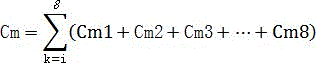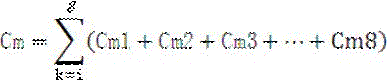Method for calculating relative contribution rate of underground soil erosion to ground surface soil erosion in karst area
A contribution rate, karst technology, applied in calculation, soil material testing, radiation measurement, etc., can solve the problems of high exposure rate of bedrock, difficult to use radionuclide tracer method, discontinuous soil distribution space, etc. small investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] A method for calculating the relative contribution rate of underground and surface water and soil loss in karst areas, which includes:
[0029] Step 1. Select monitoring objects: select reservoirs or ponds, underground rivers and different land types in karst areas as monitoring objects;
[0030] Step 2, sampling the monitoring object;
[0031] Step 3, each sampling sample 137 Determination of Cs content;
[0032] Step 4, according to the sample 137 The measured value of Cs content calculates the relative contribution rate of soil surface and underground soil erosion.
[0033] The different land types mentioned in step 1 include: forest shrub land, shrub land, sloping farmland, forest grassland, woodland, grass, shrubs and shrubs.
[0034] The monitoring object described in step 2 is sampled, and its sampling method is: for the sampling of the silt in the reservoir or pond, adopt the plum blossom-shaped distribution method to collect 5 samples, and the sample collec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com