Establishment and application of porcine respiratory tract epilhelium in-vitro 3D model
A technology of epithelial cells and porcine respiratory tract, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of no virus amplification, identification, pathogenic mechanism, and restriction research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
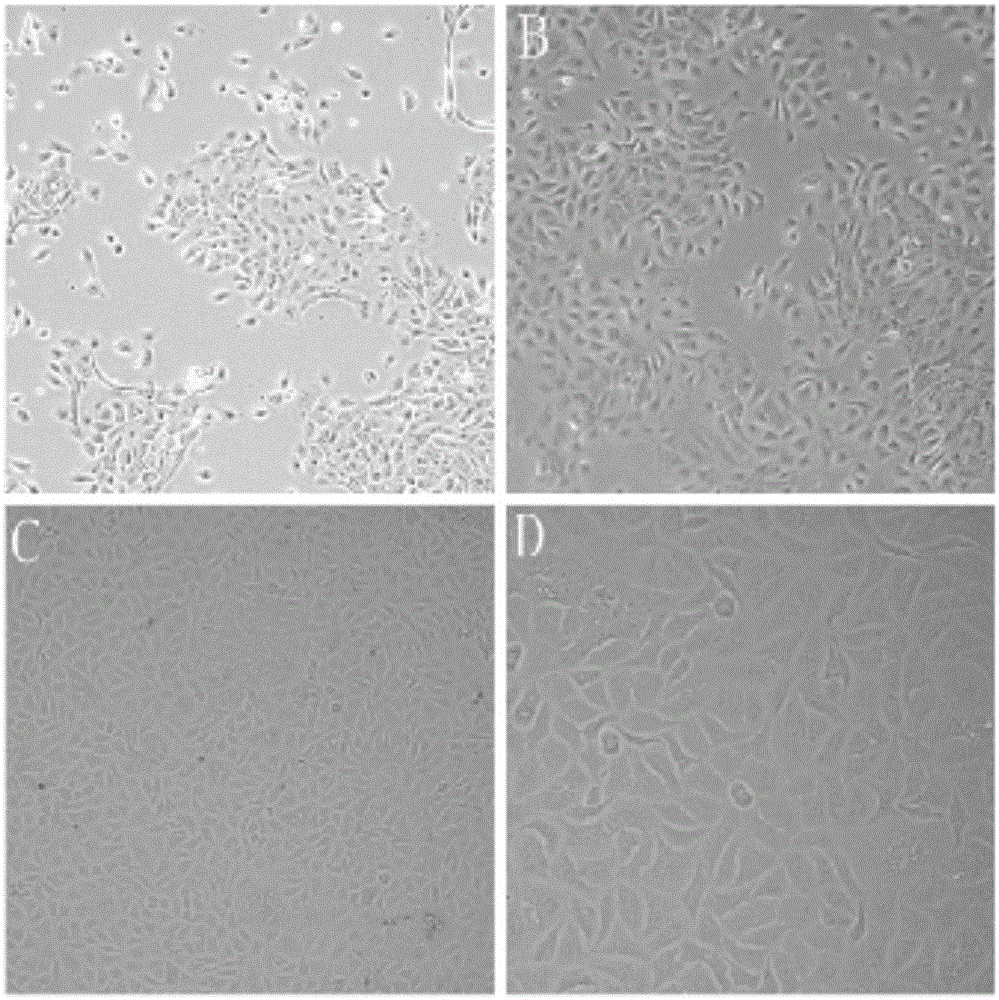
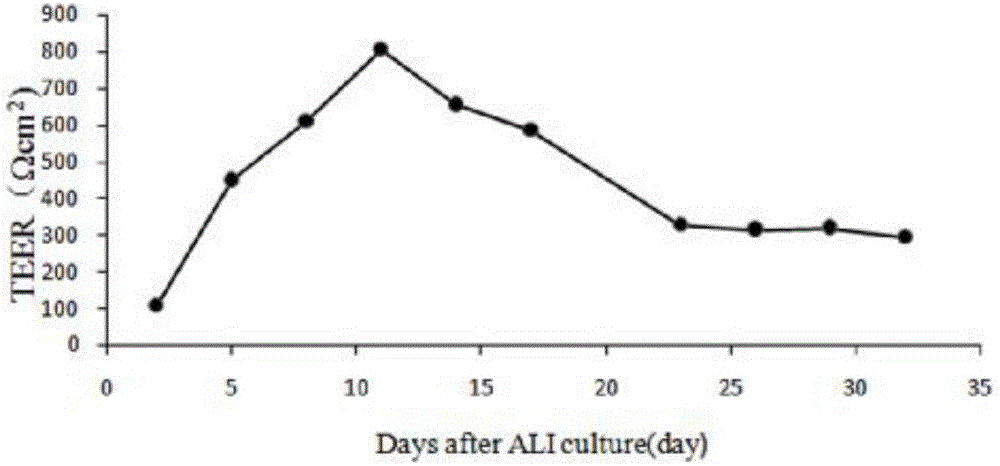
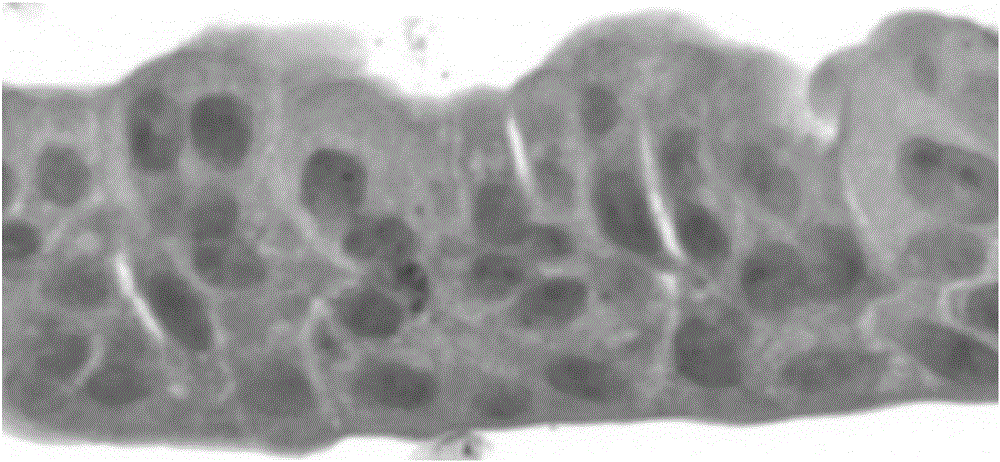
[0068] Example 1 Establishment of an in vitro differentiation model of porcine airway epithelial cells
[0069] 1.1 Isolation of porcine respiratory epithelial cells A 3.5-month-old white female pig was anesthetized with pentobarbital, fixed on the operating table, and its neck and abdomen were disinfected with iodine and alcohol in turn. Under sterile conditions, the superficial skin of the pig was cut with a scalpel, the trachea and lungs were exposed, the main trachea and lung tissue below the larynx were peeled off, immersed in a sample box containing 4 ℃ pre-cooled PBS, and placed on crushed ice shipped to the laboratory. Use sterilized forceps and scissors to dissect the tracheal tissue, and remove excess tissue and lymph nodes. After rinsing with PBS, it was transferred to another cell culture dish containing fresh PBS, and cut into 1×2 cm tissue pieces with small scissors. Soak twice in Joklik's MEM containing 0.5mg / mL DTT and 10ug / mL DNAse to remove sputum, fungi, b...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 In vitro differentiation model of porcine respiratory epithelial cells infected with recombinant AAV6-GFP
[0081] 3.1 Preparation and quantitative recovery of AAV6-GFP 293T cells cryopreserved in our laboratory were treated with complete medium (DMEM containing 10% FBS and 1% PS) at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivated and passaged to 60 150mm cell culture dishes. Transfection was performed when 293T cells reached 80% to 90% confluence. During transfection, firstly mix plasmids PSC-GFP (6ug), pXR6 (10ug) and pXX680 (12ug) in a 15mL centrifuge tube, add 500μL of serum-free DMEM medium and mix gently, then add 110μL of PEI transfection reagent , Gently pipetting and mixing, let stand at room temperature for 5-10min, and finally add the prepared transfection complex to the 293T cell dish without changing the medium. After culturing for 48h, discard the medium in the dish and use a cell scraper. The cells were scraped off the culture dish, collected in a centrifuge tube, c...
Embodiment 4
[0083] Example 4. Study on the infection and replication characteristics of EV68 in PAEC model
[0084] 4.1. Virus: EV68, TCID50=10 -6.7
[0085] Cells: PAE cells, density approximately: 1.5X10 6 / hole
[0086] 4.2. Before inoculation: wash the PAE model 3 times with 0.5ml sterile PBS, soaking for 10min each time.
[0087] 4.3. Virus inoculation: Take EV68 virus seed, add 200 μl to each well, incubate at 37°C for 1 h, remove the virus and wash twice with 0.5ml sterile PBS to remove unbound virus, and continue to culture at 37°C.
[0088] 4.4. Collection of infected samples
[0089] After infection, at different time points (6, 24, 48, 72hrs), samples were collected at each time point according to a, b, c, and d. At the same time, a control well without virus incubation was set up, marked as "Con", and the collection at each time point was also carried out.
[0090] a. Collection of top washes (two duplicate wells): add 200ul PBS to the top surface of cells, incubate at 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com