Europe and America hybrid grape variety Kyoho stress-resistant gene VlbZIP36 and application thereof
A grape and gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems affecting yield and quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
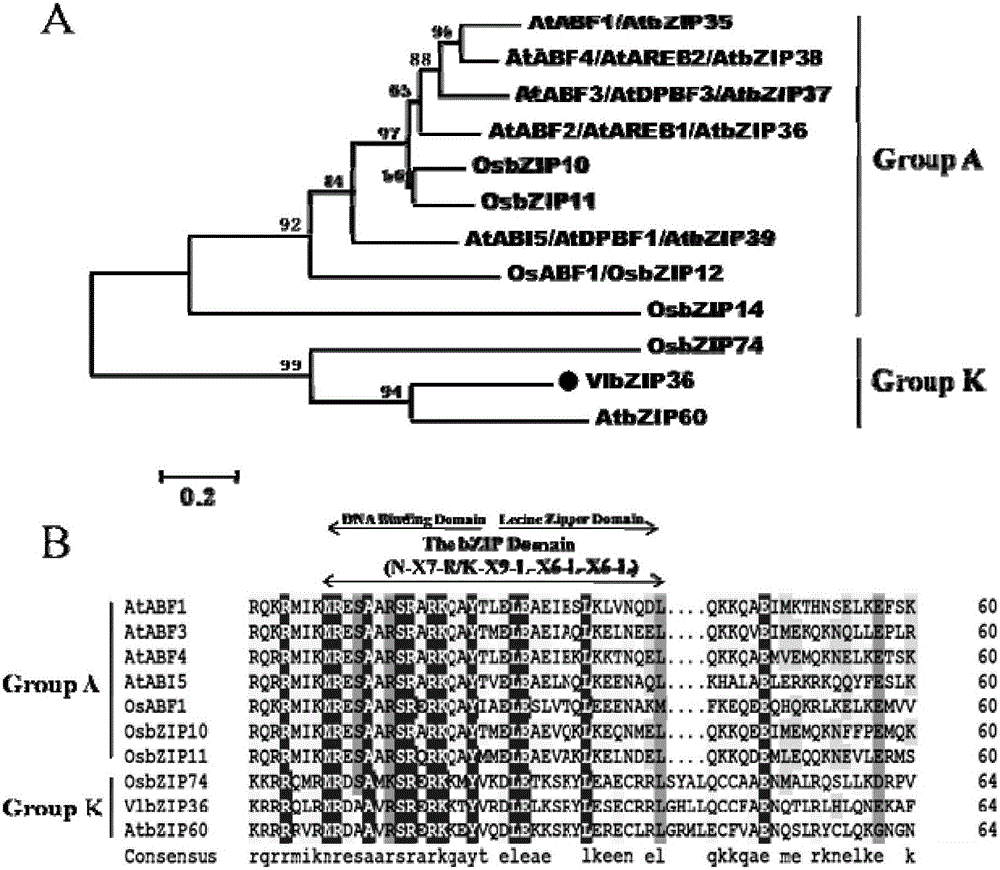
[0036] Example 1: Bioinformatics analysis of VlbZIP36
[0037] The phylogenetic tree analysis of the amino acid sequence of VlbZIP36 and the bZIP amino acid sequences of groups A and K of other studied plants and the multiple sequence alignment of highly conserved amino acid residues show that the amino acid sequence of VlbZIP36 is consistent with the amino acid sequence of Arabidopsis AtbZIP60 and rice OsbZIP74 The homology is the highest, and they all belong to the K group subfamily of the bZIP family ( figure 1 A). Analysis of the amino acid structures of VlbZIP36 and other bZIPs revealed that their amino acid sequences all contain a bZIP conserved domain consisting of a DNA binding domain and a leucine zipper domain ( figure 1 B).
Embodiment 2
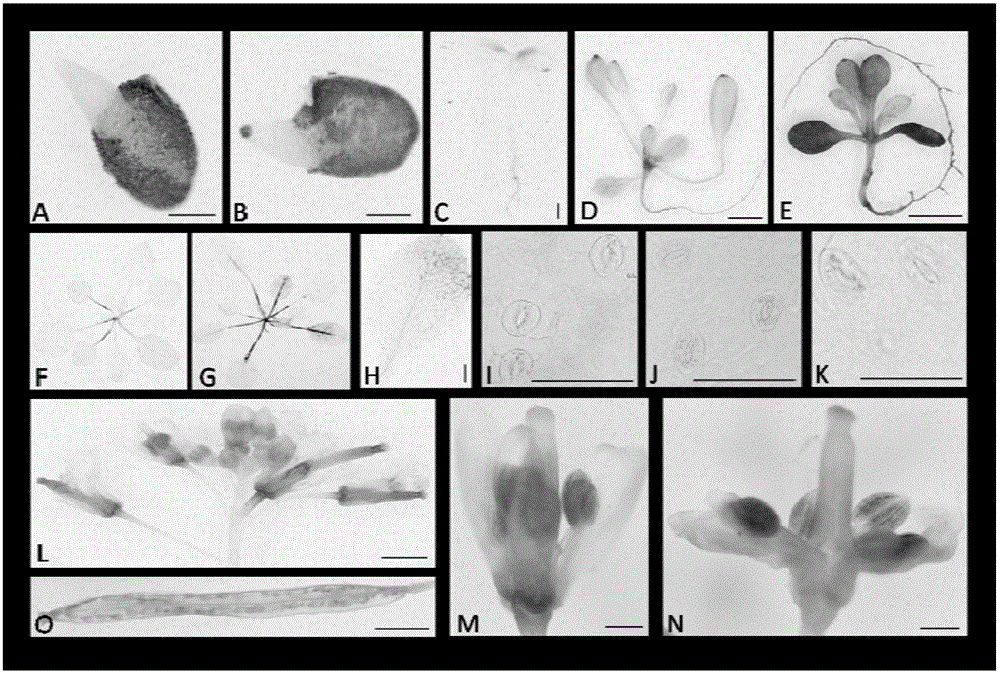
[0038] Example 2: Analysis of the expression pattern of VlbZIP36
[0039] In order to analyze the expression pattern of VlbZIP36, the inventors analyzed the VlbZIP36: GUS activity of transgenic Arabidopsis with GUS expression vector. It was found that GUS was present in the cotyledon tips and roots of 5-day-old seedlings ( figure 2 C), there is expression in most tissues of 2-week-old seedlings ( figure 2 D), but no expression in newly germinated mature embryos ( figure 2 A). However, after mannitol stress treatment, GUS was expressed at the tips of newly germinated mature embryos ( figure 2 B), and the expression was significantly enhanced in all tissues in the 2-week-old seedlings ( figure 2 E). In adult seedlings, GUS was found in 3-week-old petioles ( figure 2 F), anthers, styles, siliques ( figure 2 Higher expression in L-O), weaker expression in guard cells and sepals ( figure 2 I), but no expression in petals. After drought stress treatment and ABA tre...
Embodiment 3
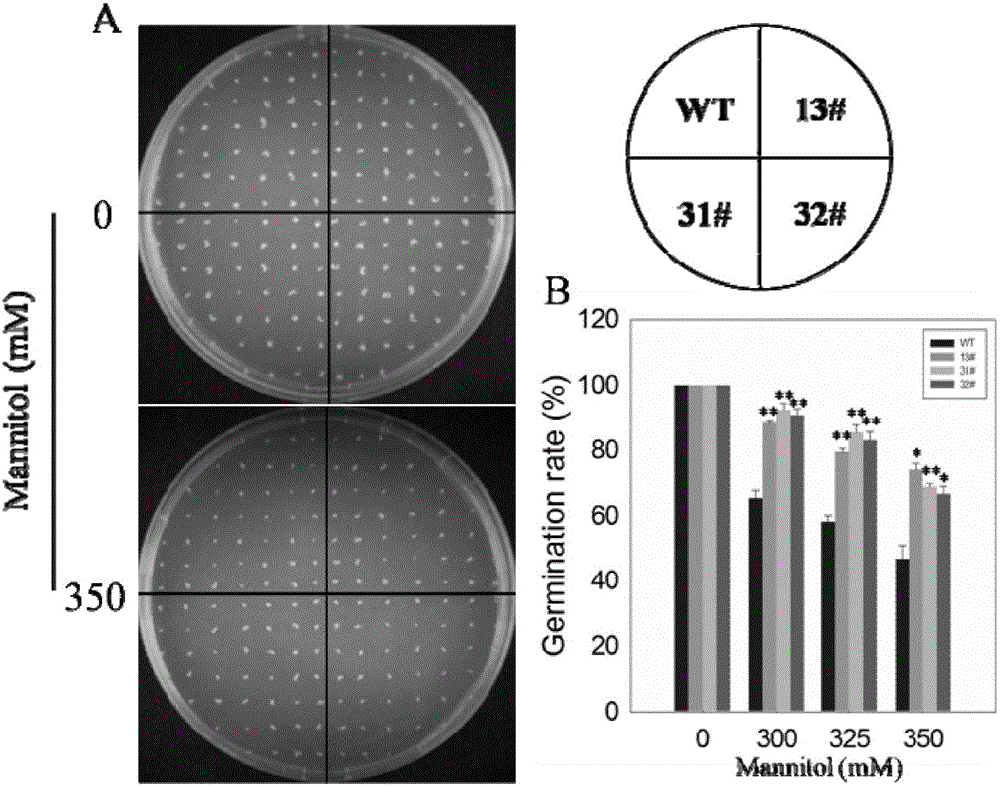
[0040] Example 3: Resistance of VlbZIP36 transgenic Arabidopsis lines to osmotic stress
[0041] The experimental results of osmotic stress treatment on the seeds of transgenic lines and wild-type plants showed that almost 100% of the transgenic lines and wild-type seeds could germinate after being cultured on MS medium for 3 days. After being cultured on the medium for 3 days, the transgenic lines showed a 21-28% higher seed germination rate than the wild type ( image 3 ). At the same time, after culturing on osmotic medium for 6 days, the cotyledon greening rate of the transgenic line was significantly higher than that of the wild type ( Figure 4 A, B). For example, when the concentration of mannitol was 300mM, the cotyledons of about 83% of the transgenic lines turned green, while only 66% of the wild-type plants turned green; when the concentration of mannitol was 350mM, the transgenic lines It showed a survival rate about 27% higher than that of the wild type. The i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com