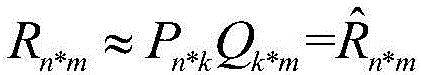Key-element-based matrix decomposition and fine tuning method
A matrix decomposition and element technology, applied in the field of matrix decomposition, can solve the problems of key influencing factors that do not take into account the decomposition effect of existing scoring data, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
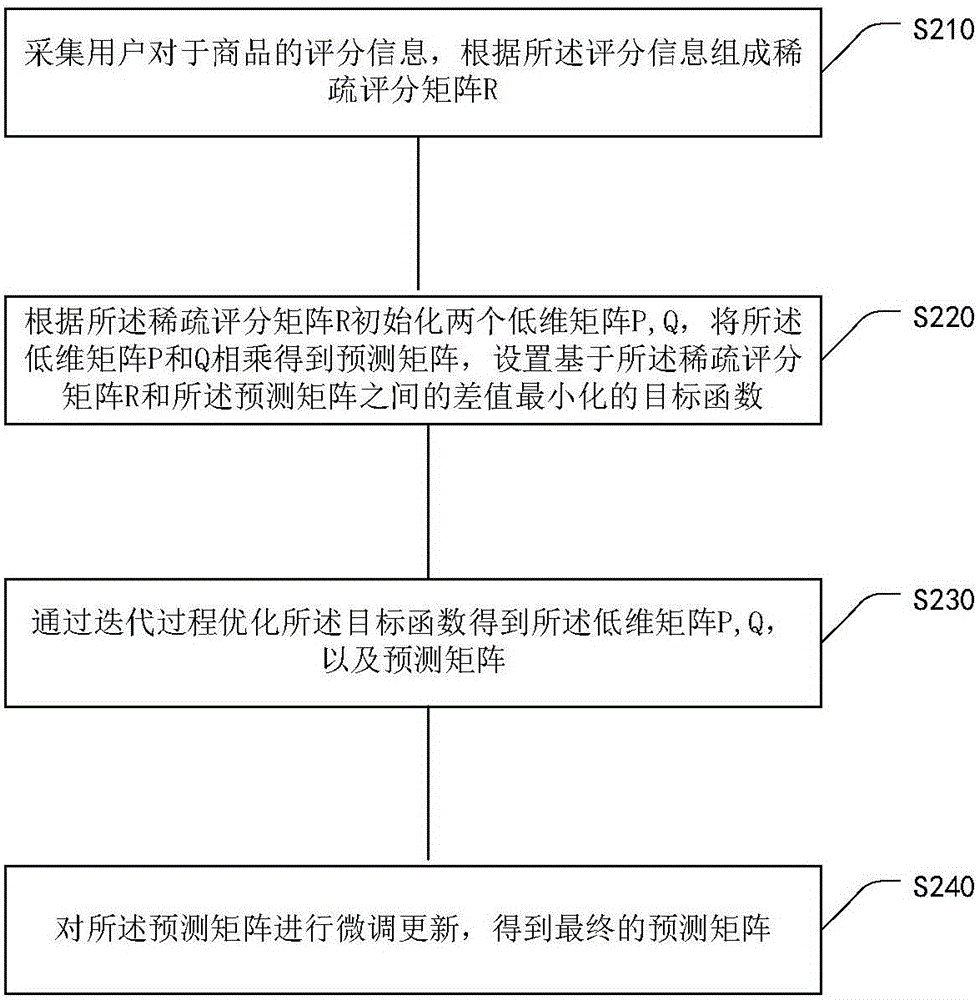
[0044] The purpose of the present invention is to solve the problems existing in the matrix decomposition algorithm and provide a fast decomposition algorithm based on key elements, and fine-tune the prediction matrix to make the decomposition result more accurate. The present invention decomposes the user-commodity sparse large matrix collected from the data into two matrices in the low-dimensional implicit space, and the initial matrix and the decomposed two matrices meet the minimum difference between the dot products. In the calculation process, the objective function of minimizing this difference is to optimize the two matrices through the gradient descent method, and finally point-multiply the two matrices to obtain the prediction matrix.
[0045] This embodiment provides a processing flow of a matrix decomposition and fine-tuning method based on key elements such as figure 1 As shown, the following processing steps are included:
[0046] Step S110 , collect the user's ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] In this embodiment, the description of the performance of the algorithm is carried out by comparing specific examples:
[0073] 1. Data preparation
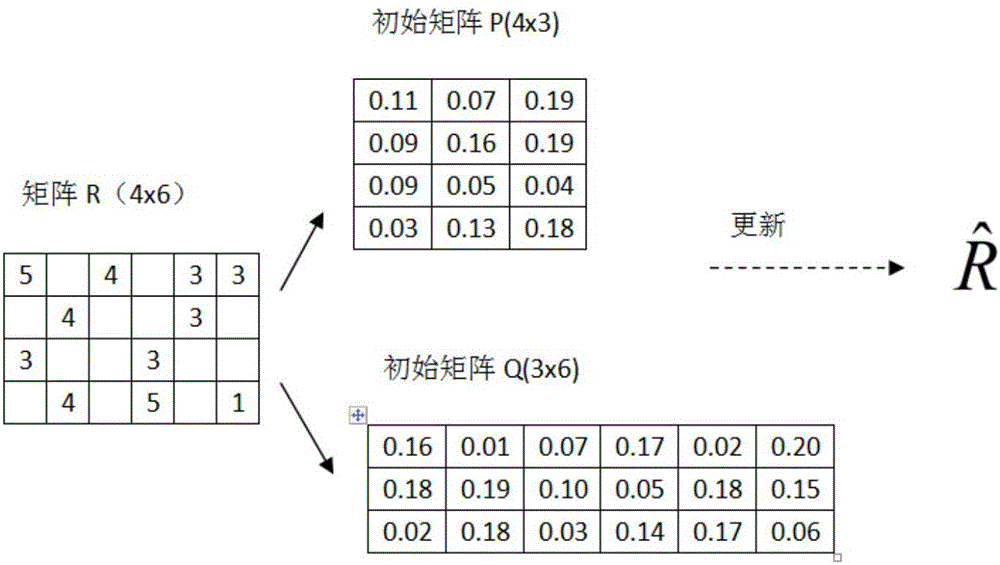
[0074] We selected Epioions, a standard scoring data set commonly used in recommendation systems. After preprocessing the data set, we extracted 100,000 pieces of data for simulation experiments. The sparsity of the matrix composed of the experimental data set was 1.5%. The scoring data in the matrix is distributed between 1-5, so we also set the predicted value of the experimental results as a value between 1 and 5.
[0075] Second, form the training set and test set
[0076] Simulation experiments are carried out by means of cross-validation. 90% of the data in the data set is extracted as the training set, and the remaining 10% of the data is used as the verification set.
[0077] Three, the experimental process
[0078] First initialize and randomly generate low-dimensional matrices P and Q, and set the dimension...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com