High-efficiency knockout method for XBP1 gene in DC cell
A gene knockout, cell technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem of reduced anti-tumor immune activity of DC cells, and achieve the effect of exerting anti-tumor immunity and ensuring immune stimulation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a DC cell XBP1 gene knockout method, comprising the following steps:
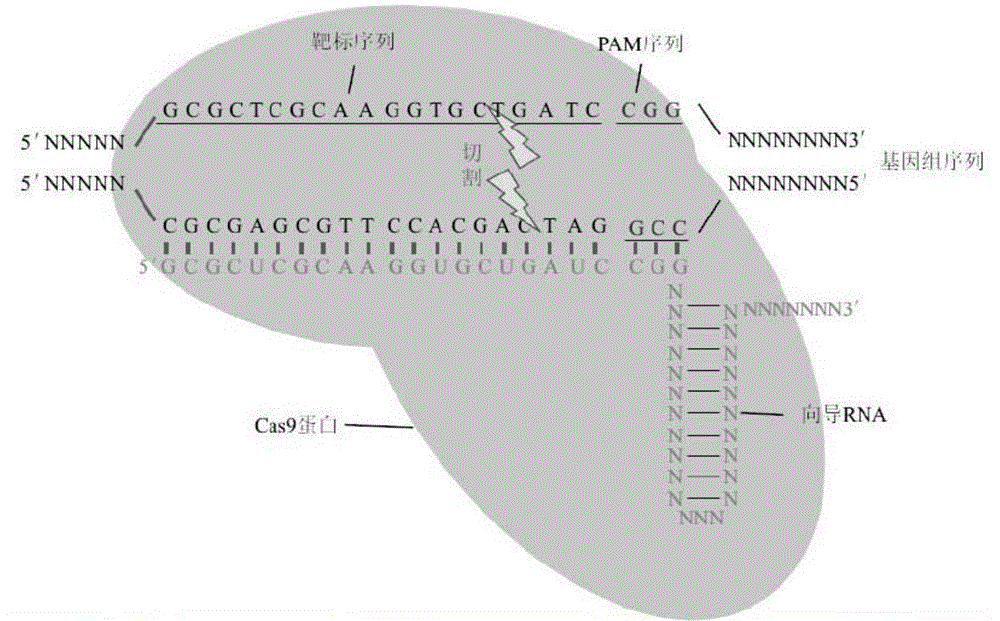
[0053] S11. Gene knockout target and oligonucleotide design
[0054] Taking the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing factor XBP1 as the target gene, the CRISPR target sequence design and off-target site prediction were carried out for the XBP1 gene through online software (http: / / crispr.mit.edu). The target sequence finally selected after comprehensive analysis is underlined.
[0055] "...CGGTGCGCGGTGCGTAGTCTGGAGCTATGGTGGTGGTGGCAG CCGCGCCGAACCCGGCCGA CGGGACCCCTAAAGTTCTGCTTCTGTCGGGGCAGCCCGCCTCCGCCGCCGGAGCCCCGGCCGGCCAGGCCCTGCCGCTCATGGTGCCAGCCCAGAGAGGGGC..." (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0056] The designed insert oligonucleotide sequence is as follows:
[0057] The forward oligonucleotide sequence is:
[0058] 5'GAAACACCG CCGCGCCGAACCCGGCCGA GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAGGCTAGTCCGTT3’
[0059] The reverse oligonucleotide sequence is:
[0060] 5'AACGGACTAGCC...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a method for knocking out XBP1 gene in DC cells. The method comprises the steps of:
[0105] S21. Gene knockout target and oligonucleotide design
[0106] Directly follow S11 in Example 1 for processing.
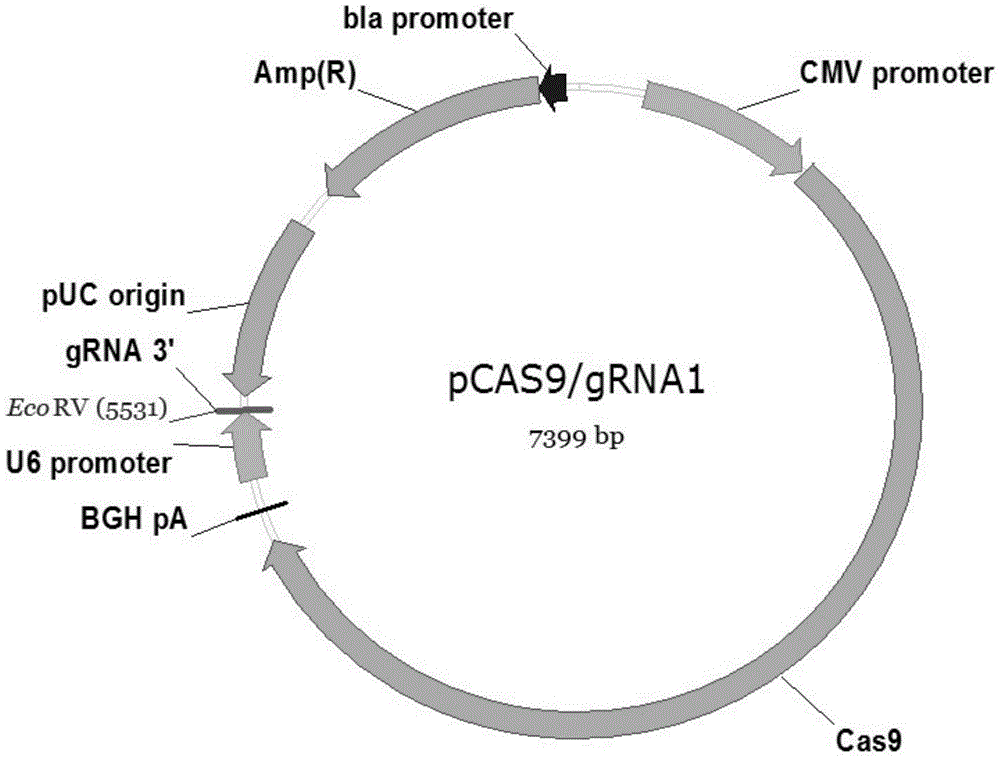
[0107] S22. Ligation and identification of pCas9 / gRNA1 gene knockout vector
[0108] Directly follow step S12 in Embodiment 1 for processing.
[0109] S23. DC cell culture
[0110] Process directly according to step S13 in Embodiment 1.
[0111] Knockout of XBP1 gene in S24.DC cells
[0112] The grouping of S241DC is as follows:
[0113] (1) negative control group; (NC-DC)
[0114] (3) pCas9 / gRNA1-XBP1+L189 group. (XBP1 / L189-DC)
[0115] S242XBP1 gene knockout
[0116] (1) On the sixth day of DC culture, plasmid dilutions were prepared according to the system in Table 4 below. Wherein, the pCas9 / gRNA1-XBP1 shown in Group 3 in Table 4 is the pCas9 / gRNA1-XBP1 plasmid prepared in Step S22 of Example 2.
[0117] T...
Embodiment 3
[0138] DC stimulated T cell anti-tumor experiment
[0139] S31DC-T cell culture
[0140] (1) Use the Alys-505 culture solution containing 0.5% autologous plasma to adjust the cell density to 1×106 / ml for the non-adherent cells before culturing DC cells in step S13 in Example 1, and transfer them to a six-well plate, 2ml / well, while adding 1000U / ml of IFN-γ to each well, placed in saturated humidity, 37°C, 5.0% CO 2 cultured in an incubator.
[0141] (2) After 24 hours, add 50ng / ml CD3 monoclonal antibody, 1000U / ml IL-2, 1000U / ml IL-1α to each well, and place in saturated humidity, 37°C, 5.0% CO 2 Continue to grow in the incubator.
[0142] (3) Adjust the cell density to 1×106 / ml every 3 days, and add Alys-505 culture solution containing 1000U / ml IL-2 and 0.5% autologous plasma.
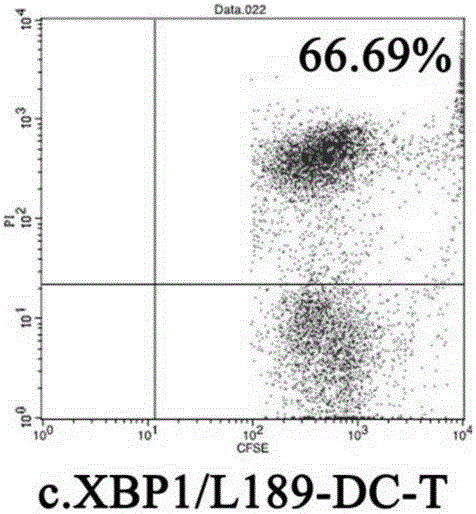
[0143] (4) On the 9th day, three kinds of DC cells (NC-DC, XBP1-DC (transfected DC in Example 2), XBP1 / L189-DC (transfected DC in Example 3)) were mixed with T cells at 1 :10, and continued to c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com