A method for characterizing the drying end point of far-infrared dried Agaricus bisporus based on moisture distribution
A technology of far-infrared drying and Agaricus bisporus, which is used in the analysis of materials, water resources assessment, and analysis by nuclear magnetic resonance, etc., can solve problems such as derivation of tedious steps and correction of working functions, and achieves saving raw materials, high accuracy, and penetrating ability. strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
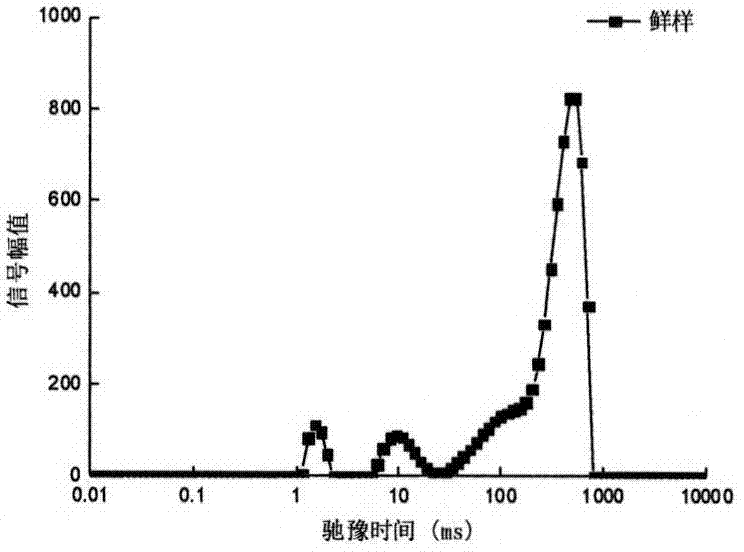
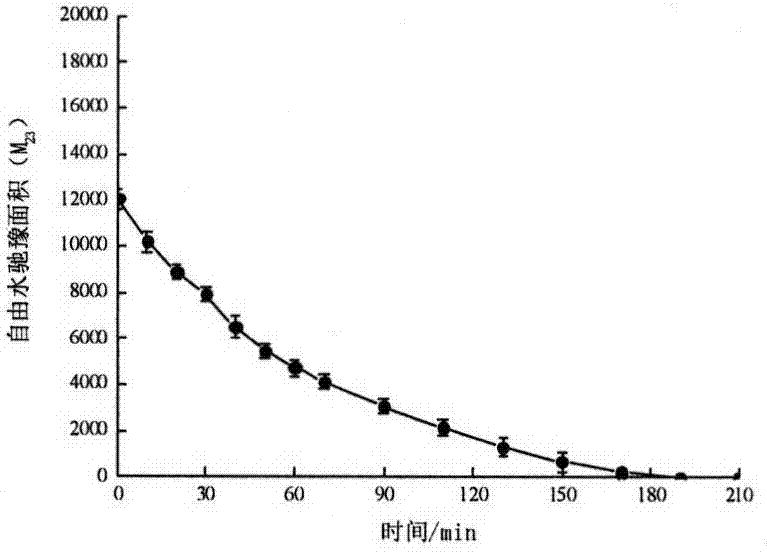
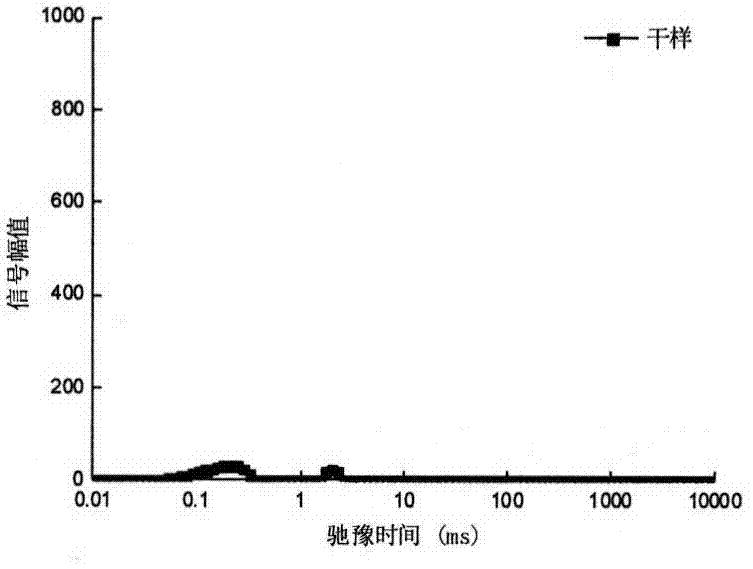
[0025] After cleaning and removing the stalk of Agaricus bisporus, cut it into thin slices of about 5mm along the growth direction, place it in the center of the radio frequency coil of the permanent magnetic field, and measure the transverse relaxation time T in the sample by using the CPMG pulse sequence 2 . The equipment parameters are set as follows: main frequency SF=23 (MHz), offset frequency Ol=425557.6Hz, hard pulse 90 degree pulse width P90=14(us), hard pulse 180 degree pulse width P180=30(us), spectrum width SW=200KHz, sampling points TD=828016, repeated scanning times NS=8, repeated sampling time TW=5000ms, echo number NECH=18000. Transverse relaxation time T using inversion software 2 value, such as figure 1 Shown, the transverse relaxation time of free water is 25 ~ 850ms. Then put the Agaricus bisporus slices into the far-infrared drying box for drying, the radiation distance is 150mm, and the radiation intensity is 2.1KW / m 2 . Scan the sample during the dry...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com