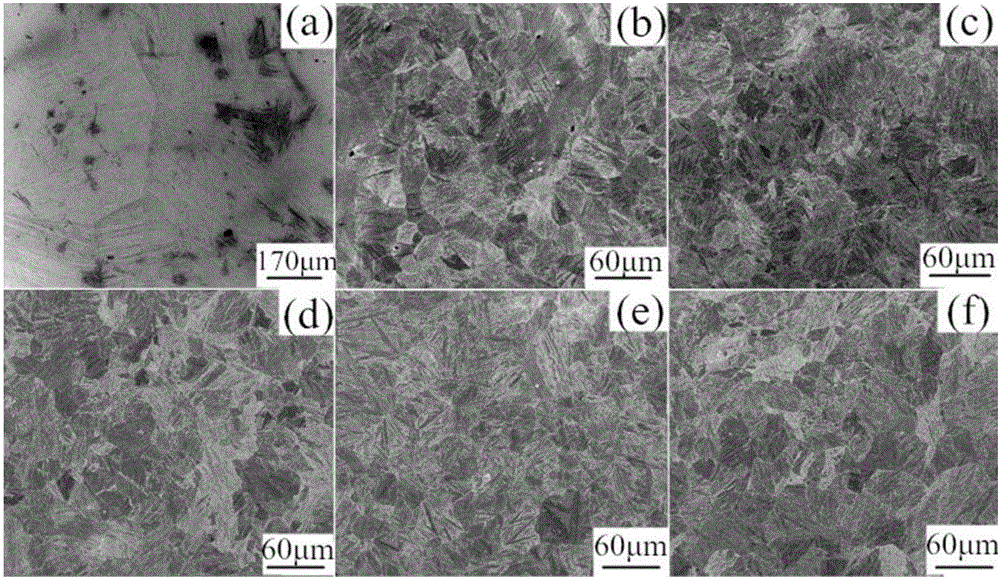
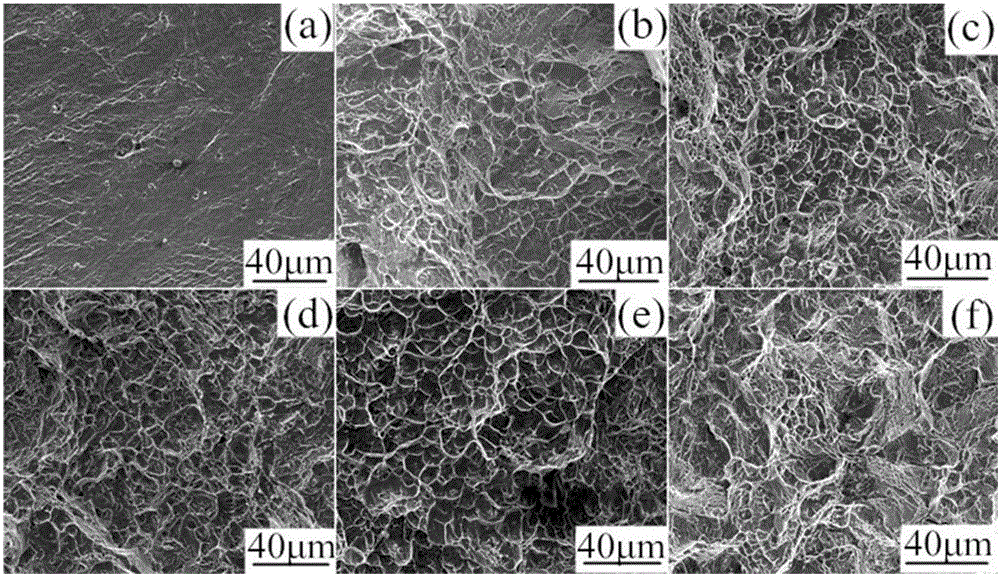
A refinement method of cualmn shape memory alloy grains
A technology of memory alloy and grain, which is applied in the field of changing the physical structure of copper-based alloys, can solve the problems of limited refinement effect, and achieve the effects of low cost, obvious grain refinement effect, and easy large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The first step is to prepare the inoculant Cu 51 Zr 14 :
[0039] Press Cu 51 Zr 14 The atomic ratio of the components shown is Cu:Zr=51:14, respectively weigh the raw material pure Cu and pure Zr of the required quality for batching, and then put it into a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace, and evacuate to 5 × 10 -3 After Pa, power on and arc smelting, and pouring after all the ingredients are melted. In order to ensure the uniformity of the alloy composition, the alloy obtained by pouring is turned upside down and re-melted under the same conditions as above. Repeat this for 3 times to obtain Cu 51 Zr 14 inoculant, and then to the prepared inoculant Cu 51 Zr 14 Pulverized, ready to use;
[0040] The second step is the refinement of CuAlMn shape memory alloy grains:
[0041] Take the copper-based shape memory alloy with the composition ratio of Cu-11.9%Al-2.5%Mn of the required mass and melt it in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, then move it to a p...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The first step is to prepare the inoculant Cu 51 Zr 14 :
[0046] Press Cu 51 Zr 14 The atomic ratio of the components shown is Cu:Zr=51:14, respectively weigh the raw material pure Cu and pure Zr of the required quality for batching, and then put it into a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace, and evacuate to 5 × 10 -3 After Pa, start energization and start arc melting. After all the ingredients are melted, pour it. In order to ensure the uniformity of the alloy composition, the alloy obtained by pouring is turned upside down and re-melted under the same conditions as above. Repeat this for 4 times to obtain Cu 51 Zr 14 inoculant, and then to the prepared inoculant Cu 51 Zr 14 Pulverized, ready to use;
[0047] The second step is the refinement of CuAlMn shape memory alloy grains:
[0048] Take the copper-based shape memory alloy with the composition ratio of Cu-11.9%Al-2.5%Mn of the required mass and melt it in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, then mo...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The first step is to prepare the inoculant Cu 51 Zr 14 :
[0053] Press Cu 51 Zr 14 The atomic ratio of the components shown is Cu:Zr=51:14, respectively weigh the raw material pure Cu and pure Zr of the required quality for batching, and then put it into a non-consumable vacuum arc furnace, and evacuate to 5 × 10 -3 After Pa, power on and arc smelting, and pouring after all ingredients are melted. In order to ensure the uniformity of alloy composition, the alloy obtained by pouring is turned upside down and re-melted under the same conditions as above. Repeat this for 5 times to obtain Cu 51 Zr 14 inoculant, and then to the prepared inoculant Cu 51 Zr 14 Pulverized, ready to use;
[0054] The second step is the refinement of CuAlMn shape memory alloy grains:
[0055] Take the copper-based shape memory alloy with the composition ratio of Cu-11.9%Al-2.5%Mn of the required mass and melt it in an intermediate frequency induction furnace, then move it to a pit cruci...
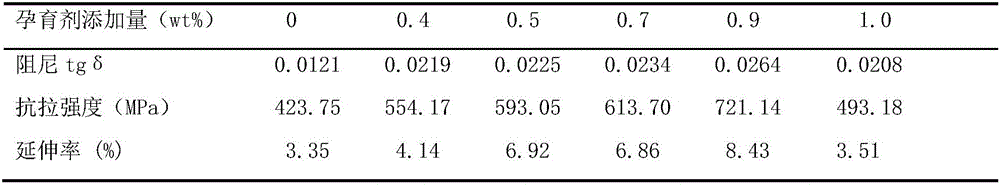
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com