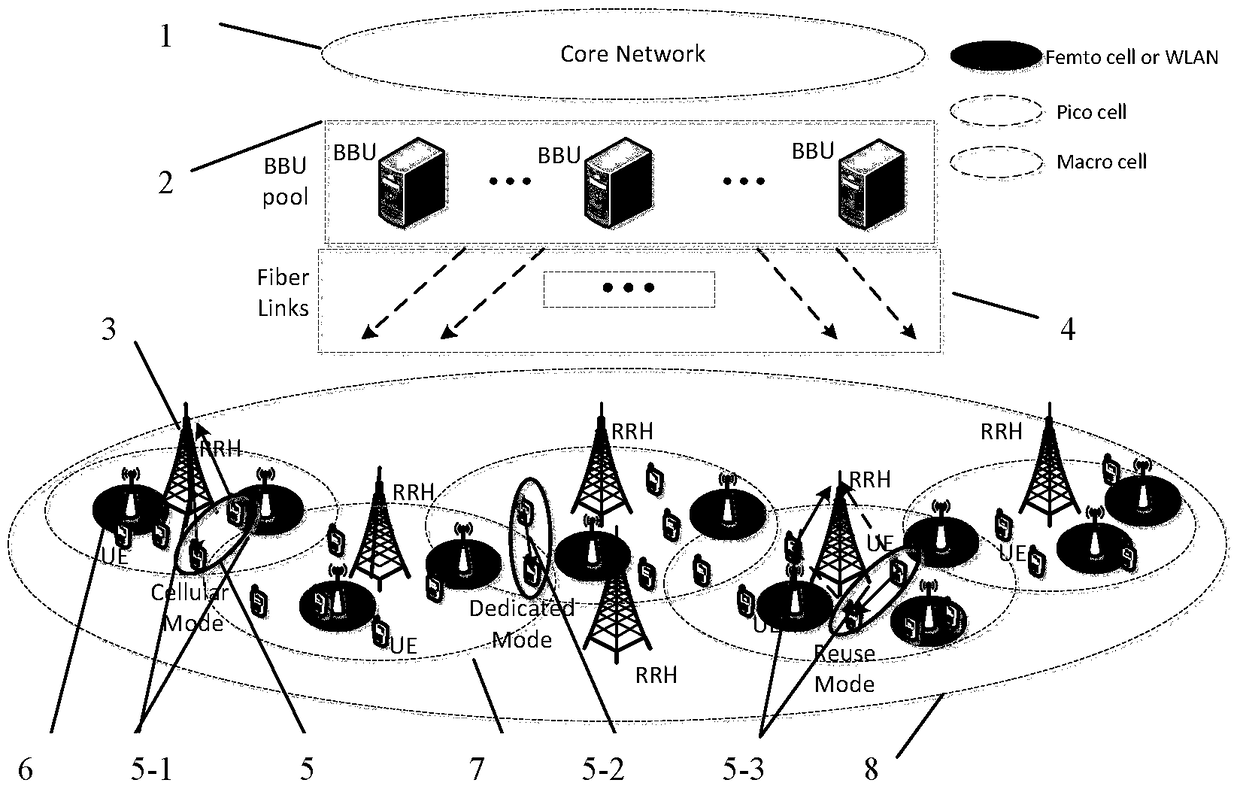
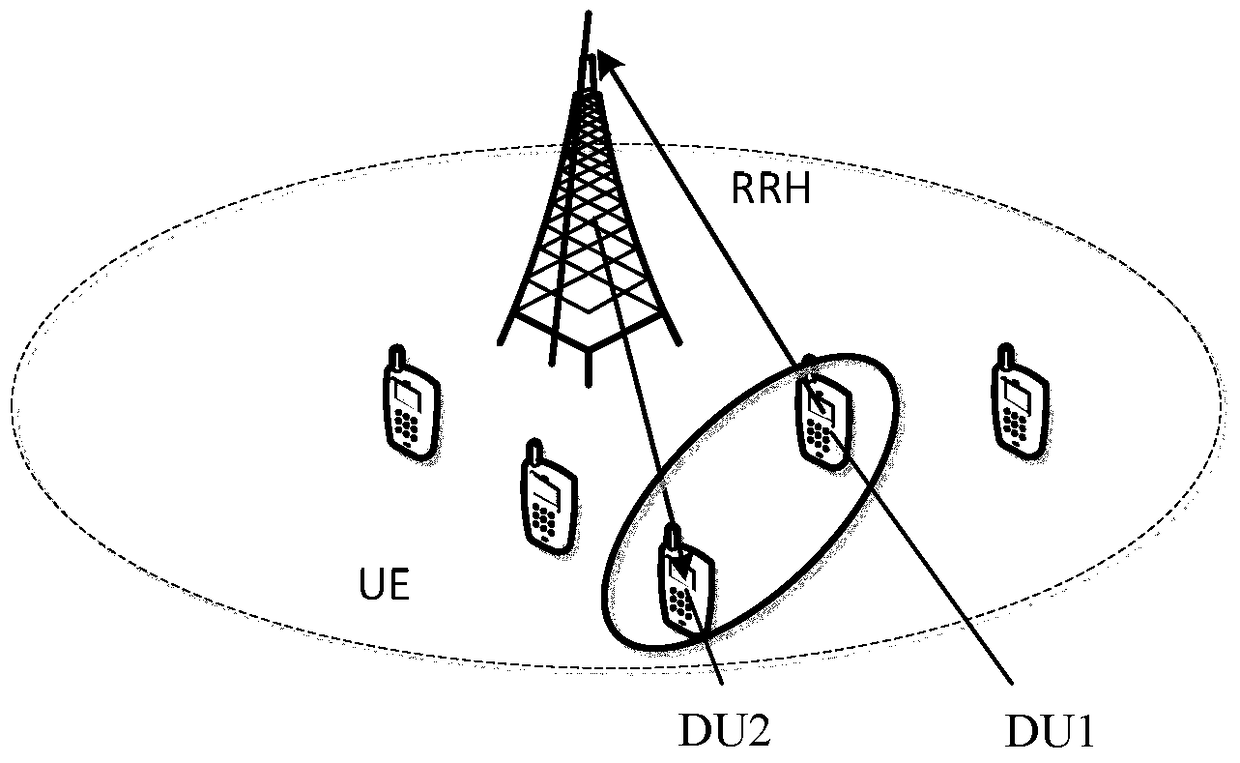
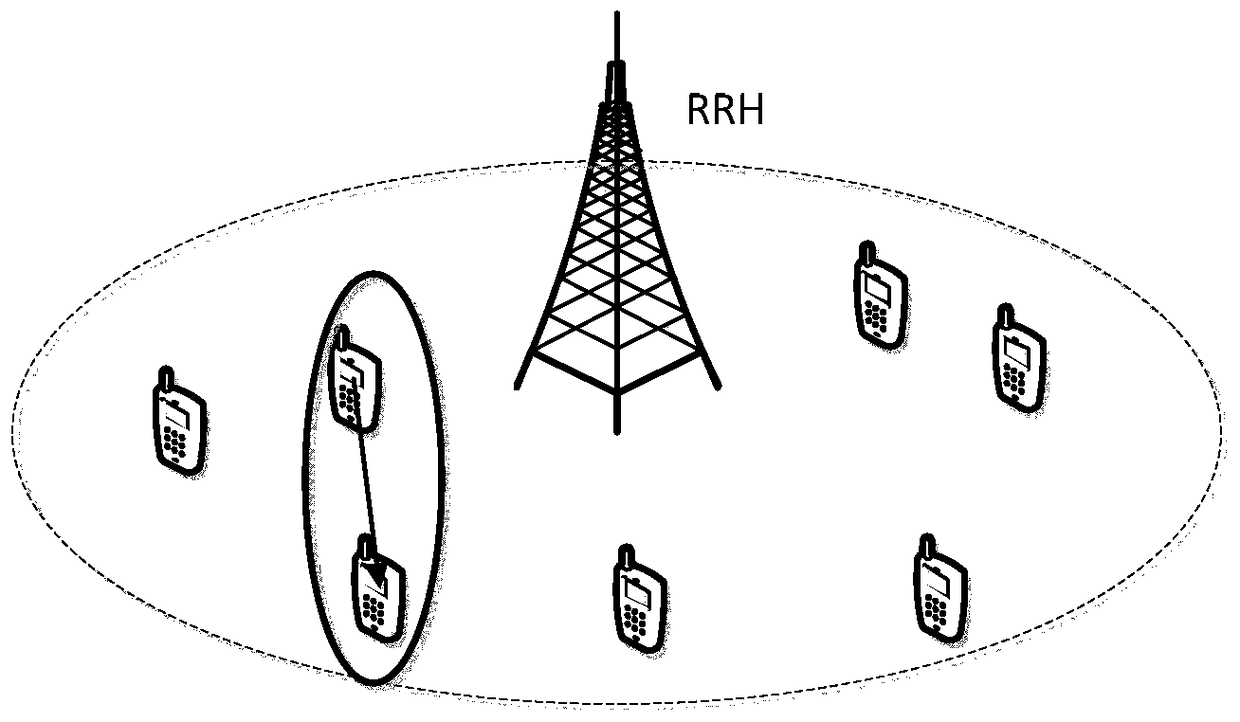
Heterogeneous c-ran network and joint optimization method of d2d communication mode selection and resource scheduling under the network
A communication mode and joint optimization technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low signal-to-noise ratio, ignoring user fairness, and unsatisfied user data traffic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0077] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 6 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment describes that when the network is in a lightly loaded state, there are sufficient idle uplinks and downlinks to choose from. Therefore, only the cellular mode and the dedicated mode are considered, and because the same The average transmission rate of DUs in the two modes for the previous time slot is the same, so it is only necessary to compare the instantaneous rate of DUs in the two modes. When calculating the maximum instantaneous rate in cellular mode and dedicated mode, there is no inter-channel interference problem, so when the user uses the maximum transmit power, the obtained instantaneous rate can be maximized. The specific algorithm can be realized through the following steps:
[0078] Step A1: Determine whether the D2D user logarithm k is less than the total logarithm K, if less, go to step A2, otherwise the algorithm ends;
[0079] Step A2: Maximum Rate in Cellu...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0093] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 7 Describe this implementation mode. This implementation mode describes that in the state of heavy network load, there is no idle spectrum to use, and D2D users can only choose the multiplexing mode, which is realized by the following steps:
[0094] Step B1: Arrange the D2D users in descending order according to the value of the proportional fairness function. The larger the proportional fairness function, the higher the priority;
[0095]Step B2: Since the average transmission rate of D2D users is known, the maximum value of the proportional fairness function can be selected through the maximum instantaneous rate; in the case of ensuring a certain SINR of D2D users and cellular users, the D2D user with the highest priority can start from Select the resources of the instantaneous rate from all the reusable spectrum for multiplexing, the maximum instantaneous rate It can be calculated by the following formula:
[...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0106] Specific implementation mode three: combination Figure 8 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment describes that when the network is in a moderately loaded state, D2D users need to choose a mode among the three modes of cellular mode, dedicated mode and multiplexing mode with the size of the proportional fairness function as the criterion . In this network state, since the number of D2D logarithms is greater than the number of available idle spectrums, D2D users need to choose from three modes. Since D2D working in multiplexing mode will cause interference to cellular users, D2D users will preferentially choose cellular mode or dedicated mode for communication when there is idle spectrum. The D2D joint mode selection and resource scheduling algorithm under moderate network load can be realized through the following steps:
[0107] Step C1: Arrange the D2D users in descending order according to the value of the proportional fairness function. The larger the proportio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com