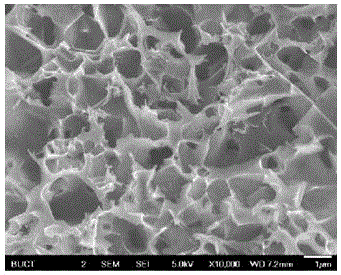
Method for preparing porous carbon by utilizing rose stems
A porous carbon and rose technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problem that rose stems are not developed and utilized
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) After cutting the rose stems into 12cm-15cm lengths, wash the rose stems and dry them in an oven at 110°C for 5 hours, then raise the temperature to 360°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a tube furnace under nitrogen protection, and Keep it for 2 hours for pre-carbonization;
[0031] (2) Mix the pre-carbonized rose stem and potassium hydroxide evenly in a mass ratio of 1:1, and heat up to 600°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a tube furnace under nitrogen protection, and keep it for 2h , for carbonization activation;
[0032] (3) The carbonized and activated product was naturally cooled to room temperature under the protection of nitrogen, washed with 1mol / L hydrochloric acid to remove the inorganic components in the product, then washed with deionized water at 100°C until neutral, and dried at 120°C for 12h to obtain a porous carbon materials;
[0033] (4) The porous carbon material is measured by the BET specific surface area test method, and its BET specific surface area reach...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) After cutting the rose stems into 12cm-15cm lengths, wash the rose stems and dry them in an oven at 110°C for 5 hours, then raise the temperature to 360°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a tube furnace under nitrogen protection, and Keep it for 2 hours for pre-carbonization;
[0036] (2) Mix the pre-carbonized rose stem and potassium hydroxide evenly in a mass ratio of 1:1, and heat up to 750°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a tube furnace under nitrogen protection, and keep it for 2h , for carbonization activation.
[0037] (3) The carbonized and activated product was naturally cooled to room temperature under the protection of nitrogen, washed with 1mol / L hydrochloric acid to remove the inorganic components in the product, then washed with deionized water at 100°C until neutral, and dried at 120°C for 12h to obtain a porous carbon materials;
[0038] (4) The porous carbon material is measured by the BET specific surface area test method, and its BET specific surface area is 22...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) After cutting the rose stems into lengths of 12cm-15cm, wash the rose stems and dry them in an oven at 110°C for 5 hours, then raise the temperature to 360°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a tube furnace under nitrogen protection, and Keep it for 2 hours for pre-carbonization;
[0041] (2) Mix the pre-carbonized rose stem and potassium hydroxide evenly in a mass ratio of 1:2, and heat up to 650°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a tube furnace under nitrogen protection, and keep it for 2h , for carbonization activation;
[0042] (3) The carbonized and activated product was naturally cooled to room temperature under the protection of nitrogen, washed with 1mol / L hydrochloric acid to remove the inorganic components in the product, then washed with deionized water at 100°C until neutral, and dried at 120°C for 12h to obtain a porous carbon materials;
[0043] (4) The porous carbon material is measured by the BET specific surface area test method, and its BET specific surface area re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com