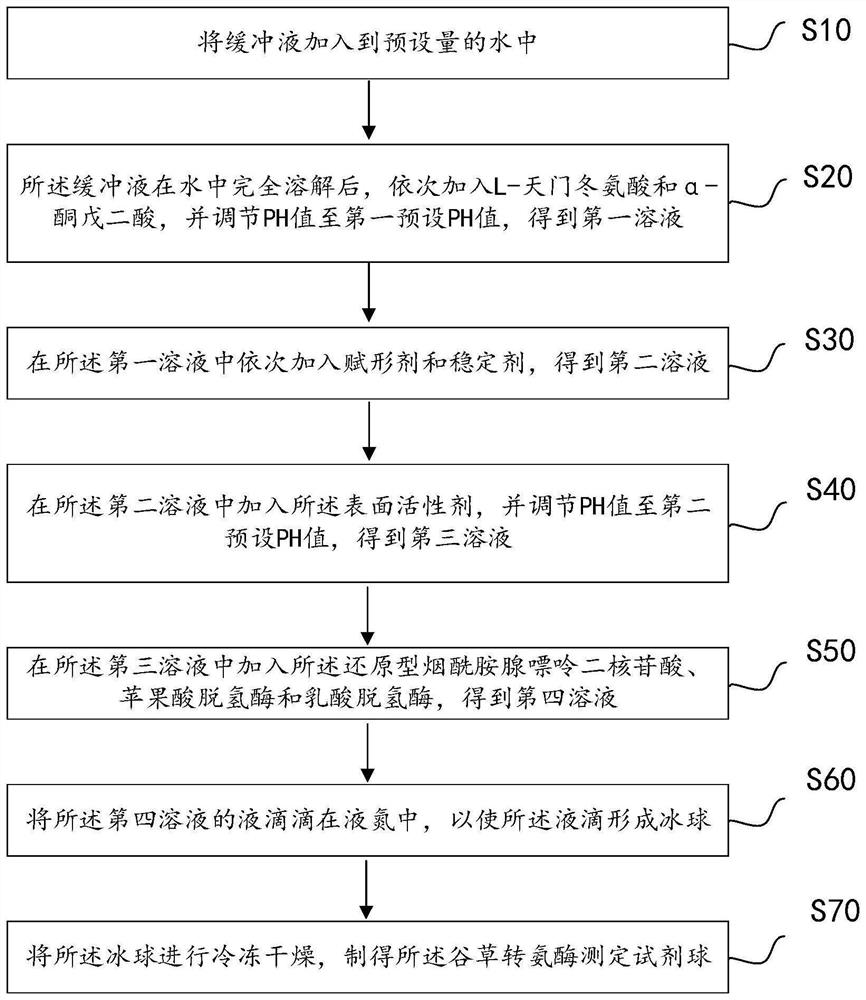
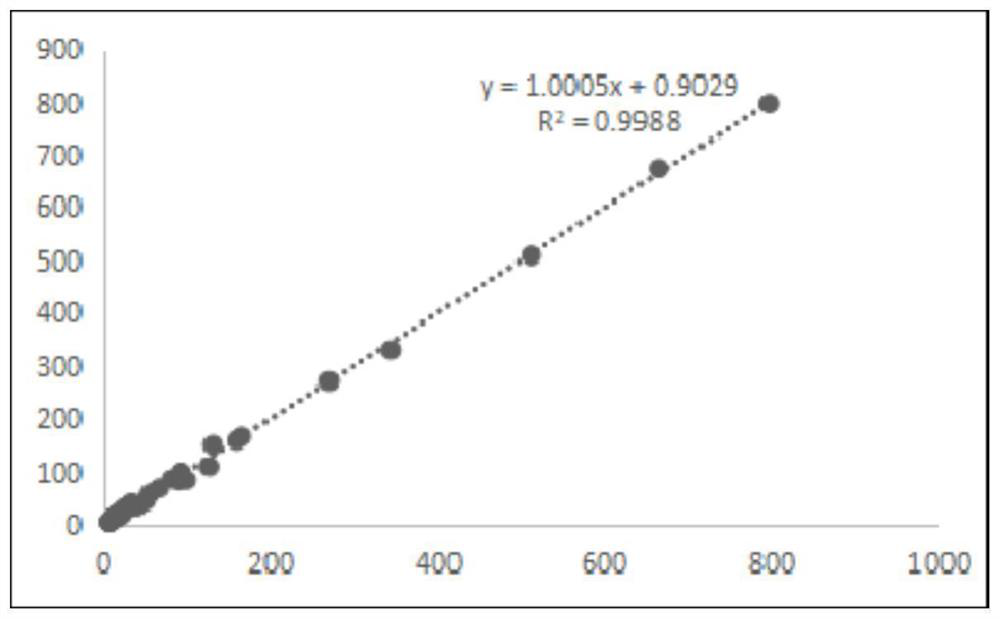
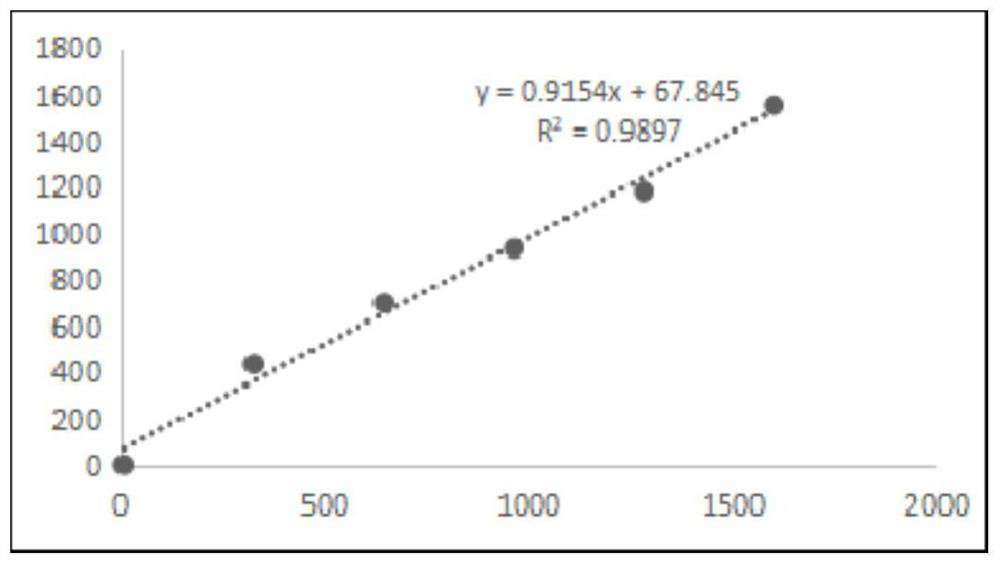
Glutamic oxalacetic transaminase determination reagent, preparation method of reagent ball and determination chip
PendingCN114292898AImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementActive agentNicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of detection reagents, in particular to a glutamic oxalacetic transaminase determination reagent, a preparation method of a reagent ball and a determination chip. The glutamic oxalacetic transaminase determination reagent provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises a buffer solution, L-asparaginic acid, alpha-ketoglutaric acid, an excipient, a stabilizer, a surfactant, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, malate dehydrogenase and D-lactic dehydrogenase. The glutamic oxalacetic transaminase determination reagent contains an effective stabilizer component, and the stability of enzyme and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in the determination reagent is improved, so that the stability is better when the concentration of glutamic oxalacetic transaminase is detected, and the accuracy of a determination result is improved.
Owner:GENRUI BIOTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid Synthesis method of 3[alpha],7[beta]-dihydroxy-5[alpha]-cholanic acid](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1b315145-f6d9-4f90-a1e5-9e6dc92b0acb/HDA0002893083090000011.png)