Device for generating hydrogen-rich water through electrolysis
A generation device and technology of hydrogen-rich water, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of unsuitability for direct drinking, low chlorine evolution overpotential, high oxygen evolution overpotential, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of being oxidized and increasing the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
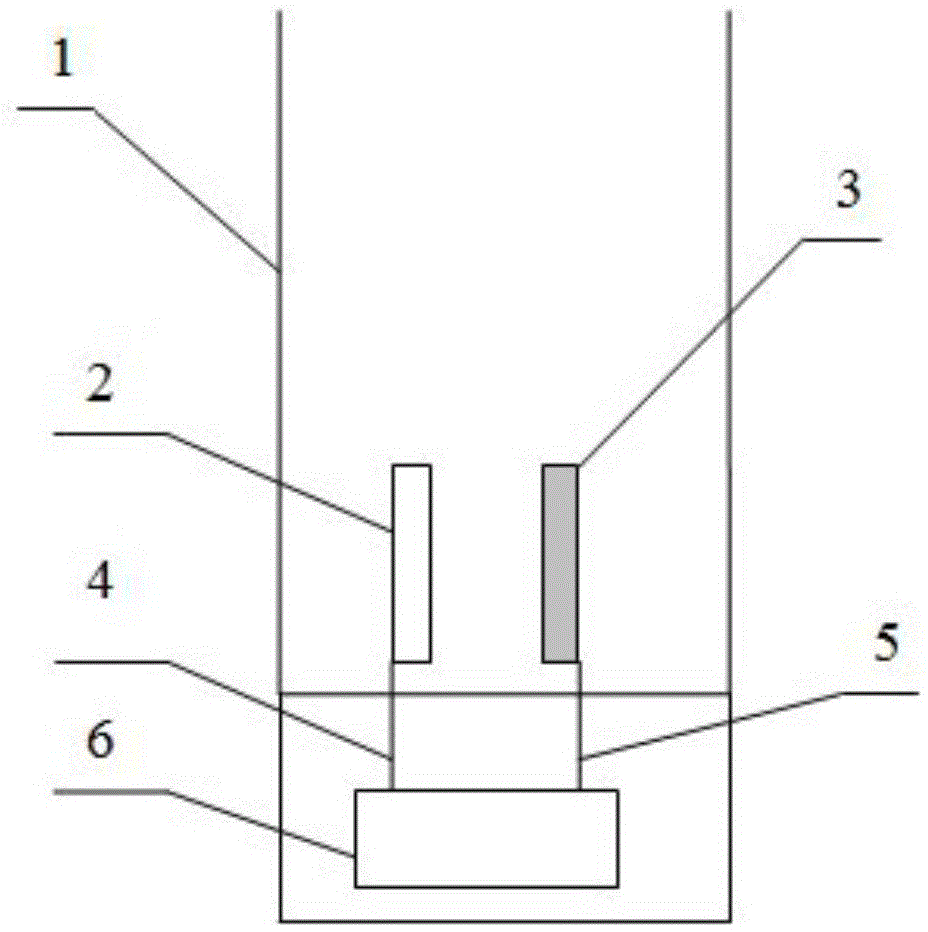
[0018] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment comprises an electrolytic cell 1, a negative electrode 2 and a positive electrode 3 placed in the electrolytic cell 1, the negative electrode is a stainless steel flat plate electrode, and the positive electrode is a titanium-based gold-plated flat plate electrode; the negative electrode 2 and the positive electrode 3 are passed through respectively The first wire 4 and the second wire 5 are connected to the negative pole and the positive pole of the controllable electrolysis power supply 6, add 200ml of Nanjing local tap water containing chloride ions in the electrolytic cell 1, the electrolysis current is 100mA, the distance between the pole plates d=1mm, the negative electrode 2 and the positive electrode 3 have a reaction area ratio of 1:1; let the electrolysis device start to work, and record relevant data in Table 1.
[0019] The PH and residual chlorine test instruments used in this embodiment are respectively: th...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment comprises an electrolytic cell 1, a negative electrode 2 and a positive electrode 3 placed in the electrolytic cell 1, the negative electrode is a stainless steel flat plate electrode, and the positive electrode is a titanium-based gold-plated flat plate electrode; the negative electrode 2 and the positive electrode 3 are passed through respectively The first wire 4 and the second wire 5 are connected to the negative pole and the positive pole of the controllable electrolysis power supply 6, add 200ml of Nanjing local tap water containing chloride ions in the electrolytic cell 1, the electrolysis current is 100mA, the distance between the plates d=10mm, the negative electrode The reaction area ratio between 2 and the positive electrode 3 is 1:1; let the electrolysis device start to work, and record relevant data in Table 3.
[0028] The PH and residual chlorine test instruments used in this embodiment are respectively: t...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment comprises an electrolytic cell 1, a negative electrode 2 and a positive electrode 3 placed in the electrolytic cell 1, the negative electrode is a stainless steel flat plate electrode, and the positive electrode is a titanium-based gold-plated flat plate electrode; the negative electrode 2 and the positive electrode 3 are passed through respectively The first wire 4 and the second wire 5 are connected to the negative pole and the positive pole of the controllable electrolysis power supply 6, add 200ml of Master Kong mineral water in the electrolytic tank 1, the electrolysis current is 100mA, the distance between the plates is d=1mm, the negative electrode 2 and the positive electrode The reaction area ratio of electrode 3 is 1:1; let the electrolysis device start to work, and record relevant data in Table 5.
[0037] The PH and residual chlorine test instruments used in this embodiment are respectively: the PHB-3PH teste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com