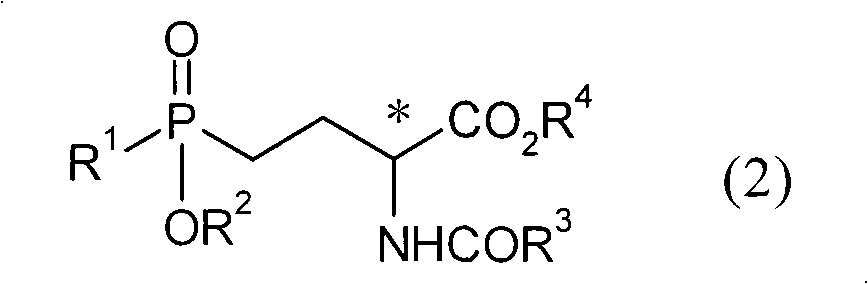
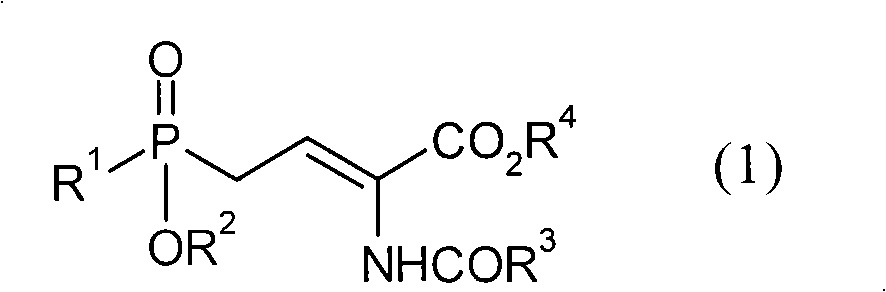
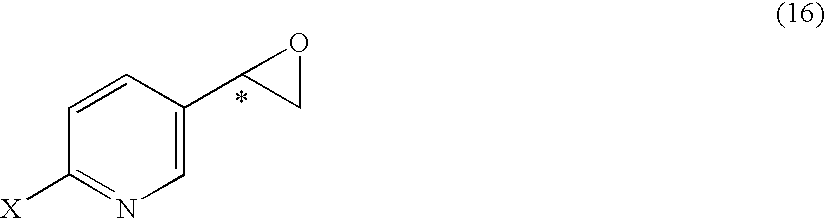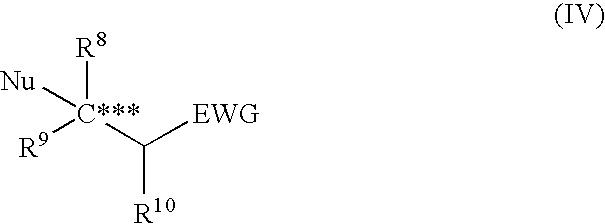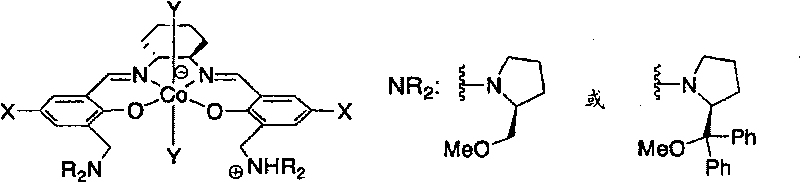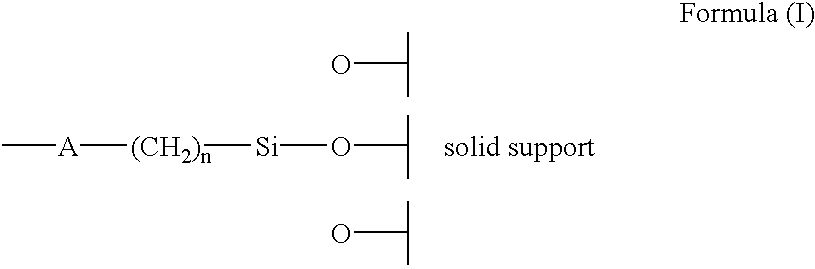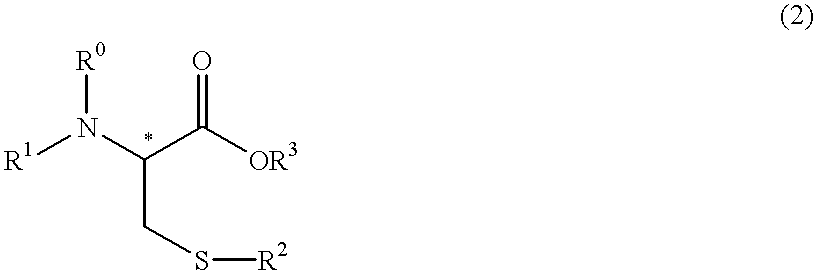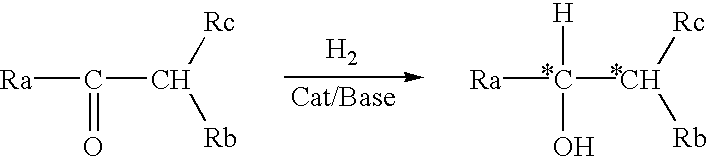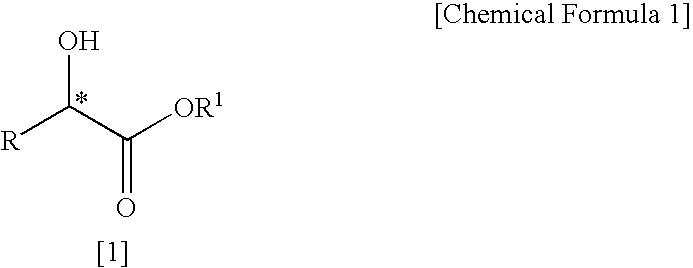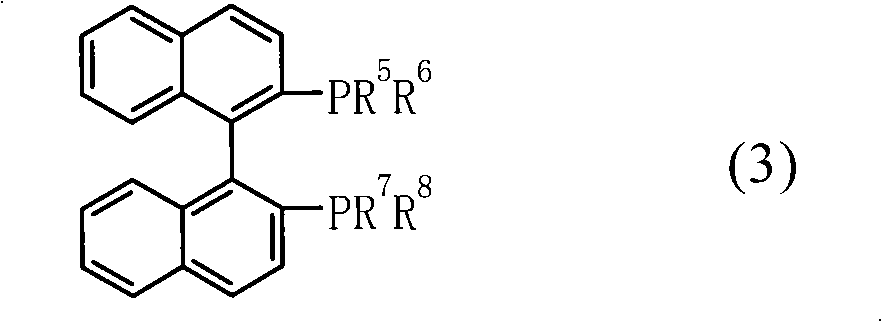Patents
Literature
154 results about "Asymmetric carbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
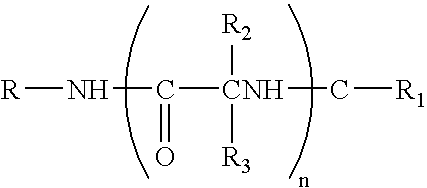
An asymmetric carbon atom (chiral carbon) is a carbon atom that is attached to four different types of atoms or groups of atoms. Le Bel-van't Hoff rule states that the number of stereoisomers of an organic compound is 2ⁿ, where n represents the number of asymmetric carbon atoms (unless there is an internal plane of symmetry); a corollary of Le Bel and van't Hoff's simultaneously announced conclusions, in 1874, that the most probable orientation of the bonds of a carbon atom linked to four groups or atoms is toward the apexes of a tetrahedron, and that this accounted for all then-known phenomena of molecular asymmetry (which involved a carbon atom bearing four different atoms or groups). Knowing the number of asymmetric carbon atoms, one can calculate the maximum possible number of stereoisomers for any given molecule as follows...
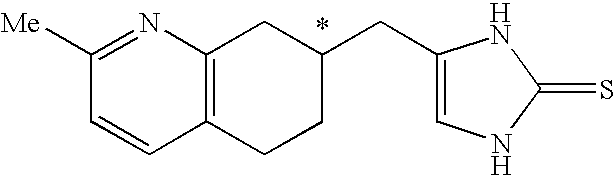
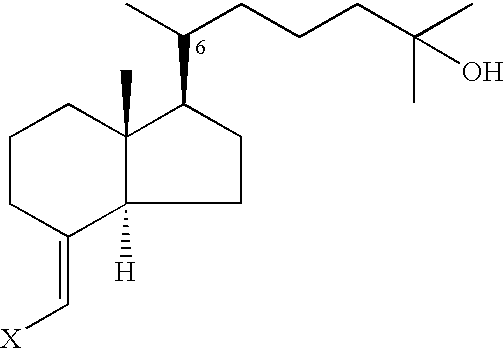
4-(2-Methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-quinolin-7-ylmethyl)-1,3-dihydro-imidazole-2-thione as specific alpha2B agonist and methods of using the same
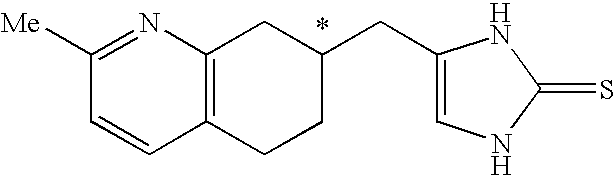
The compound of the formula wherein the * indicates an asymmetric carbon, is specific to alpha2B adrenergic receptors in preference over alpha2A and alpha2C adrenergic receptors, and as such has no or only minimal cardivascular and / or sedatory activity. The compound is useful as medicament in mammals, including humans, for treatment of diseases and or alleviations of conditions which are responsive to treatment by agonists of alpha2B adrenergic receptors.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Anticonvulsant enantiomeric amino acid derivatives
The present invention is directed to a compound in the R configuration about the asymmetric carbon in the following formula: ##STR1## pharmaceutical compositions containing same and the use thereof in treating CNS disorders in animals.
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
Stereoselective alternating copolymerization of epoxide with carbon dioxide
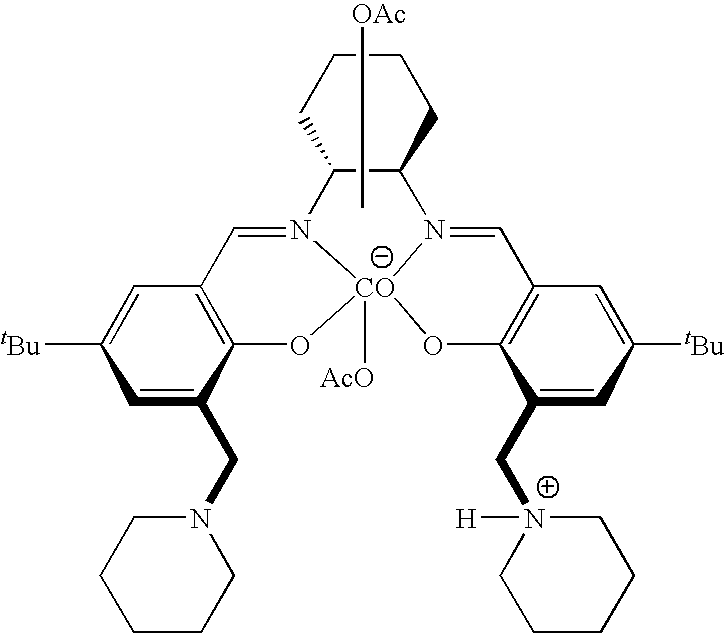
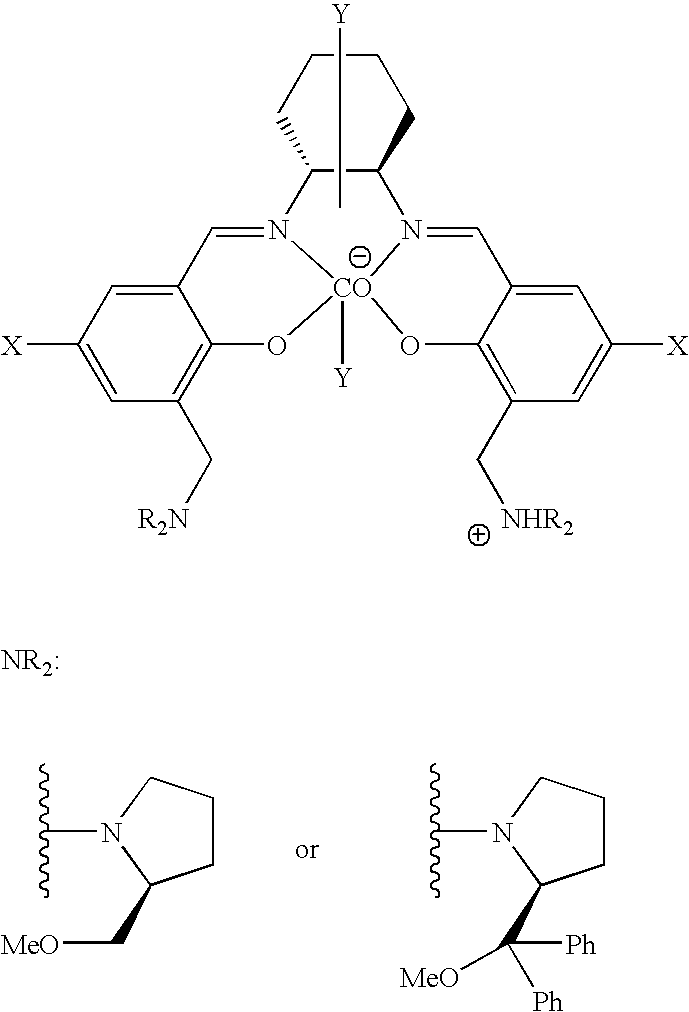
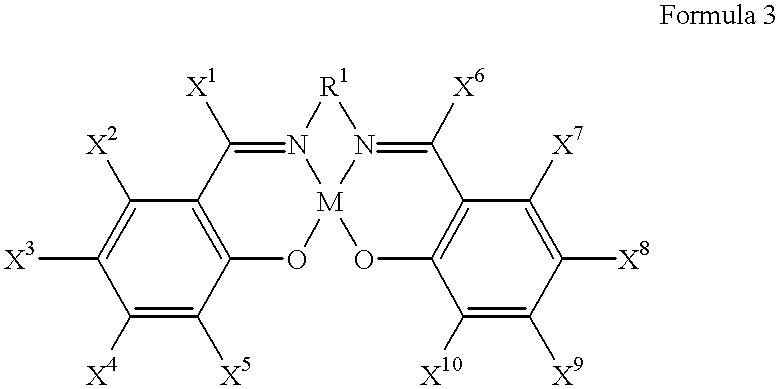
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing polycarbonate, which has a high conversion rate of a propylene oxide material into a polymer and can control stereoregularity of the macromolecular structure, and a catalytic compound for the manufacturing method.The manufacturing method of the present invention is a method for manufacturing a polycarbonate copolymer by copolymerizing an epoxide compound as a monomer with carbon dioxide in the presence of a planar tetracoordinate-type cobalt-Schiff base complex, wherein a ligand of the Schiff base is N,N′-bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene)ethylenediamine, N,N′-bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene)phenylenediamine, or a derivative thereof, and a methyl group substituted with an amino group having an asymmetrical carbon atom or an asymmetrical axis is introduced to the 3- and / or 3′-position of the benzene ring derived from the salicyl group. In addition, the catalytic compound of the present invention is a cobalt-Schiff base complex, wherein a methyl group substituted with an amino group having an asymmetrical carbon atom or an asymmetrical axis is introduced to the 3- and / or 3′-position of the salicyl group.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
4-(substituted cycloalkylmethyl) imidazole-2-thiones, 4-(substituted cycloalkenylmethyl) imidazole-2-thiones, 4-(substituted cycloalkylmethyl) imidazol-2-ones, 4-(substituted cycloalkenylmethyl) imidazol-2-ones and related compounds
The compound of the formulawherein the * indicates an asymmetric carbon, is specific to alpha2B adrenergic receptors in preference over alpha2A and alpha2C adrenergic receptors, and as such has no or only minimal cardivascular and / or sedatory activity. The compound is useful as medicament in mammals, including humans, for treatment of diseases and or alleviations of conditions which are responsive to treatment by agonists of alpha2B adrenergic receptors.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Method for treating neurocognitive dysfunction
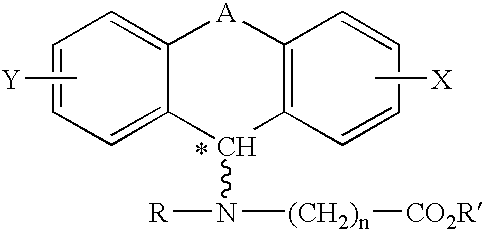
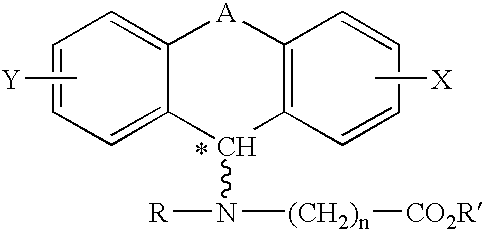
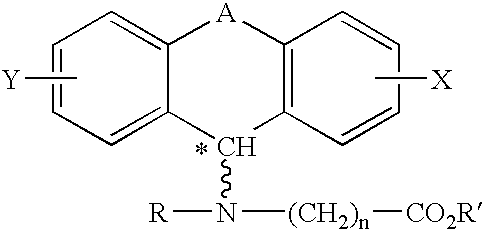
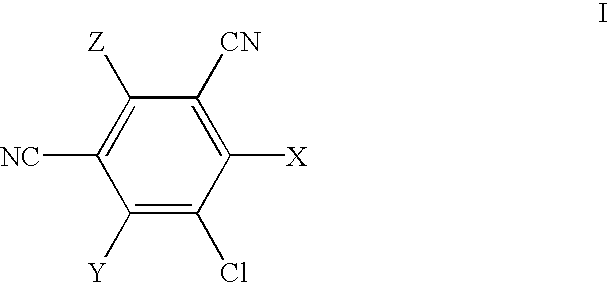
A method of treating corticosteroid-induced cognitive impairment comprises administering an effective amount of at least one compound of formula I, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, to a subject in need of such treatment. Formula I is:wherein: A is a bridge selected from the following radicals: —(CH2)m—, —CH═CH—, —(CH2)p—O—, —(CH2)p—S—, —(CH2)p—SO2—, —(CH2)p—NR1— and —SO2—NR2—, and wherein: m is an integer of from 1 to 3 inclusive; p is an integer selected from 1 and 2; R1 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and C1-C5 alkyl; and R2 is C1-C5 alkyl; X and Y are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and halogen; R and R′ are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and C1-C5 alkyl; n is an integer from 1 to 12 inclusive; and * denotes an asymmetric carbon.
Owner:TONIX PHARMA HLDG LTD
Process for Producing alpha Substituted Ester
InactiveUS20110213176A1Low costEffective combinationOrganic compound preparationSulfuric acid esters preparationGrignard reagentTriflic acid
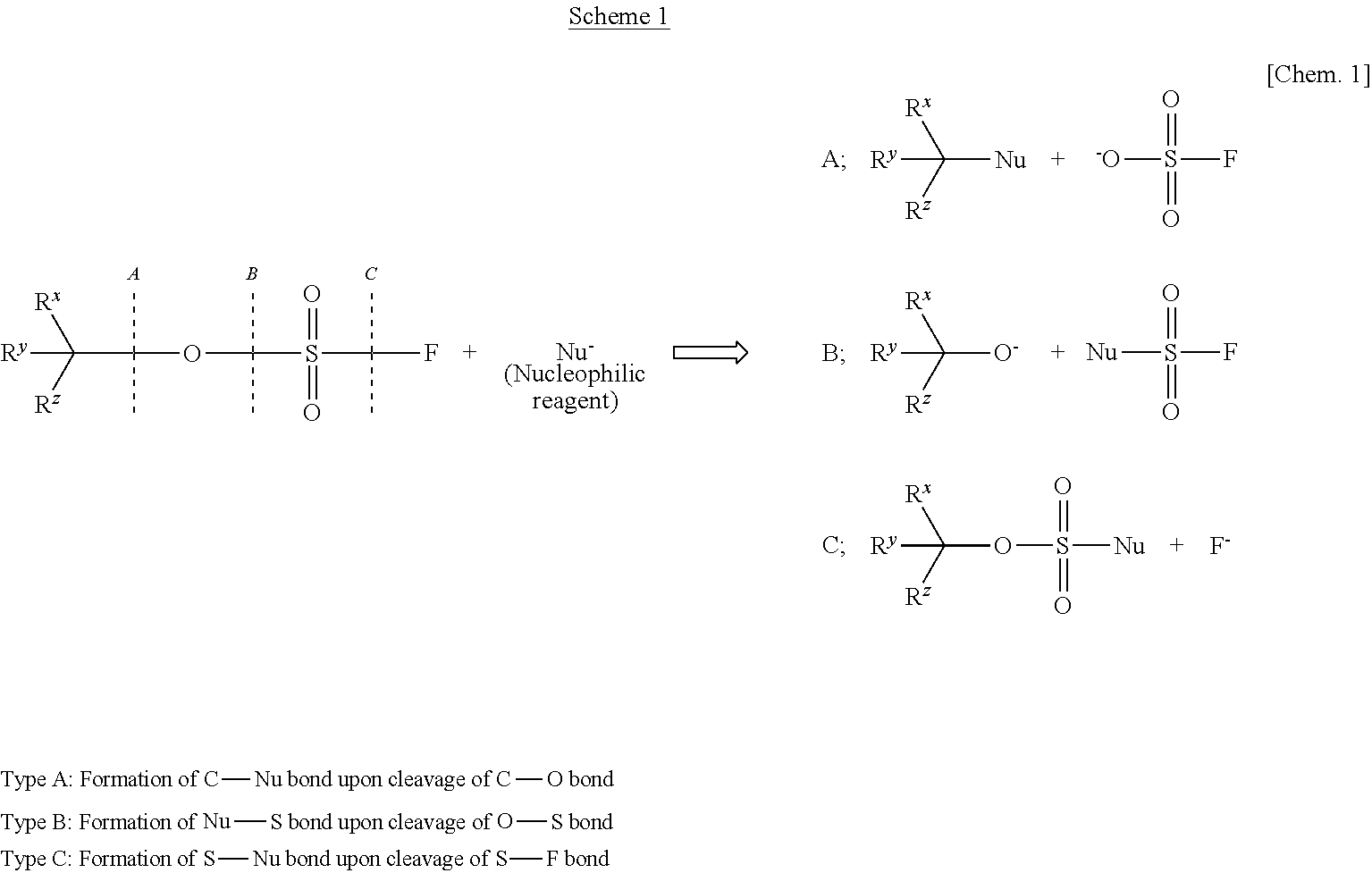
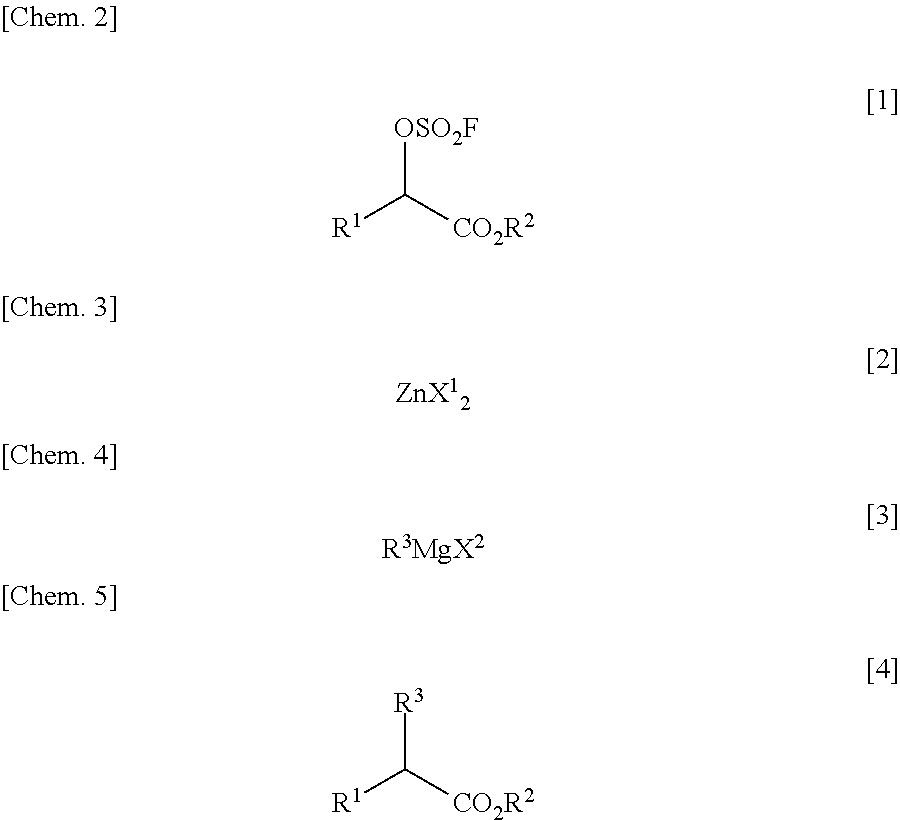
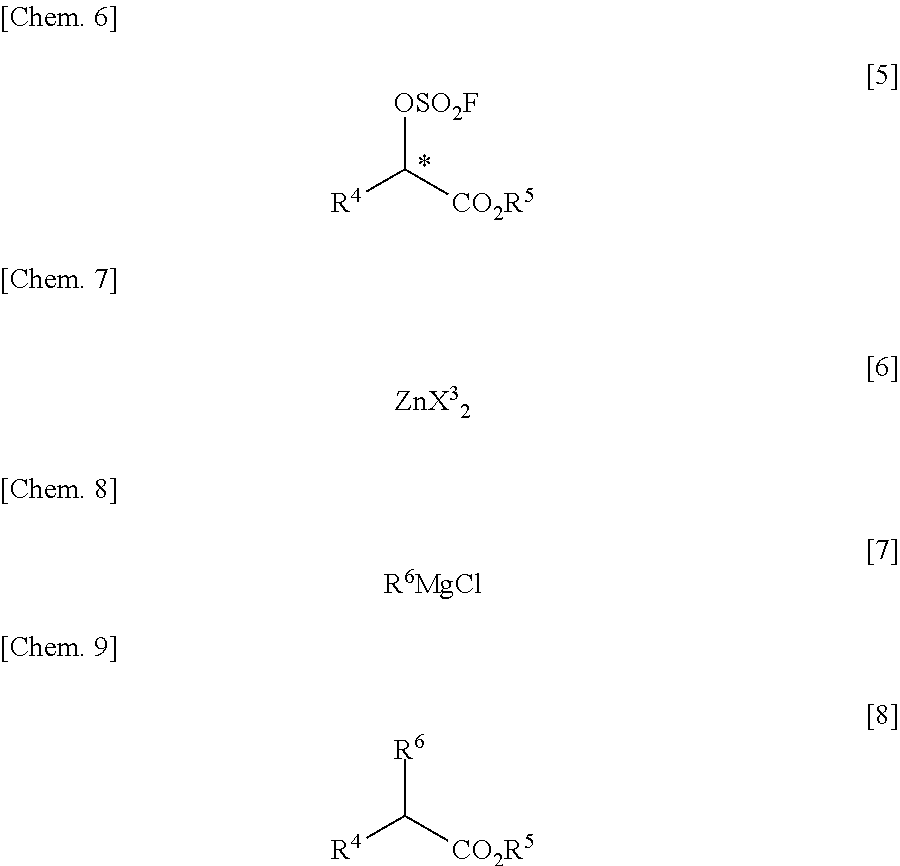
There is provided a process for producing an α-substituted ester by reaction of a fluorosulfuric acid ester of α-hydroxyester with a Grignard reagent in the presence of a zinc catalyst. It is newly found that the reaction for production of α-substituted esters, in which the raw reaction substrate is limited to expensive trifluoromethanesulfonic acid esters, can proceed favorably with the use of fluorosulfuric acid esters suitable for mass-production uses. By the use of the fluorosulfuric acid ester high in optical purity, it is possible to obtain the α-substituted ester with high optical purity upon inversion of the asymmetric carbon configuration. The process of the present invention can solve all of the prior art problems and can be applied for industrial uses.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Method for stereoselectively producing substituted polycyclic pyridone derivative
ActiveCN111386276AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsCombinatorial chemistryPerylene derivatives
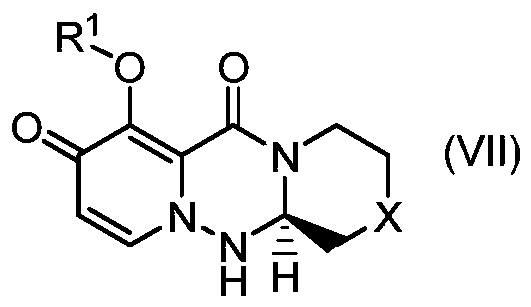
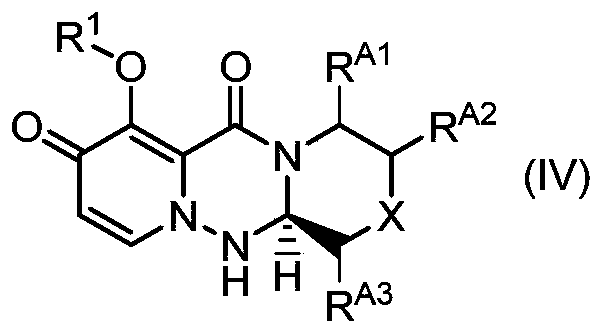
The present invention provides a commercially applicable method for producing an intermediate of a substituted polycyclic pyridone derivative exhibiting cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitory activity.In the production method shown in the reaction formula (in the formula, the symbols are as defined in the description), by means of an intramolecular cyclisation reaction in which the stereochemistryof a compound shown in formula (III) or formula (VI) is controlled, a compound shown in formula (IV) and including an eliminable functional group on an asymmetric carbon is obtained, and said eliminable functional group is eliminated, whereby an optically active substituted 3-ring pyridone derivative shown in formula (VII) is highly enantioselectively obtained in a high yield.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Substituted acetylpridine derivatives and process for the preparation of intermediates for optically active beta-3 agonist by the use of the same
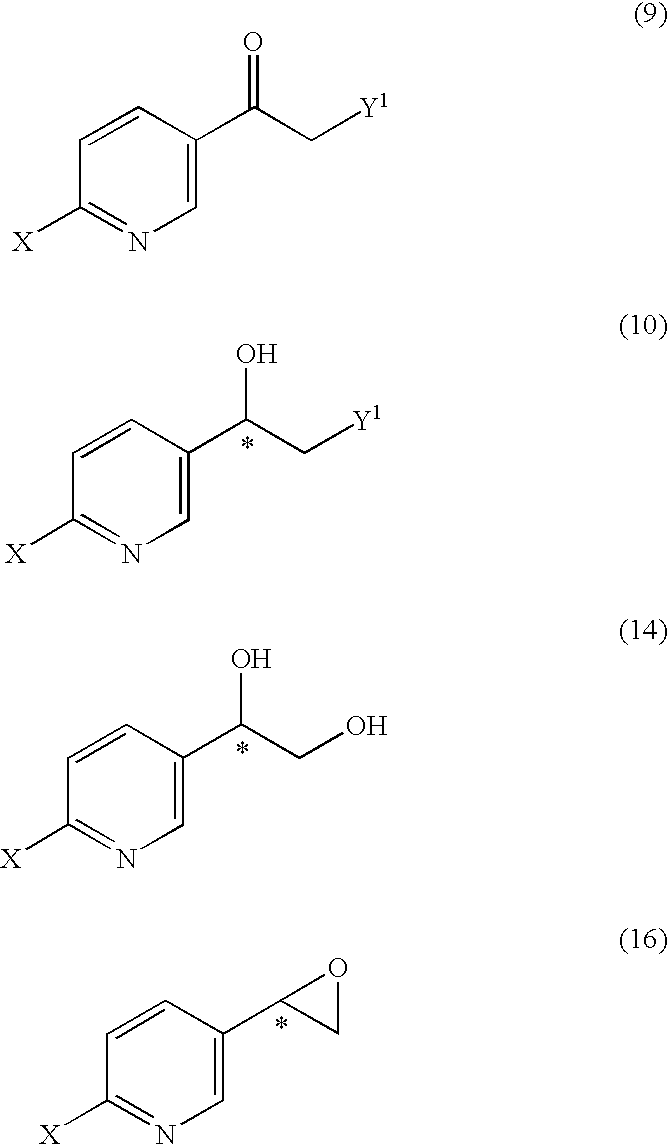
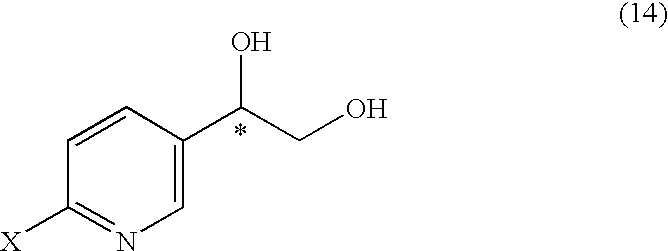
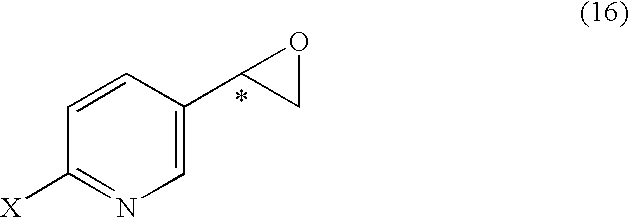
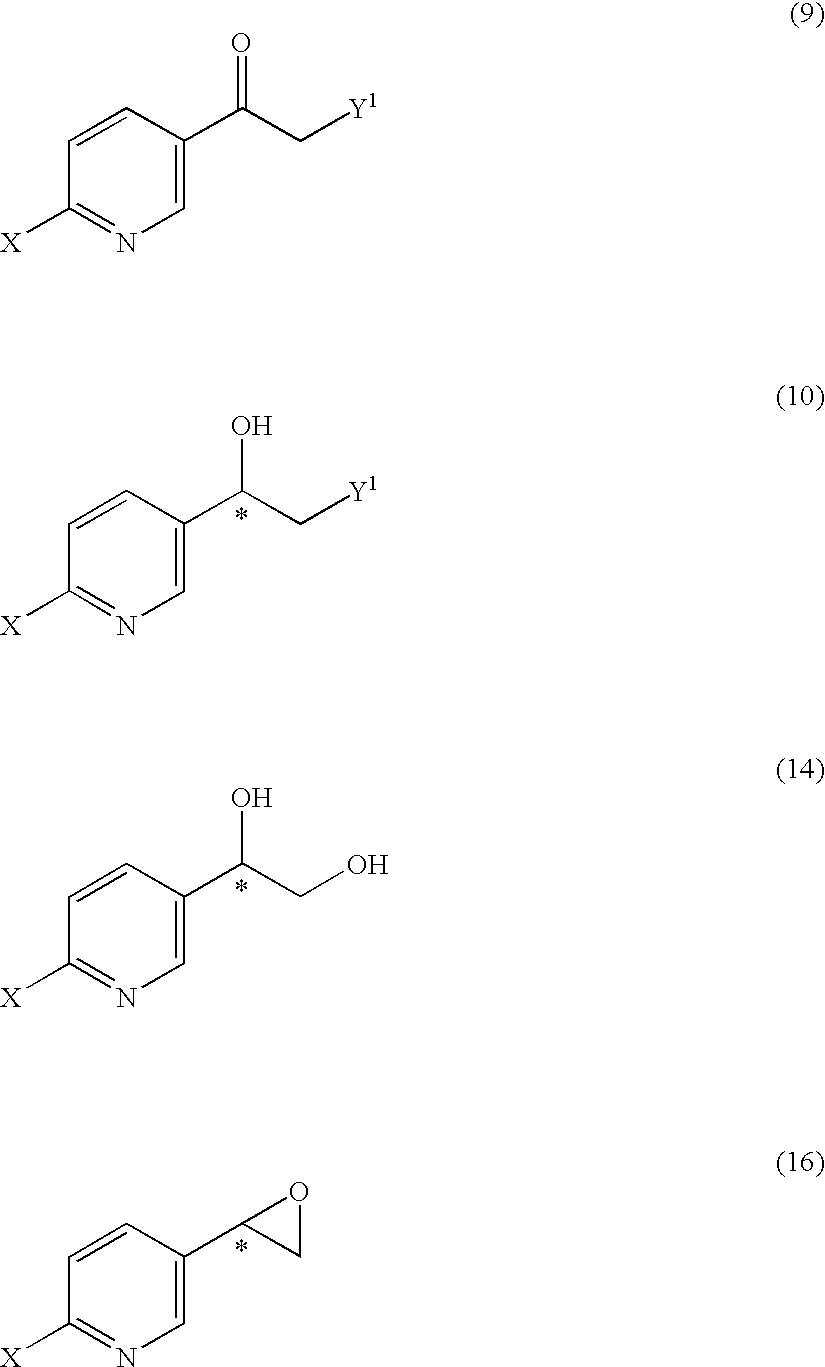
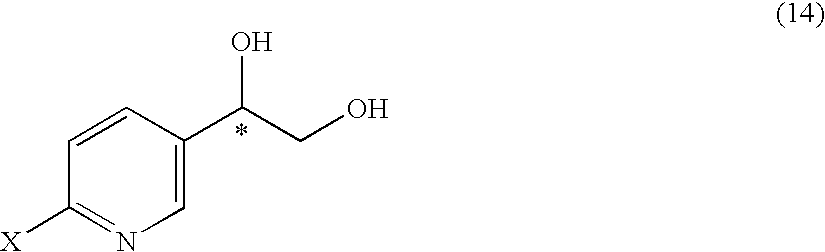
It is an objective to produce intermediates of optically active beta-3 adrenaline receptor agonists from readily available raw materials in a safe, efficient and industrially advantageous manner. A substituted acetylpyridine derivative represented by the general formula (9) is reduced by enantioselective reduction to produce an optically active hydroxyethyl derivative represented by the general formula (10) (wherein * represents an asymmetric carbon atom), and it is further derivatized to an intermediate of an optically active beta-3 adrenaline receptor agonist, such as an optically active dihydroxyethylpyridine derivative represented by the general formula (14) or an optically active oxirane derivative represented by the general formula (16).
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Substituted acetylpyridine derivatives and process for the preparation of intermediates for optically active beta3 agonist by the use of the same
It is an objective to produce intermediates of optically active beta-3 adrenaline receptor agonists from readily available raw materials in a safe, efficient and industrially advantageous manner. A substituted acetylpyridine derivative represented by the general formula (9) is reduced by enantioselective reduction to produce an optically active hydroxyethylpyridine derivative represented by the general formula (10) (wherein * represents an asymmetric carbon atom), and it is further derivatized to an intermediate of an optically active beta-3 adrenaline receptor agonist, such as an optically active dihydroxyethylpyridine derivative represented by the general formula (14) or an optically active oxirane derivative represented by the general formula (16).
Owner:KANEKA CORP
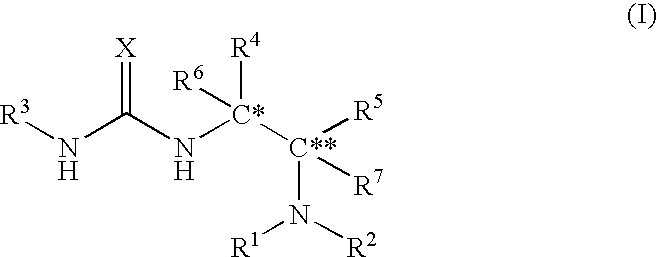
Asymmetric urea compound and process for producing asymmetric compound by asymmetric conjugate addition reaction with the same as catalyst
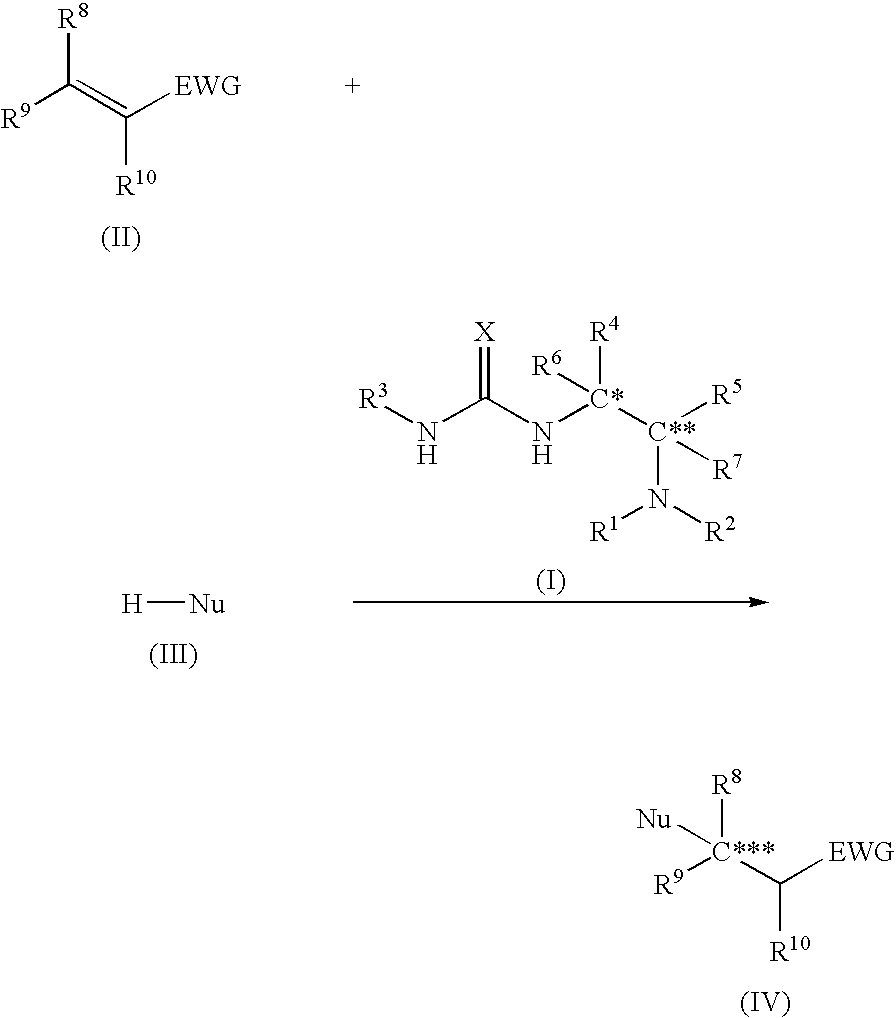
ActiveUS20060161006A1High yieldUrea derivatives preparationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationArylHydrogen atom
The present invention relates to a production method of asymmetric compound (IV) which includes conjugately adding nucleophilic reagent (III) to compound (II) in the presence of asymmetric urea compound (I). The present invention provides a non-metallic asymmetric catalyst capable of realizing a highly stereoselective asymmetric conjugate addition reaction in a high yield, and an advantageous production method of an asymmetric compound by an asymmetric conjugate addition reaction using the asymmetric catalyst. wherein X is an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom; C*, C** and C*** are asymmetric carbons; R1, R2, R4, R5, R8, R9 and R10 are each a lower alkyl group optionally having substituent(s) and the like, or R4 and R5 and the like in combination optionally form a homocyclic ring optionally having substituent(s) and the like; R3 is an aryl group optionally having substituent(s) and the like; R6 and R7 are each a hydrogen atom and the like; Nu is —CR16 (COR17)(COR18) wherein R16, R17 and R18 are each a lower alkyl group optionally having substituent(s) and the like, and the like; and EWG is an electron withdrawing group.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Epoxide-carbon dioxide stereoselective alternating copolymer
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing polycarbonate, which has a high conversion rate of a propylene oxide material into a polymer and can control stereoregularity of the macromolecular structure, and a catalytic compound for the manufacturing method. The manufacturing method of the present invention is a method for manufacturing a polycarbonate copolymer by copolymerizing an epoxide compound as a monomer with carbon dioxide in the presence of a planar tetracoordinate-type cobalt-Schiff base complex, wherein a ligand of the Schiff base is N,N'-bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene) ethylenediamine, N,N'-bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene) phenylenediamine, or a derivative thereof, and a methyl group substituted with an amino group having an asymmetrical carbon atom or an asymmetrical axis is introduced to the 3- and / or 3'-position of the benzene ring derived from the salicyl group. In addition, the catalytic compound of the present invention is a cobalt-Schiff base complex, wherein a methyl group substituted with an amino group having an asymmetrical carbon atom or an asymmetrical axis is introduced to the 3- and / or 3'-position of the salicyl group.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
3-Amino-3-arylpropionic acid n-alkyl esters, process for production thereof, and process for production of optically active 3-amino-3-arylpropionic acids and esters of the antipodes thereto
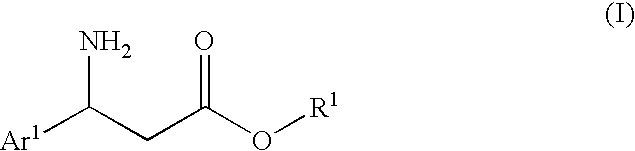
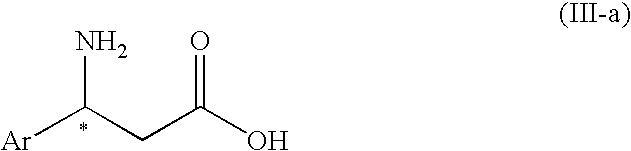
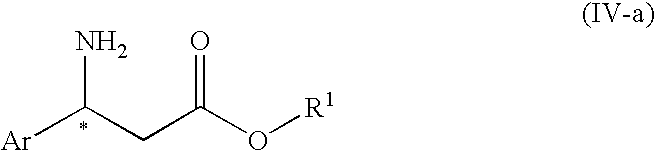
The present invention is to provide an n-alkyl 3-amino-3-arylpropionate represented by the formula (I): wherein Ar1 represents an aryl group which may have a substituent(s), provided that a phenyl group and 4-methoxyphenyl group are excluded, R1 represents an n-propyl group or an n-butyl group, and a process for preparing the same, and its optically active compound and an optically active (S or R)-3-amino-3-arylpropionic acid represented by the formula (III-a): wherein Ar represents an aryl group which may have a substituent(s), and * represents an asymmetric carbon, and a process for preparing an optically active n-alkyl (R or S)-3-amino-3-arylpropionate represented by the formula (IV-a): wherein Ar and R1 have the same meanings as defined above, * represents an asymmetric carbon, provided that it has a reverse absolute configuration to the compound of the formula (III-a).
Owner:UBE IND LTD
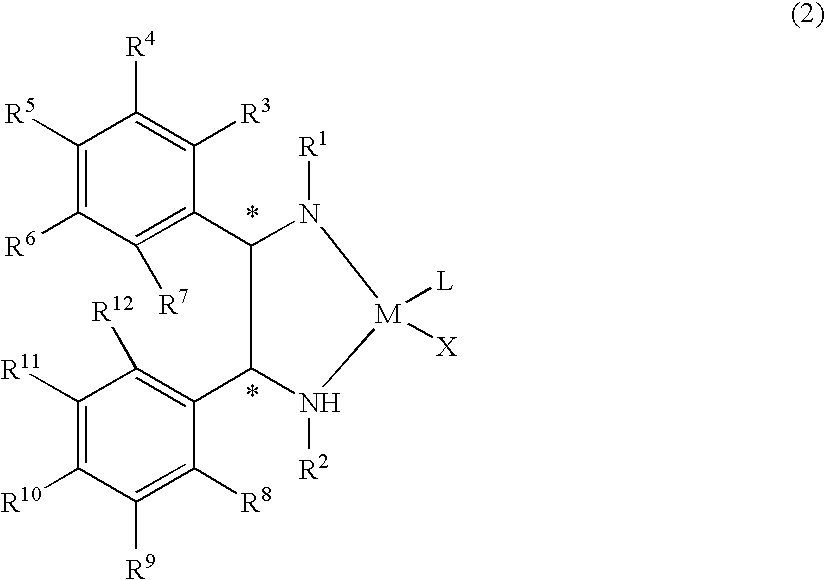
Optically active transition metal-diamine compound and process for producing optically active alcohol with the same
InactiveUS20070149831A1Clean chemical reactionPromote recoveryRuthenium organic compoundsRhodium organic compoundsKetoneChemistry
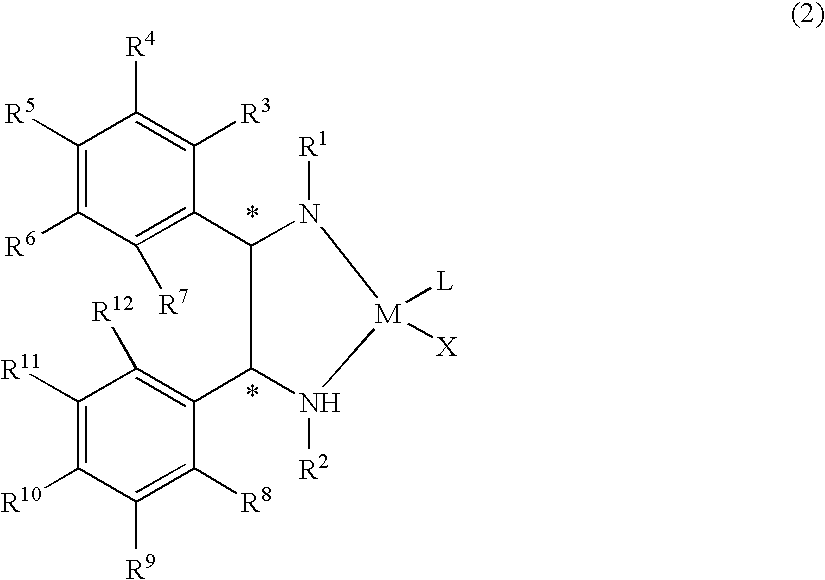
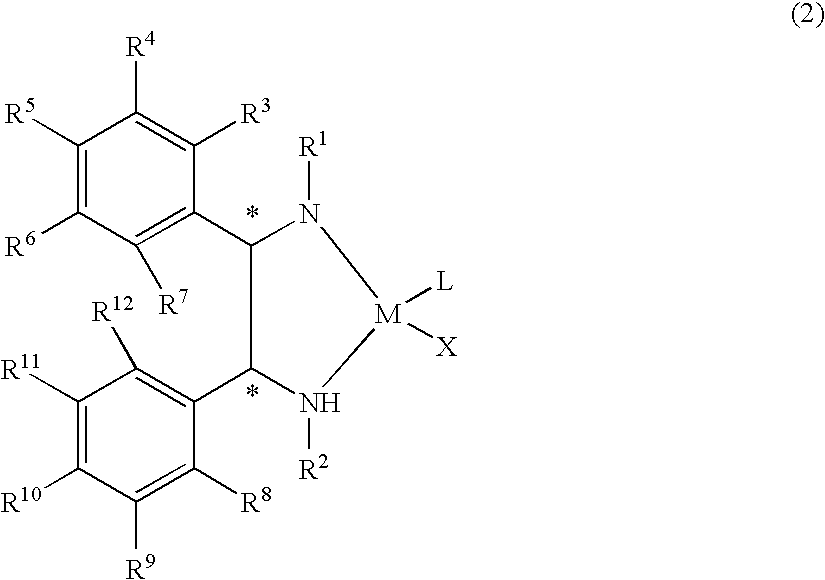
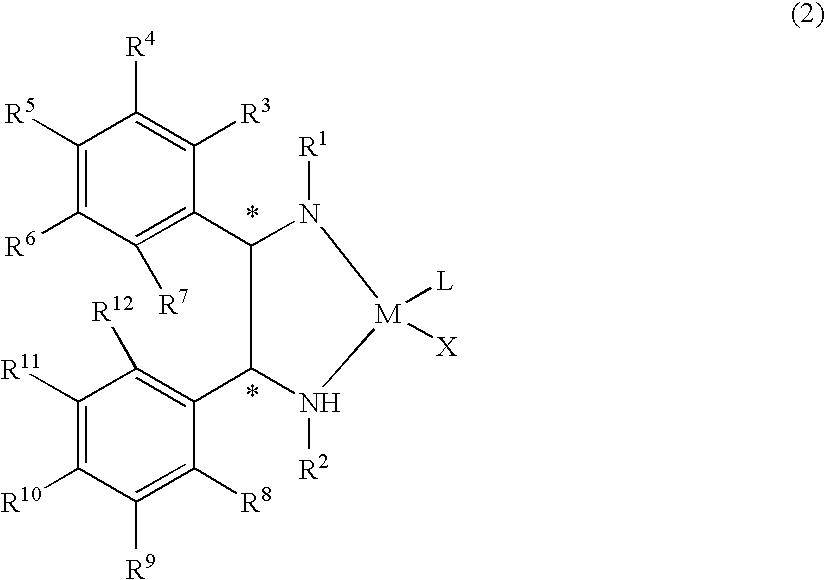
The present invention provides a water-soluble transition metal-diamine complex which can be easily separated from reaction products through liquid separation, etc. and is recycleable; an optically active diamine compound constituting the ligand of the complex; and a catalyst for asymmetric synthesis which comprises these. The present invention relates to a water-soluble optically active transition metal-diamine complex represented by the formula (2): [wherein R1 and R2 each represents hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group, —SO2R13 (wherein R13 is a hydrocarbon group, substituted amino, etc.), etc.; R3 to R12 each represents hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group, alkoxy, substituted amino, etc.; M represents a transition metal; X represents halogen; L represents a ligand; and * indicates an asymmetric carbon atom; provided that at least one of R3 to R7 and R8 to R12 is substituted amino], a catalyst for asymmetric synthesis containing the complex, and a process for producing an optically active alcohol, which comprises using the catalyst to asymmetrically reduce a ketone.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Chiral stationary phases for enantiomers separation and their preparation
InactiveUS6437167B1Ion-exchange process apparatusSilicon organic compoundsStationary phaseChiral stationary phase
The present invention describes new chiral stationary phases and optically active compounds therein contained. The optically active compounds contained in the stationary phases are represented by the formula of structure (I), containing at least one asymmetric carbon atom, and a substituent acting as a spacer. The stationary phases of the present invention are useful in the preparation of chromatographic columns useful for the separation of enantiomers.
Owner:SOC COOP CENT RICERCE +1
Process for producing optically active chromene derivative
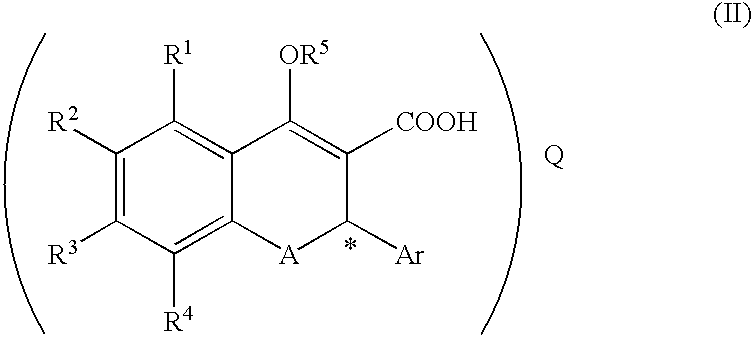
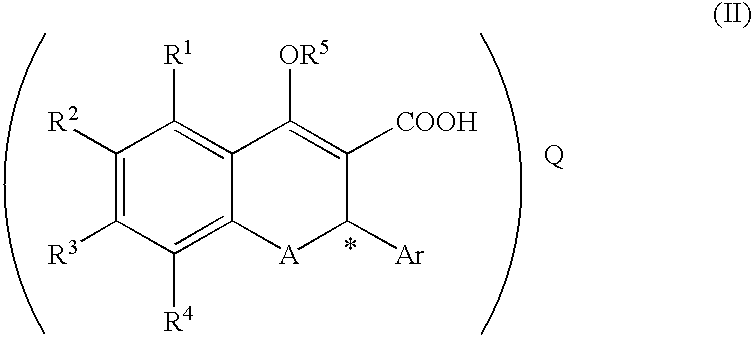
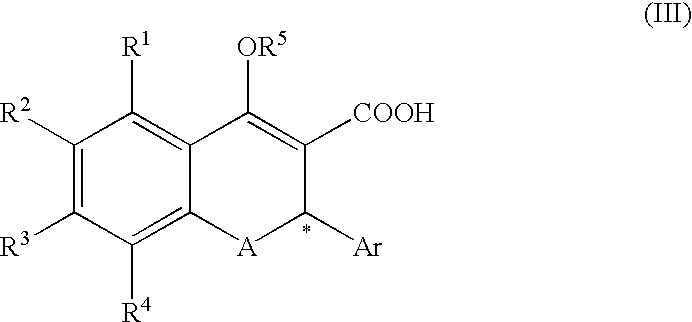
A process for producing a compound of the formula (II):(wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are each independently hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy or the like, R5 is alkyl or alkoxyalkyl, A is O or S, Ar is aryl or the like, * represents the position of an asymmetric carbon atom and that the compound is the (R) or (S) isomer and Q is an optical resolution reagent)comprising isolating the compound as crystals from a solution or suspension containing the compound of the formula (II) (wherein * represents that the compound is the (R) or (S) isomer or a mixture thereof and the other symbols are the same as the above).
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Method for augmenting spiral torsion, optical active compound, liquid crytal composite and liquid crystal display element untaining it
InactiveCN1495246AIncrease the HTP valueLarge HTP valueLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsCrystallographyHalogen
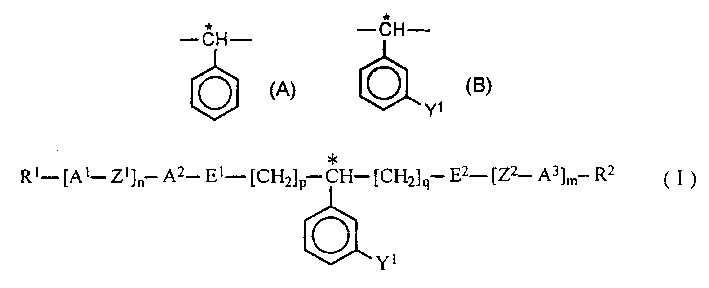
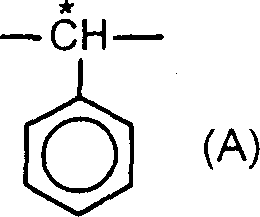
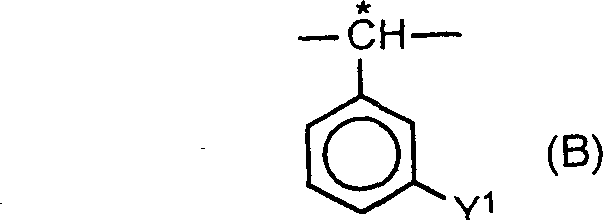
A method of increasing helical twisting power (HTP) in an optically active compound used in a liquid crystal material is provided. An optically active compound which exhibits a large HTP value is also provided. Furthermore, a liquid crystal composition which exhibits a high upper temperature limit of the liquid crystal after the addition of the optically active compound, and a liquid crystal display device using the same are provided. In a method, an HTP of a compound having a partial structure represented by formula (A), which has an asymmetric carbon atom, is increased by replacing the partial structure represented by formula (A) by a partial structure represented by formula (B). (wherein * represents the position of an asymmetric carbon atom, Y<1 >represents a substituent such as an alkyl group and a halogen). A compound is represented by formula (I).
Owner:DIC CORP
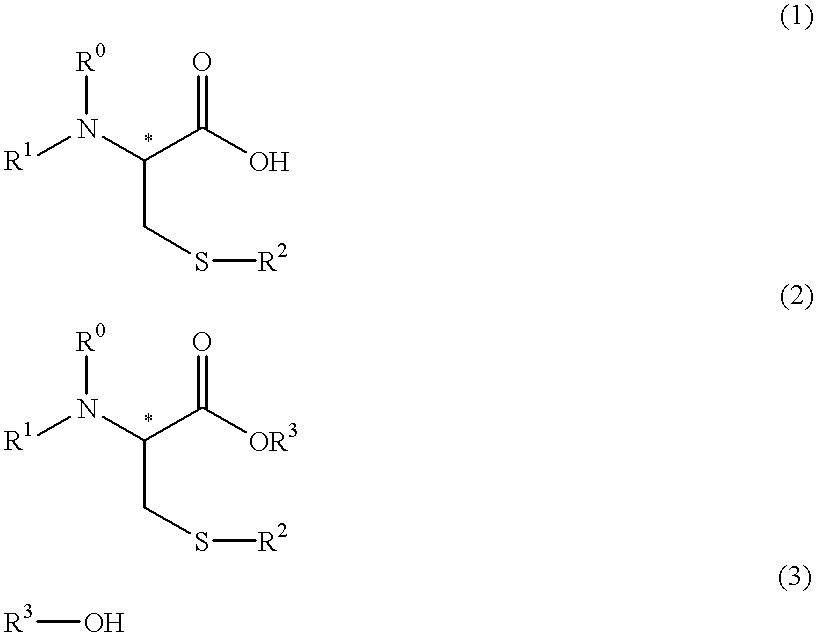
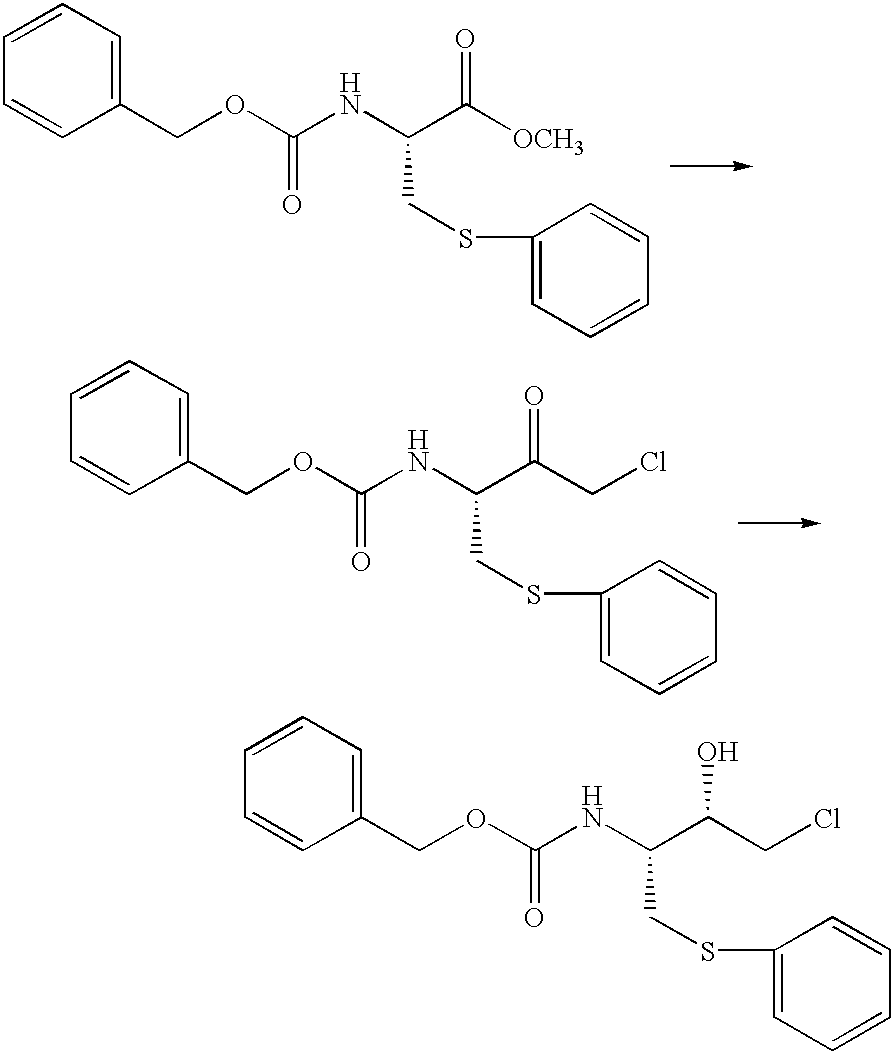
Process for producing optically active cysteine derivatives
InactiveUS6407281B1Decrease in optical purityAvoid racemizationOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCarbamateDecomposition
A process for producing optically active cysteine derivatives with high optical purity and good quality which is economically advantageous and is high in productivity even on a commercial scale is provided.A process for producing an optically active cysteine derivative which comprises synthesizing a D-form or L-form optically active cysteine derivative of the general formula (2) shown below (R1 represents an amino-protecting group of the urethane or acyl type, R0 represents a hydrogen atom or, taken together with R1, an amino-protecting group, R2 represents an alkyl, aryl or aralkyl group, R3 represents a univalent organic group and * represents the position of an asymmetric carbon) by reacting the corresponding D-form or L-form optically active amino acid derivative of the general formula (1) shown below with an alcohol of the general formula (3) shown below and a strong acid and / or a thionyl halide and recovering the above cysteine derivative (2) from the reaction mixture, the procedural series from reaction to recovery being carried out under conditions such that the medium contacting the above optically active cysteine derivative (2) is within the range from acidic to weakly basic to thereby recover the above cysteine derivative (2) from the reaction mixture while suppressing the decomposition and racemization thereof.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Process for the preparation of optically active amino alcohols
InactiveUS6410749B1Prevent effectCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationAlcoholHydrogen
Process for preparing optically active beta-amino alcohols represented by a general formula (2): Ra-C*H(OH)-C*H(Rb)-Rc wherein Ra and Rc are each independently hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl, optionally substituted cycloalkyl, Rb is one member selected from among groups represented by the following general formulae; (3) R1CO(R2)N-, and (4) R1CO(R1'CO)N-, and C* is an asymmetric carbon atom, characterized by reacting a racemic alpha-aminocarbonyl compound represented by the general formula (1): Ra-CO-CH(Rb)-Rc, with hydrogen in the presence of an optically active transition metal compound represented by a general formula (7): MaXY(Px)m(Nx)n wherein Ma represents a metal atom belonging to VIII-group of the periodic law, X and Y represent each independently hydrogen, halogeno, Px represents a phosphine ligand, Nx represents an amine ligand, at least one of Px and Nx is optically active, and m and n each independently represent 0 or an integer of 1 through 4 and a base.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
Method for selectively recycling noble metal ions of gold and silver
ActiveCN107502745AAchieving Selective RecyclingAchieve recyclingMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingRefluxComposite film
The invention provides a method for selectively recycling noble metal ions of gold and silver. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a carbon tube undergoes reflux treatment in a nitric acid solution to form a carboxylation carbon tube; 2, a carbon tube film is prepared by macroscopic interface recombination of a carboxylation carbon nano tube; 3, a macroscopic carbon tube thin film is tightly pressed to form a transferable self-supporting carbon tube thin film; 4, the carbon tube thin film is transferred to the surface of a dopamine aqueous solution so as to form an asymmetric carbon tube composite thin film; 5, the asymmetric carbon tube composite thin film is transferred to the surface of an aqueous solution, and residual impurities are cleaned and removed to obtain a macroscopic carbon tube interface reactor; 6, the carbon tube composite thin film is transferred to the surface of noble metal waste liquid; 7, the carbon tube composite thin film is transferred to the surface of the noble metal waste liquid to form a carbon tube and noble metal nanoparticle composite thin film material; and 8, the noble metal nanoparticle material is recycled and utilized. The method is simple to operate and high in selectivity.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing an optically active 1-substituted 2-propanol
A method for producing an optically active 1-substituted 2-propanol of the following formula 1, which comprises reacting a hydroxy aromatic compound of the following formula 2 with an optically active propylene oxide in the presence of a catalyst:wherein A is a univalent aromatic group, and C* is an asymmetric carbon atom.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
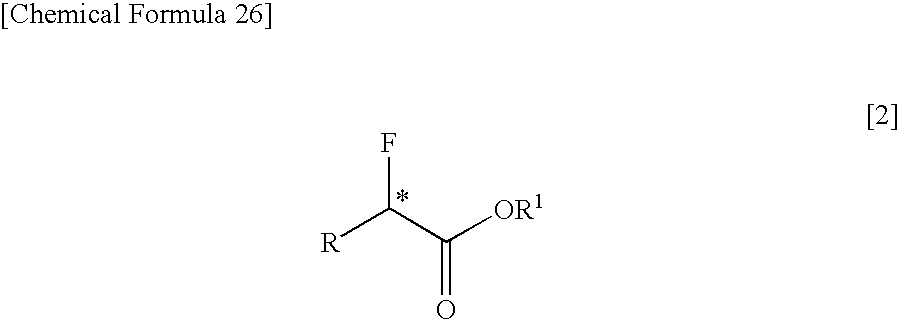
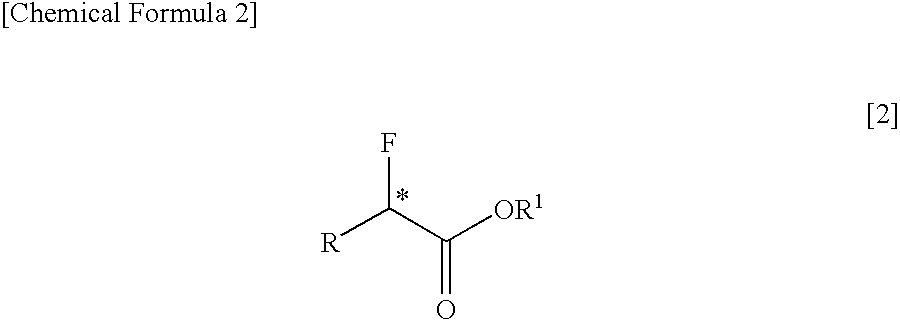
Process for production of optically active α-fluoro-carboxylic ester derivatives
InactiveUS7462734B2Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCarbon numberCarboxyl radical
The present invention relates to a process for producing an optically active α-fluorocarboxylate derivative represented by the formula [2],by reacting an optically active α-hydroxycarboxylate derivative with trifluoromethanesulfonyl fluoride (CF3SO2F) in the presence of an organic base, in the formula [2], R represents a straight-chain or branched-chain alkyl group of a carbon number of 1 to 12; one of or two by any combination of aromatic hydrocarbon groups, unsaturated hydrocarbon groups, straight-chain or branched alkoxy groups of a carbon number of 1 to 6, aryloxy groups, halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine), protected carboxyl groups, protected amino groups or protected hydroxyl group can be substituted on any carbon atoms of the alkyl group; R1 represents a straight-chain or branched-chain alkyl group of a carbon number of 1 to 8; any carbon atoms of the alkyl groups of R and R1 may form a covalent bond; and * represents an asymmetric carbon.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Process for production of optically active aminophosphinylbutanoic acid
ActiveCN101495491AEfficient and high optical purityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsArylHydrogen atom
A process for producing an optically active aminophosphinylbutanoic acid represented by the general formula (2), comprising the step for conducting the asymmetric hydrogenation of a compound represented by the general formula (1) in the presence of a ruthenium-(optically active phosphine) complex. In the general formula (2), R1 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R2 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R3 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an aryl group, an aryloxy group or a benzyloxy group; R4 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; and symbol '*' means that a carbon having this symbol is an asymmetric carbon atom. In the general formula (1), R1 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R2 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R3 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbonatoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, an aryl group, an aryloxy group or a benzyloxy group; R4 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; The process enables to produce a compound useful as a herbicide such as L-AHPB, at good efficiency and at high asymmetric yield.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM AGRO INC +1
Process for producing optically active azetidine-2-carboxylic acid derivative
There is provided a process for producing N-substituted azetidine-.2-carboxylic acid of the formula I: wherein R1 denotes an aralkyl group or an arylated lower alkoxycarbonyl group and * designates an asymmetric carbon atom, which is characterized by: reacting an N-substituted azetidine-2-carboxylic acid ester of the formula II: wherein R1 has the same meaning as defined above and R2 denotes an alkyl group, an aralkyl group or an allyl group, with an enzyme capable of selectively hydrolyzing a stereoisomer based on the carbon atom of the 2-position of the azetidine ring.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Organic metal compound and process for preparing optically-active alcohols using the same
InactiveUS20090062573A1Improve efficiencyEfficiently obtainedOrganic reductionIndium organic compoundsIridiumAlcohol
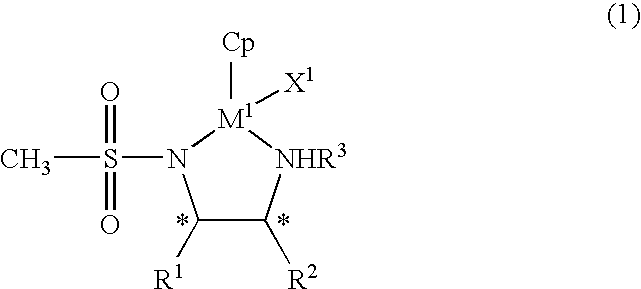
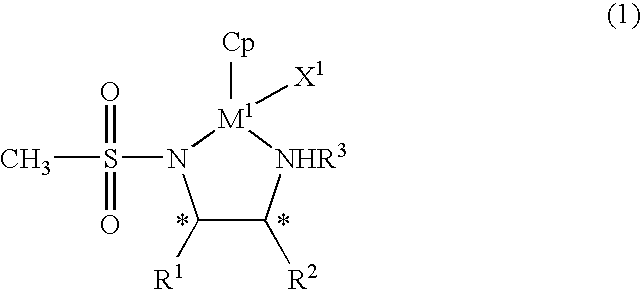
The present invention provides an asymmetric reduction catalyst effective in preparing optically-active alcohol compounds having various functional groups, and a process for preparing optically-active alcohol compounds using said asymmetric reduction catalyst.The organic metal compound of the present invention is represented by the following general formula (1):wherein R1 and R2 may be mutually identical or different, and are an alkyl group, a phenyl group, a naphthyl group, a cycloalkyl group, or an alicyclic ring formed by binding R1 and R2, which may have a substituent; R3 is a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group; Cp is a cyclopentadienyl group, which may have a substituent, bound to M1 via a π bond; X1 is a halogen atom or a hydrido group; M1 is rhodium or iridium; and * denotes asymmetric carbon.
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC
Vitamin D3 derivative and its production method
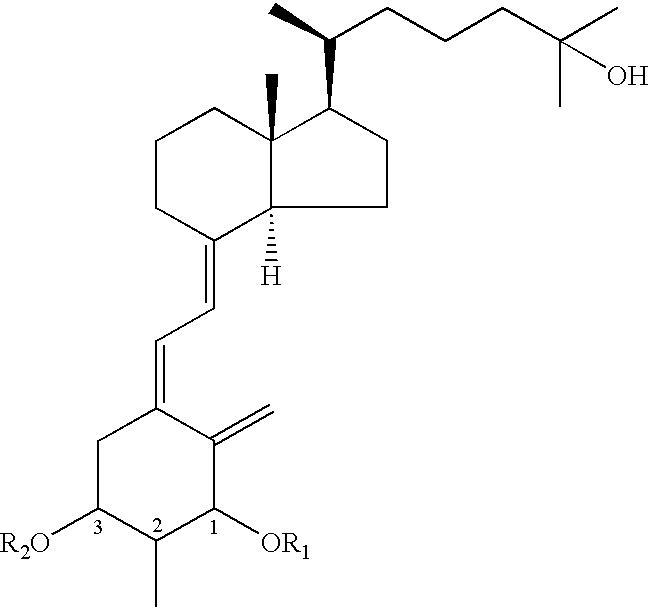
Provided are 1,25-dihydroxy-2-methylvitamin D3 derivatives expressed by the general formula (I), [wherein each of R1 and R2 is independently a hydrogen atom or a tri(C1 to C7 alkyl)silyl group; herein configurations of asymmetric carbons at the 1-, 2- and 3-positions are each independently α-configuration or β-configuration] and their production methods.The compound is useful as a treating agent for osteoporosis, rickets, hyperthyroidism, etc.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Optically active transition metal-diamine compound and process for producing optically active alcohol with the same
InactiveUS7754889B2Promote recoveryClean chemical reactionRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationKetoneCoordination complex
The present invention provides a water-soluble transition metal-diamine complex which can be easily separated from reaction products through liquid separation, etc. and is recycleable; an optically active diamine compound constituting the ligand of the complex; and a catalyst for asymmetric synthesis which comprises these. The present invention relates to a water-soluble optically active transition metal-diamine complex represented by the formula (2):[wherein R1 and R2 each represents hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group, —SO2R13 (wherein R13 is a hydrocarbon group, substituted amino, etc.), etc.; R3 to R12 each represents hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group, alkoxy, substituted amino, etc.; M represents a transition metal; X represents halogen; L represents a ligand; and * indicates an asymmetric carbon atom; provided that at least one of R3 to R7 and R8 to R12 is substituted amino], a catalyst for asymmetric synthesis containing the complex, and a process for producing an optically active alcohol, which comprises using the catalyst to asymmetrically reduce a ketone.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Pharmaceutical composition containing optically active compound having thrombopoietin receptor agonist activity, and intermediate therefor
ActiveUS20100267783A1Promote oral absorptionHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSolventBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
An optically active 4-phenylthiazole derivative having a thrombopoietin receptor agonist activity and a pharmaceutical composition containing the present compound as an active ingredient are created, and a platelet production regulating agent which can be orally administered is provided.Disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition containing, as an active ingredient, an optically active compound represented by the formula:wherein, R1 is a halogen atom or C1-C3 alkyloxy; R2 is C1-C8 alkyl; R3 is C1-C8 alkyl; R4 and R5 are each independently a fluorine atom or chlorine atom; R6 is C1-C3 alkyl or C1-C3 alkyloxy; * indicates that a carbon atom marked with an asterisk is an asymmetric carbon,a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Methylmenthol derivative and cool-sensation imparter composition containing same
ActiveUS20200024221A1Clear cool-feelingGood for persistenceCosmetic preparationsOrganic chemistryMentholAryl
A cooling agent composition includes a methyl menthol derivative represented by the following general formula (1). In the formula (1), a symbol * indicates an asymmetric carbon atom, X represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent, and Y represents an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms which may have a substituent.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
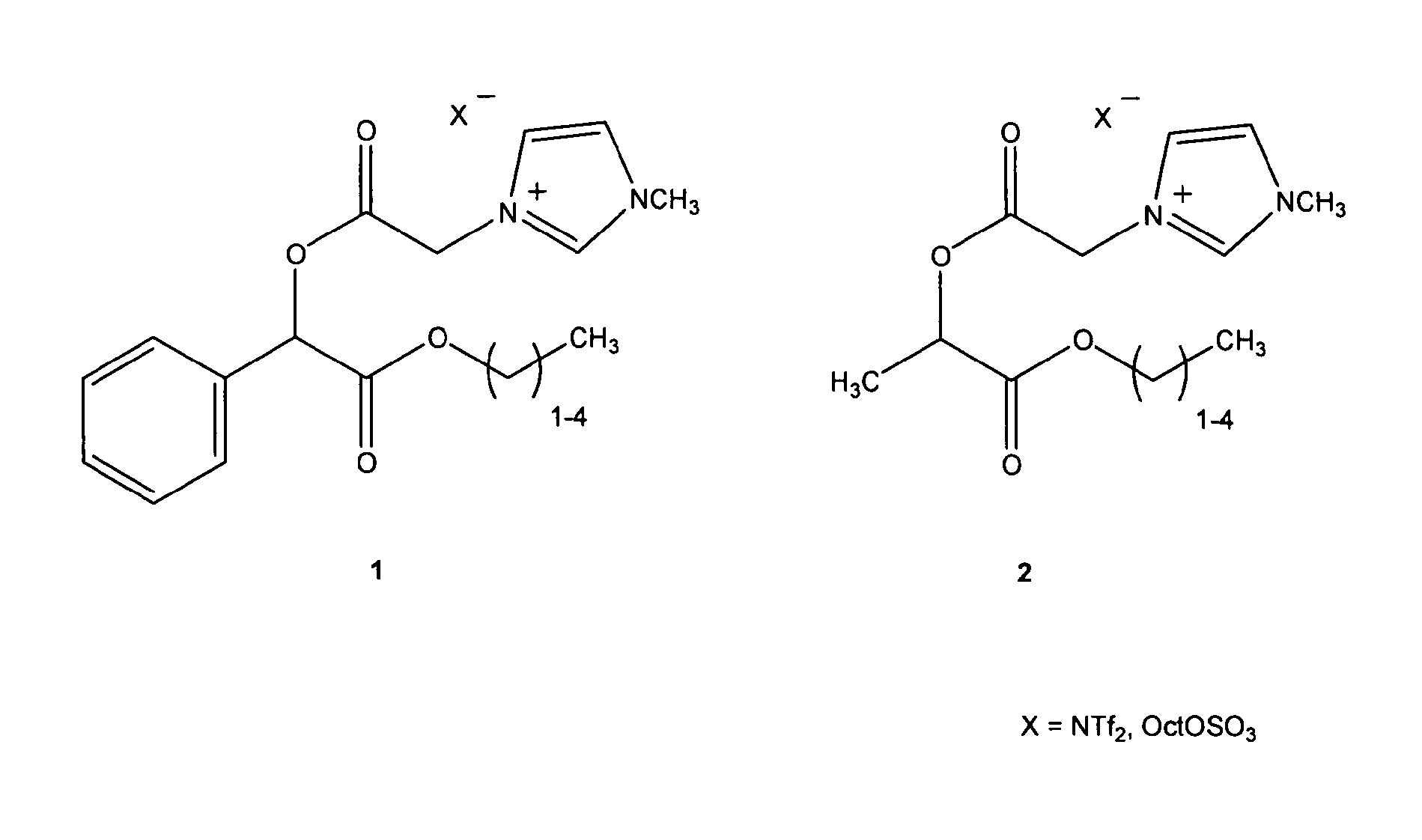
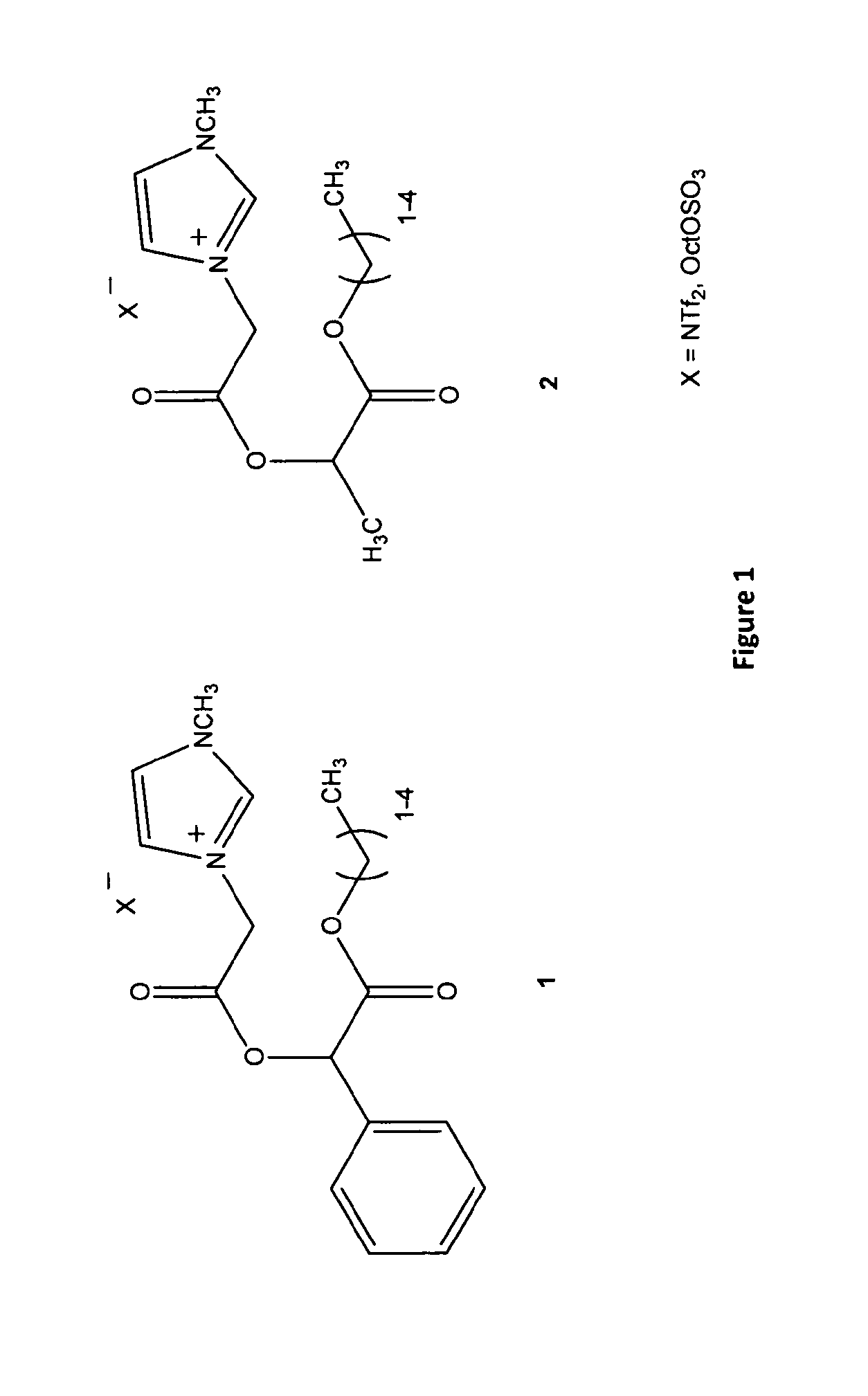
Ionic Liquid Solvents
InactiveUS20120071661A1Easy to functionalizeConvenient solvent tailoringOrganic chemistryPyridiniumOrganic synthesis
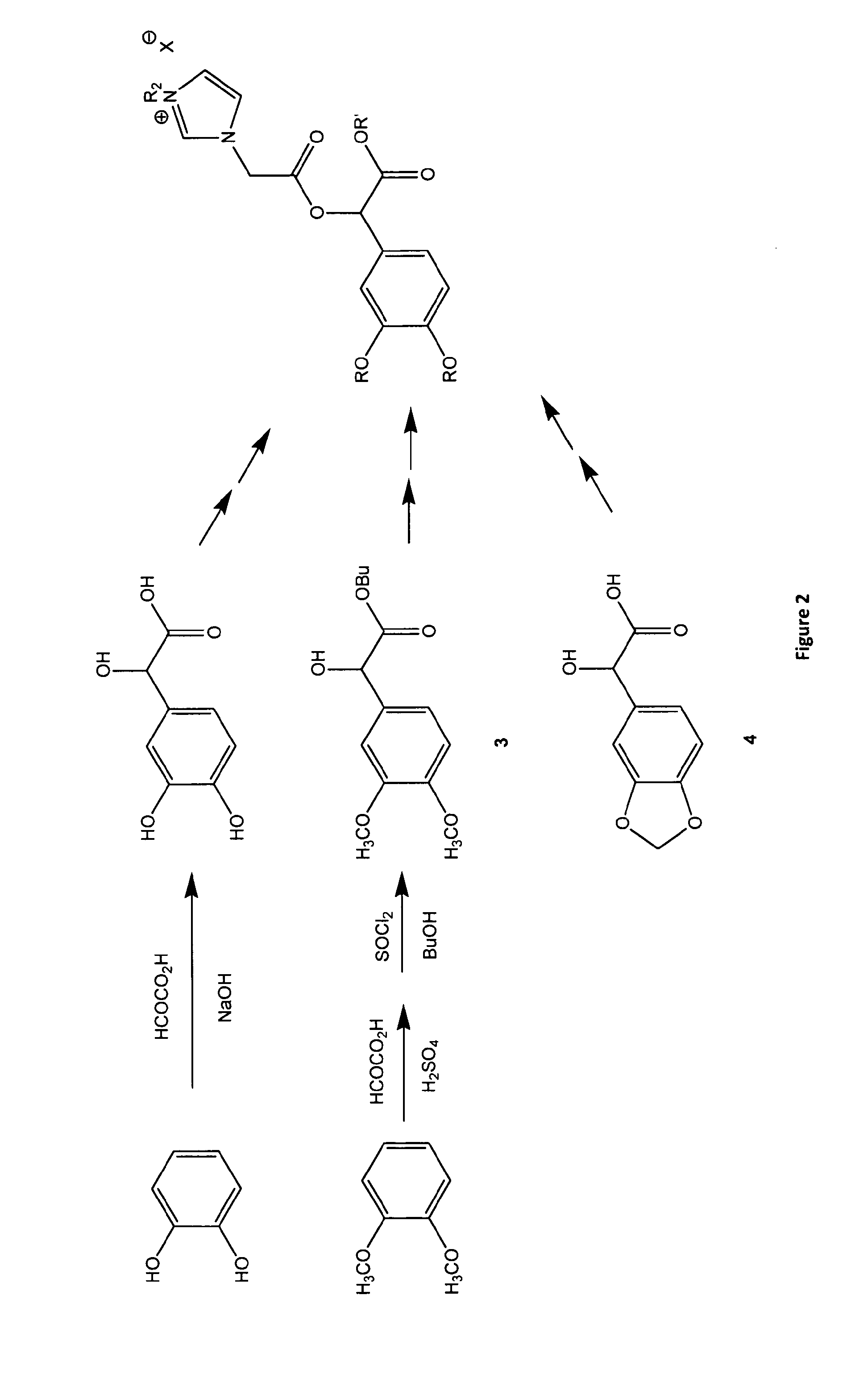
A chiral ionic compound comprising an alkyl substituted imidazolium or pyridinium cationic core having an alkyl ester side chain (-alkyl-C(O)O—) directly linked to the core and an associated counter anion, characterized in that the —O— atom of the ester side chain is linked to an alpha, a beta or a gamma hydroxycarboxylic acid functionality via the alpha, beta or gamma hydroxy of the acid functionality and the hydroxycarboxylic acid functionality has at least one asymmetric carbon, or characterized in that an —N═ atom of the alkyl substituted imidazolium or pyridinium cationic core is substituted with an alpha, a beta or a gamma hydroxy group of a alpha, a beta or a gamma hydroxycarboxylic acid functionality and the hydroxycarboxylic acid functionality has at least one asymmetric carbon. The chiral ionic liquids (CILs) may be used as novel solvents, in particular for organic synthesis. The CILs have the potential to induce asymmetry into substrates or catalysts in a variety of organic transformations. A number of the compounds have low antimicrobial and low antifungal toxicities and are also biodegradable CILs.
Owner:DUBLIN CITY UNIVERSITY
Process for producing optically active nitroalcohols
InactiveUS6977315B2Improve productivityOrganic compound preparationAsymmetric synthesesAlkanePtru catalyst
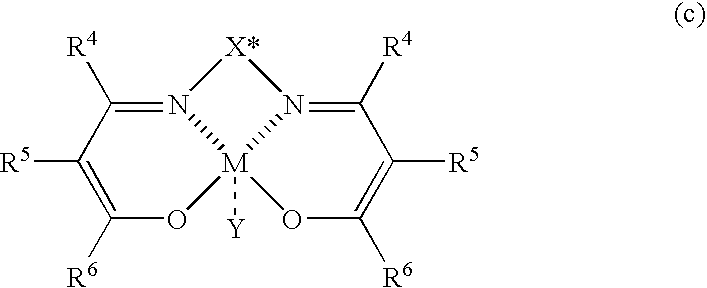
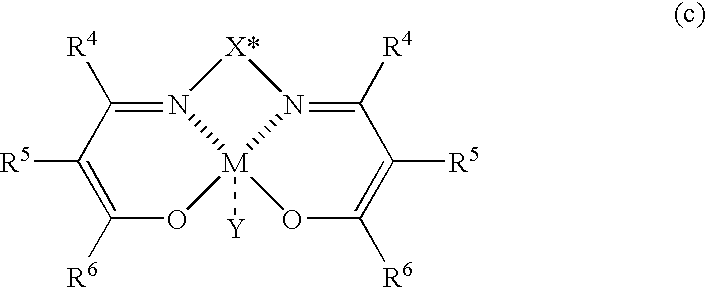
The present invention relates to a process for producing optically active β-nitroalcohols wherein nitroaldol reactions of aldehydes and nitroalkanes are carried out in the presence of a base and an optically active metal complex catalyst represented by the following formula (c): (where R4, R5, and R6 represent a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, an aryl group, an acyl group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, or an aryloxycarbonyl group, and R5 and R6 may be linked together to form a ring; X* represents a hydrocarbon group having an asymmetric carbon atom or axial asymmetry; M represents a cobalt ion or a chromium ion; and Y represents an anion capable of forming a salt when the valence of M is larger than that of a ligand).
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com