A recycling process of electroplating wastewater
A technology for electroplating wastewater and wastewater, which is applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient emission reduction, reverse osmosis membrane erosion, high reuse cost, etc., and achieve easy automatic operation, The effect of stable reuse system and low reuse cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
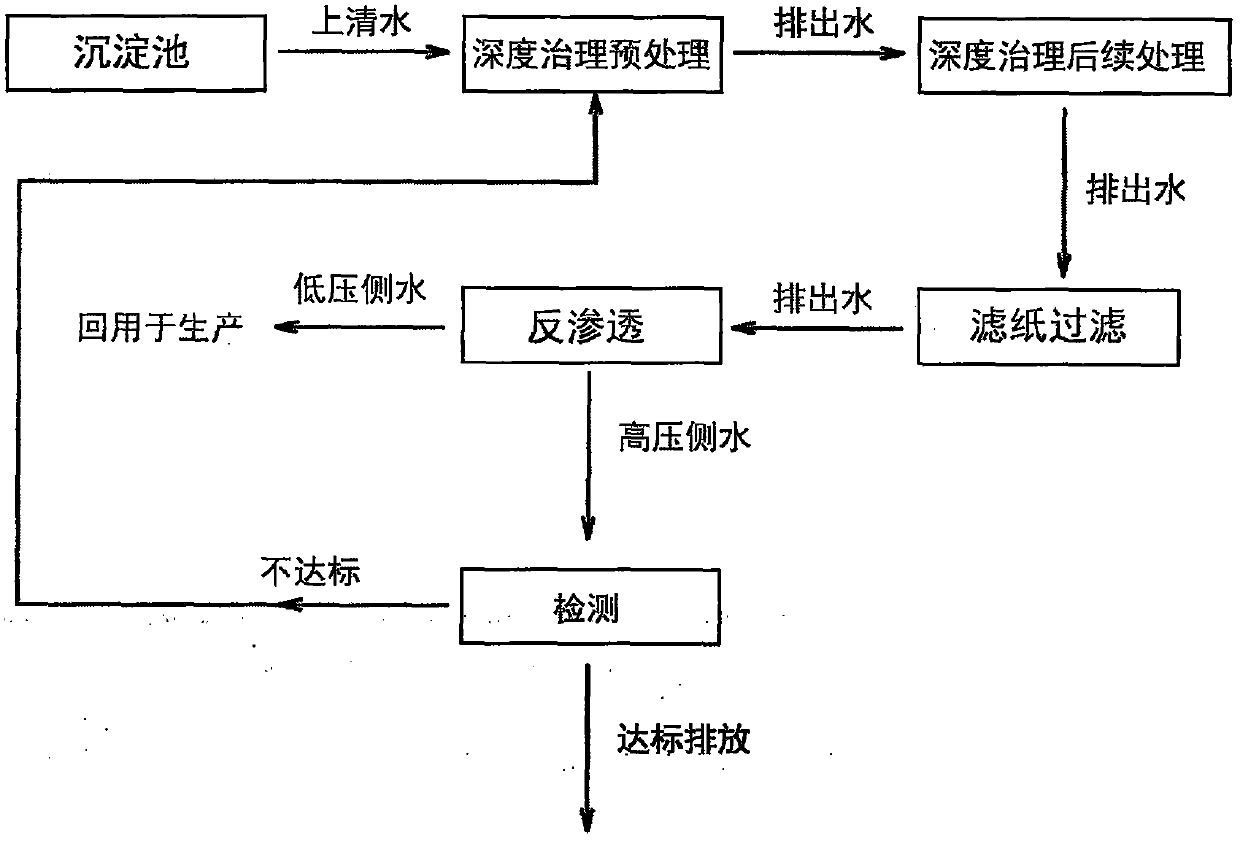
[0025] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of recycling process of electroplating waste water, comprises the following steps:
[0026] (1) Pretreatment of advanced treatment of electroplating wastewater:
[0027] The supernatant wastewater discharged from the sedimentation tank uses an air flotation machine to remove a small amount of heavy metals and COD remaining in the wastewater. The heavy metal trapping agent is preferably sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (DDTC); its dosage is generally 5mg / L wastewater The specific dosage is based on the appropriate increase or decrease in the amount of heavy metals contained in the wastewater discharged from the sedimentation tank during the production process, so that the wastewater still contains a small amount (below 1 mg / L) of DDTC after the heavy metals contained in the wastewater are completely removed.
[0028] Specif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com