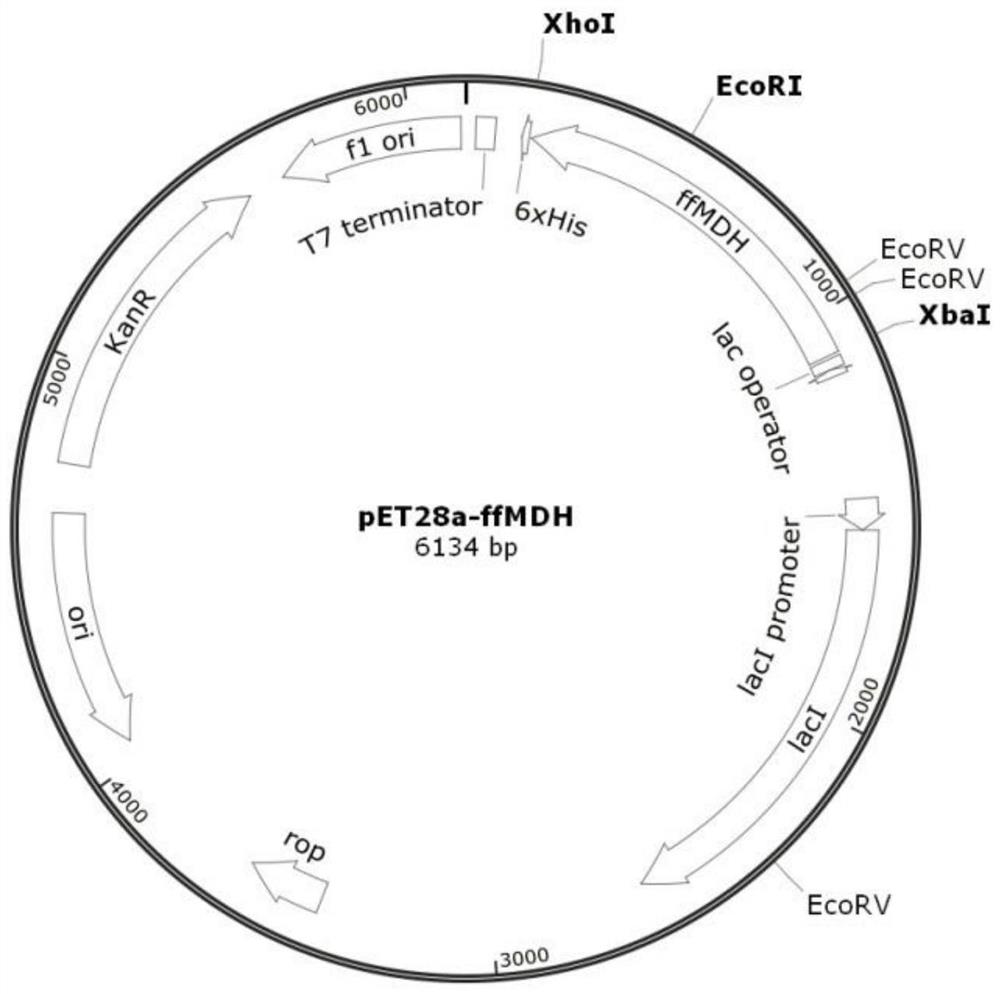
L-malate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
A malate dehydrogenase and mutant technology, applied in the field of enzyme catalysis, can solve the problems of complex culture conditions, inability to meet market demands, and high cost of industrialized production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Directed mutation of wild-type L-malate dehydrogenase
[0053] The molecular biology experiments in the examples include plasmid construction, enzyme digestion, connection, competent cell preparation, transformation, medium preparation, etc., mainly referring to "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" (third edition), J. Sambrook, Edited by D.W. Russell (US), translated by Huang Peitang et al., Science Press, Beijing, 2002). The specific experimental conditions can be determined by simple experiments if necessary.
[0054] PCR amplification experiments were carried out according to the reaction conditions or kit instructions provided by the plasmid or DNA template suppliers. It can be adjusted by simple experiment if necessary.
[0055] Using the sequence of wild-type L-malate dehydrogenase ffMDH (Genbank: AB161423) as a template, E. coli codon optimization was performed, and the optimized nucleotide sequence was SEQ ID NO:2. Perform whole gene synthesis. The...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 High-throughput screening of highly active mutant library
[0061] Pick single-clonal transformants on each LB plate obtained in Example 1, inoculate into 500 μL of 96-well deep-well culture plate containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin LB liquid medium, cultivate overnight, and then take 80 μl of overnight culture , transferred to 800μl LB liquid medium containing 50μg / mL kanamycin, cultured at 37°C for 3h, added a final concentration of 0.5mM IPTG, cooled to 30°C, continued to cultivate for 16h, centrifuged at 4000rpm for 5min, used for sedimentation Add 150 ul of 50 mM Glycine-NaOH (pH 7.0) buffer with a final concentration of 1 mg / ml lysozyme to suspend, and place at 30° C. for 30 min. After the cells were lysed, add L-malic acid at a final concentration of 10mM, 2mM NAD + , Judging the size of the activity by measuring the change of the absorbance value at 340nm.
[0062] Enzyme activity assay method:
[0063] Enzyme activity (U / mg) = ΔOD340×Vt×df / (ε×b×Vs×c)
...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 malate dehydrogenase mutant and catalytic performance identification
[0069] From the mutant transformant obtained in embodiment 2, select 5 high-energy bacterial strains detected by 96-orifice plate, and express bacterial strain (transferring into the transformant of plasmid pET28a-ffMDH) with wild-type L-malate dehydrogenase ffMDH As a control strain, culture in LB shake flasks was carried out according to the method for preparing bacterial cells on a 96-well plate described in Example 2. Collect bacterial cells for enzyme catalytic performance identification. The enzyme activity parameter determination method is the same as above. Before the enzyme activity measurement, the enzyme solution was incubated at 30°C for 2 hours; at the same time, the plasmid was extracted (Axygen small amount plasmid preparation kit) and sent to Nanjing Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for sequencing Validation of ffMDH mutation targets. The enzyme activity test and sequen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com