Hub electric system, electromobile and driving, braking and stroke-increasing method thereof
A technology for electric vehicles and hubs, applied in electric vehicles, control drives, vehicle energy storage, etc., can solve problems such as failure to achieve expected success, low cost performance, and low practical power consumption indicators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
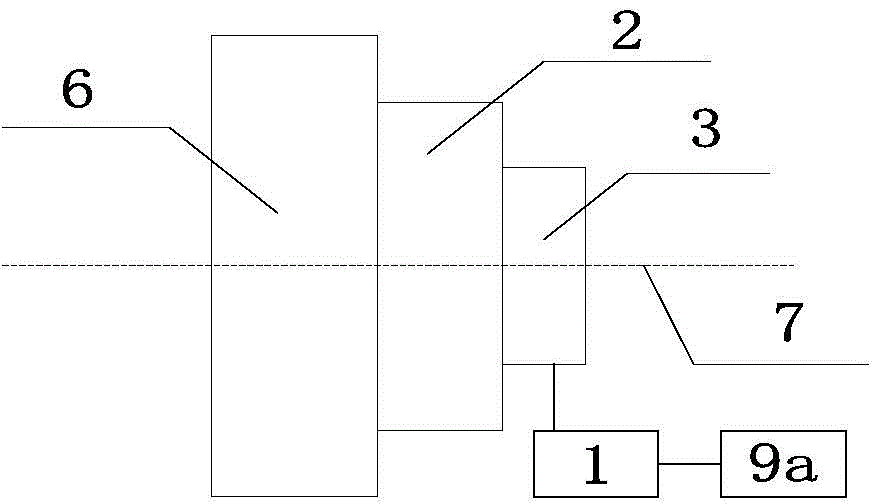
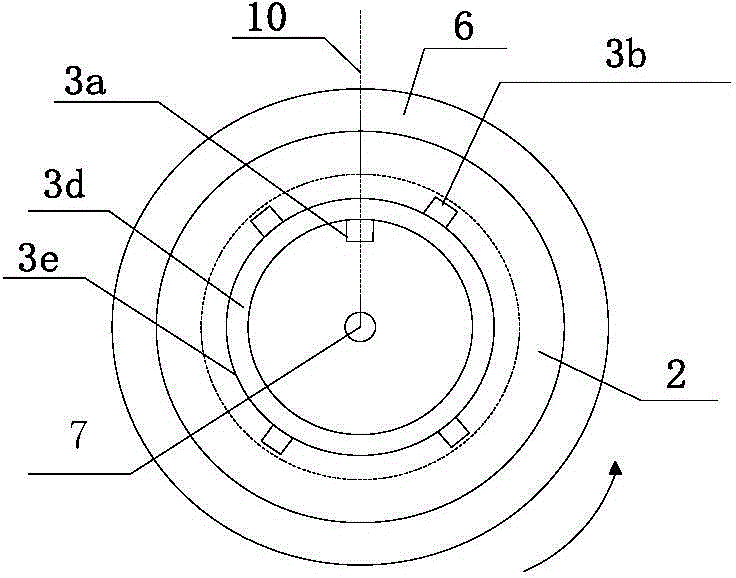
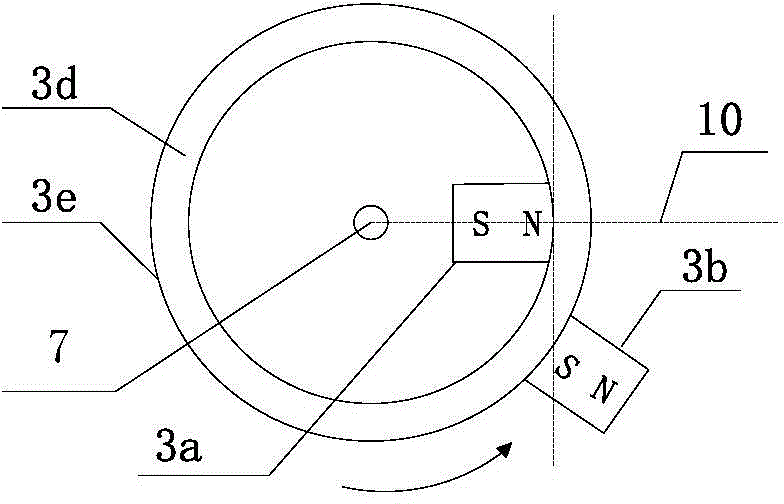
[0096] A wheel hub electric system of an electric vehicle and its matching electric two-wheeled vehicle are selected such as Figure 10a Shown vehicle frame 4, the circumference of wheel 5 is 1000mm, and battery pack 8b selects 24V12Ah lithium iron phosphate battery to be installed in the inside of vehicle frame; Electric device is located at the rear wheel of vehicle. The coaxial rotating body 3e of the electric device is a ring-shaped titanium-aluminum alloy ring with a rotating shaft and a circumference of 300mm. The outer edge of the alloy ring is fixedly connected with 8 rotor units 3b, and the inner part of the alloy ring is fixedly connected with the fixed shaft. On the device, a stator unit 3a is installed; the coaxial rotating body 3e is coaxially installed with the hub 6, and a deceleration / torque conversion device 2 composed of several gears is arranged in between, and the deceleration / torque conversion device 2 is used to realize the connection with the hub 6 Mecha...
Embodiment 2
[0104] The initial start-up current of embodiment 1 is changed to: power modulator in 5s with I 1 The intensity is 8A as the benchmark, corresponding to the rotation cycle of the coaxial body, the current intensity is automatically increased by 1.5% every next cycle, and the next work instruction of the drive control device 9a is waited for from the 6th second: if there is no input command from the drive control device, power modulation If the command given by the driving control device is to accelerate, the power modulator will execute T 1 with (T 2 +T 0) current sequence with a ratio of 1:5, and the average strength of real-time energization is given by the drive control device.
[0105] Others are the same as in Embodiment 1, and the slow acceleration mode is more suitable for safety design requirements. The moment when the aforementioned stator unit winding starts to be energized can also be changed to (T 1 +T 2 ) time period is a delay of 1% to 5% of the reference va...
Embodiment 3
[0107] An electromagnetic braking function is added to the electric device described in Embodiment 1.
[0108] The electromagnetic braking device is a ten-level rheostat, and the power supply modulator correspondingly adds a braking signal input terminal 1e to electrically connect the electromagnetic braking device 9b, such as Figure 5c Shown; when the manual control electromagnetic brake device sends a braking signal, the power modulator cuts off T 1 corresponding to the timing current, start T 2 The time domain is energized, and the energization time domain is set so that the sensing unit 3c senses the rotor unit 3b around the shaft to from (about 5 degrees) position to The time period for the 0 position.
[0109] The brake current output by the power modulator corresponds to the ten-level resistance setting of the electromagnetic braking device 9b as ten-level intensity, and the set output current intensity is: the first level is 6A, the last level is 11A, and the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com