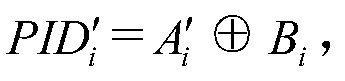A lightweight anonymous authentication and key agreement method in a multi-server environment
A multi-server, anonymous authentication technology, applied in the field of information security, which can solve the problems of account vulnerability to impersonation attacks, limited computing power, storage capacity and communication capacity, and single function.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
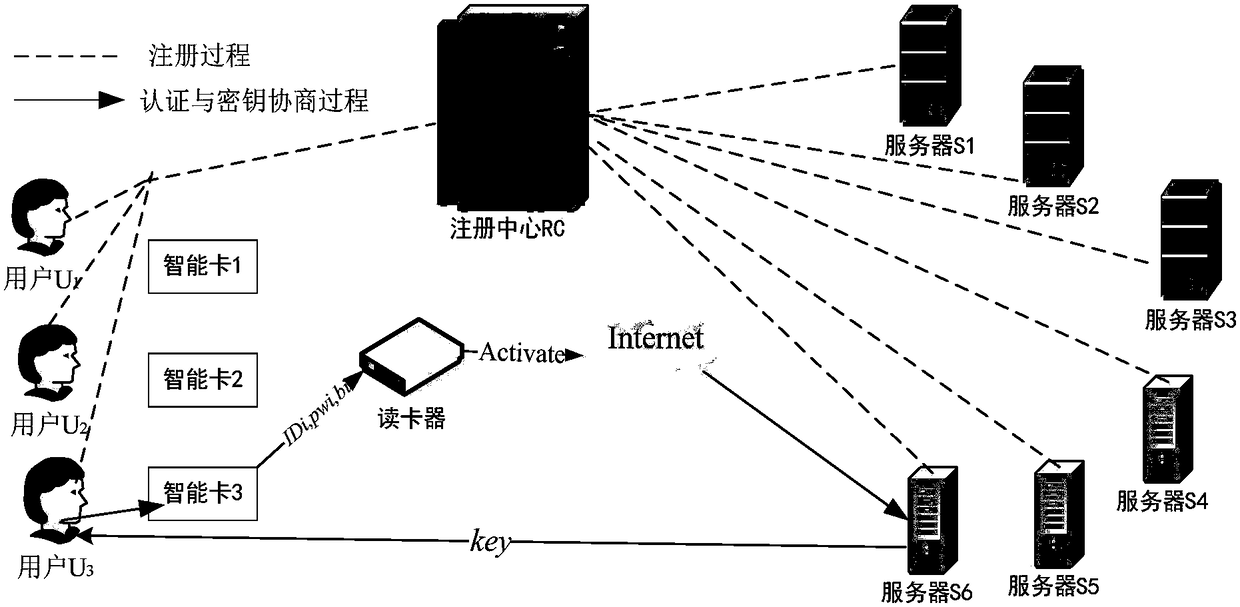
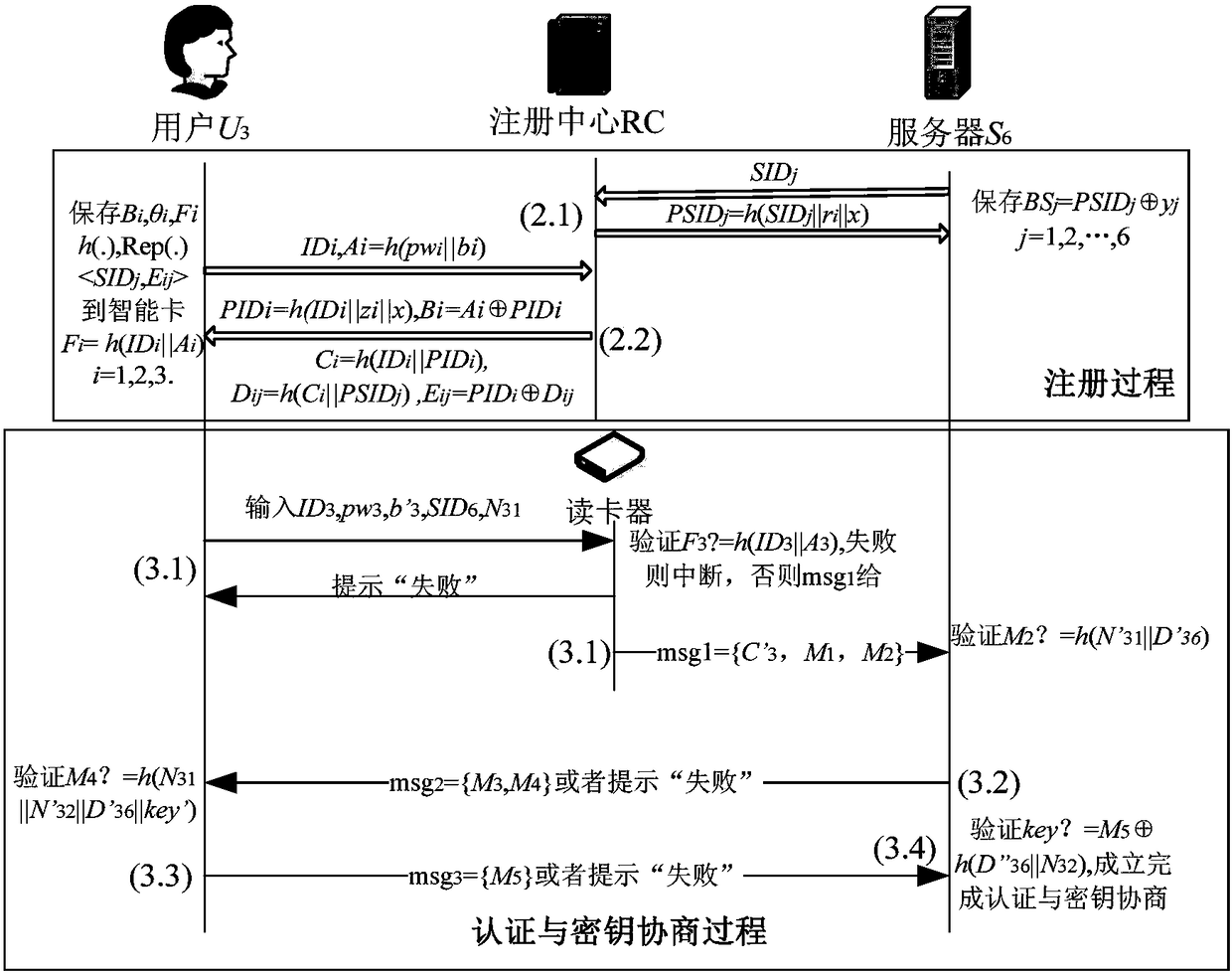
[0038] Now as user U 3 to server S 6 Take anonymous authentication and key agreement as an example, the specific method is as follows:
[0039] (1) System establishment and selection of system parameters
[0040] The registration center RC selects the SHA-2 algorithm and the fuzzy extractor according to the security requirements of the system, and makes the SHA-2 algorithm and the fuzzy extractor public, and then writes the SHA-2 algorithm and the Rep(.) algorithm of the fuzzy extractor into the user's smart card In SC, the smart card has certain storage capacity, computing power and the ability to connect to a remote server, such as OR1200, an open source 32-bit processor RISC.
[0041] (2) The server and the user are registered in the registration center RC
[0042] Assume that the server and the user register their real identities in the registration center and become legal members of the system. First, the registration center RC selects a key x with a binary length of l...
Embodiment 2
[0055] In this embodiment, after the server and the user are all registered in the registration center RC in step (2), because the fingerprint of user 3 is accidentally damaged, the password pw needs to be changed 3 and / or biometricsb 3 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0056] (a) password pw 3 and / or biometricsb 3 Buzz for
[0057] The specific method is: User U 3 Insert user smart card SC into card reader and enter ID 3 、pw 3 , b' 3 , the user smart card SC uses the Rep(.) algorithm of the fuzzy extractor to recover the user U 3 The biological key Rep(Δ 3,b' 3 ) = θ' 3 , and calculate A' 3 = h(pw 3 ||θ′ 3 ), verify F 3 =h(ID 3 ||A' 3 ) is established, if not established, the user smart card SC automatically interrupts the request; if established, the user is prompted to enter a new password and / or biometric information user U 3 Re-collect your own biological information and choose a new password to pass Calculate the user U 3 The new bio-key recalculation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com