A kind of Australian freshwater lobster hatching method in vitro
A freshwater lobster, in vitro technology, applied in the field of lobster farming, can solve the problems that fertilized eggs are difficult to develop larvae, it is difficult to ensure the supply of seedlings, and the number of eggs is small, so as to prevent infection of bacteria such as saprolegnia, increase the output of larvae, The effect of increased shrimp production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
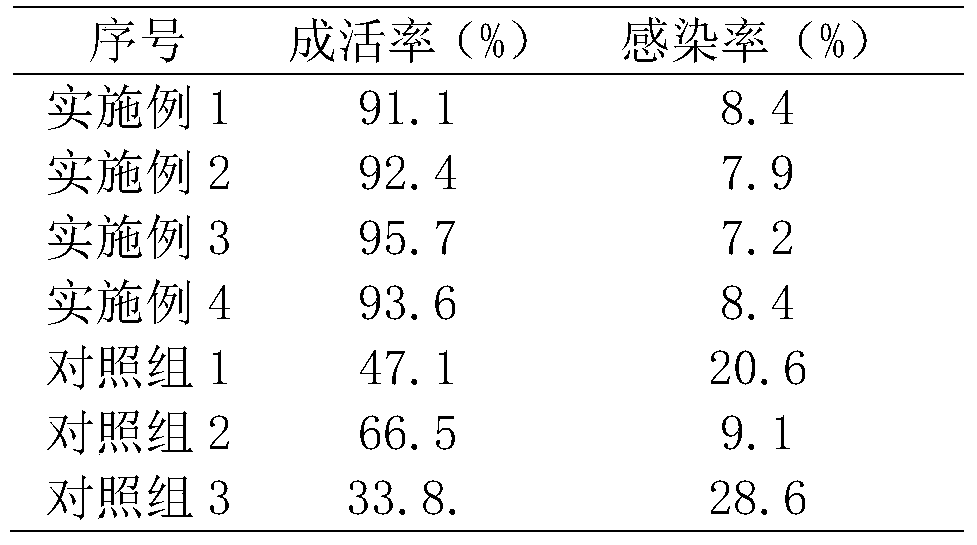
Embodiment 1
[0022] A method for hatching Australian freshwater lobsters in vitro, comprising the following steps:
[0023] (1) After the female shrimp is fertilized, determine the developmental degree of the fertilized eggs according to the living conditions of the female shrimp, catch the female shrimp and place them on the production bed respectively, adjust the temperature of the water body to 29°C, and increase the temperature by 0.4°C every day to 34°C ℃ is the spawning time; collect the fertilized eggs laid by the female shrimp, soak them in salt water with a mass fraction of 2% for 3 minutes for cleaning, and then put them into the in vitro hatching tray for in vitro incubation after cleaning;
[0024] (2) Put the cleaned fertilized eggs into the in vitro hatching tray for in vitro incubation until the larvae are released; the in vitro hatching tray is equipped with a pre-filter bucket, an ozone sterilizer, a heating tube and an aerator that match the water body The pre-filter barr...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A method for hatching Australian freshwater lobsters in vitro, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) After the female shrimp is fertilized, determine the development degree of the fertilized eggs according to the living conditions of the female shrimp. When the female shrimp is in labor, the female shrimp is caught and placed on the production bed respectively, and the temperature of the water body is adjusted to 30 ° C. ℃ is the spawning time; collect the fertilized eggs laid by the female shrimp but not fertilized and the fertilized eggs left by the dead female shrimp during the fertilization process, wash them with 4% salt water for 6 minutes, and wash them Put it into an in vitro incubation tray for in vitro incubation;
[0028] (2) The in vitro hatching tray is equipped with a pre-filter barrel, an ozone sterilizer, a heat pipe and an aerator that match the water body; the pre-filter barrel can filter and disinfect the water in the in-vitro hatching tray to ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A method for hatching Australian freshwater lobsters in vitro, comprising the following steps:
[0031] (1) After the female shrimp is fertilized, determine the development degree of the fertilized eggs according to the living conditions of the female shrimp. When the female shrimp is in labor, the female shrimp is caught and placed on the production bed, and the temperature of the water body is adjusted to 28°C. ℃ is the spawning time; collect the fertilized eggs left by the dead female shrimp during the ovipositing process, soak them in 3% salt water for 5 minutes for cleaning, and put them into the in vitro incubation tray for in vitro incubation after cleaning;
[0032] (2) The in vitro hatching tray is equipped with a pre-filter barrel, an ozone sterilizer, a heat pipe and an aerator that match the water body; the pre-filter barrel can filter and disinfect the water in the in-vitro hatching tray to maintain in-vitro hatching The water quality in the tray is stable,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com