Method for improving maltose yield in malt syrup production adopting starch saccharification at high concentration
A maltose syrup, high-concentration technology, applied in the field of starch sugar making, can solve the problems of low enzymatic hydrolysis yield, insufficient raw material utilization, and decreased saccharification yield, etc. rate increase effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 The composition of the saccharification solution for 50% (w / w) saccharification by different compound enzyme combinations
[0023] After starch milk with an initial concentration of 50% (w / w) was liquefied by high-temperature-resistant α-amylase, the DE value of the starch liquefaction product was controlled to be 15, the pH was adjusted to 5.0, and the temperature was 60°C. Add β-amylase and glucoamylase or β-amylase and pullulanase, and react for 48 hours. Single-enzyme saccharification with β-amylase was used as a control. After regular sampling and dilution, the maltose content was detected by HPLC, and the yield was calculated.
[0024] The results are shown in Table 1: Compared with single-enzyme saccharification, the addition of compound enzymes can increase the yield of maltose, because both glucoamylase and pullulanase can cut α-1,6 glycosidic bonds and make full use of raw materials , to avoid the formation of β-limit dextrin; but adding glucoamyla...
Embodiment 2
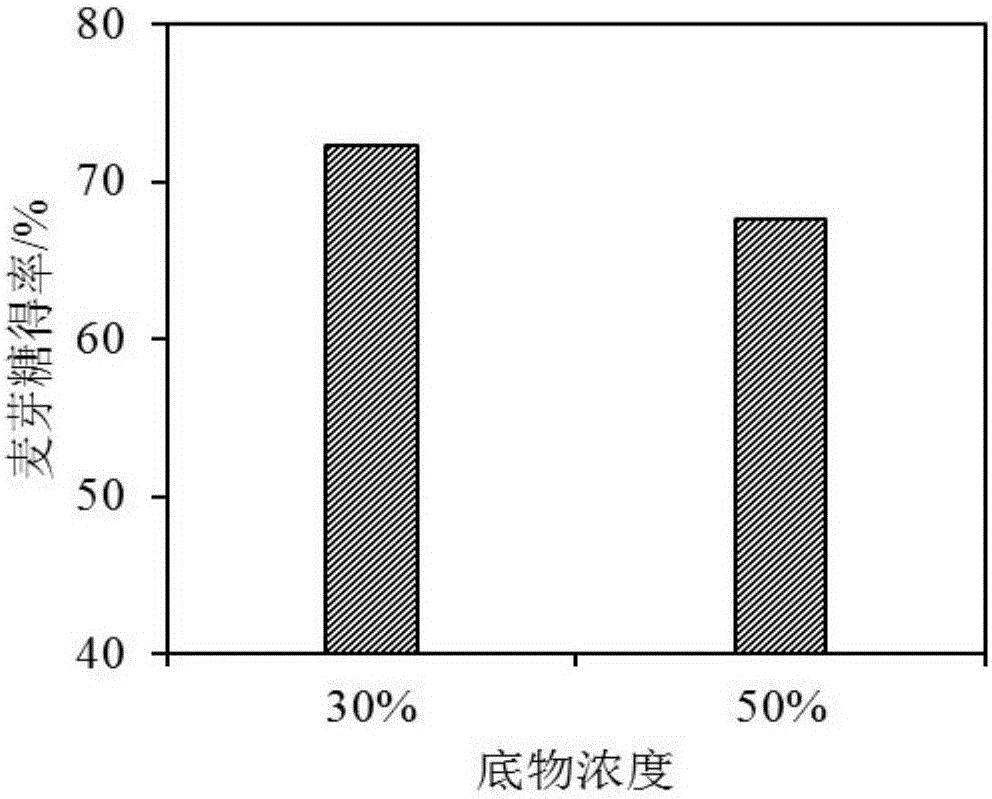
[0027] Example 2 The maltose yield of different substrate concentrations through saccharification of compound enzyme for 48h
[0028] After starch milk with initial concentrations of 30% and 50% (w / w) was liquefied by high temperature resistant α-amylase, the DE value of the starch liquefaction product was controlled to be 15, the pH was adjusted to 5.0, and the temperature was 60°C. Add 50U / g of β-amylase and 4ASPU / g of starch pullulanase, and react for 48h. After regular sampling and dilution, the maltose content was detected by HPLC, and the yield was calculated. The result is as figure 1 As shown, when the substrate concentration increased from 30% to 50%, the yield of maltose at 48h saccharification decreased slightly.
Embodiment 3
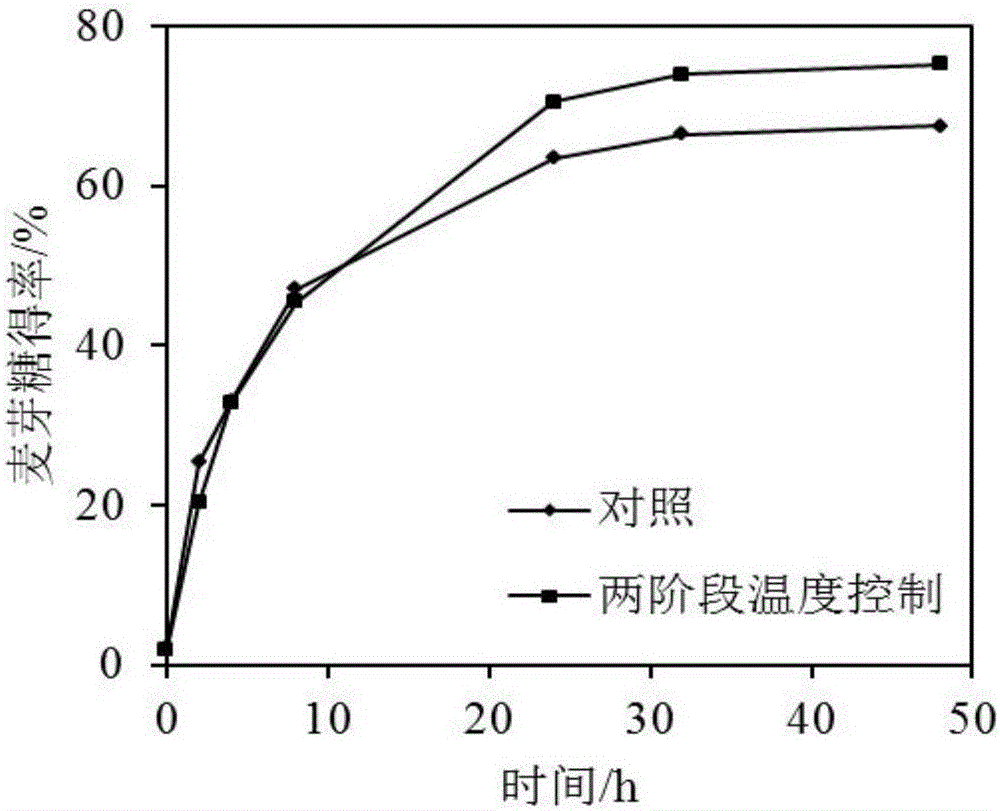
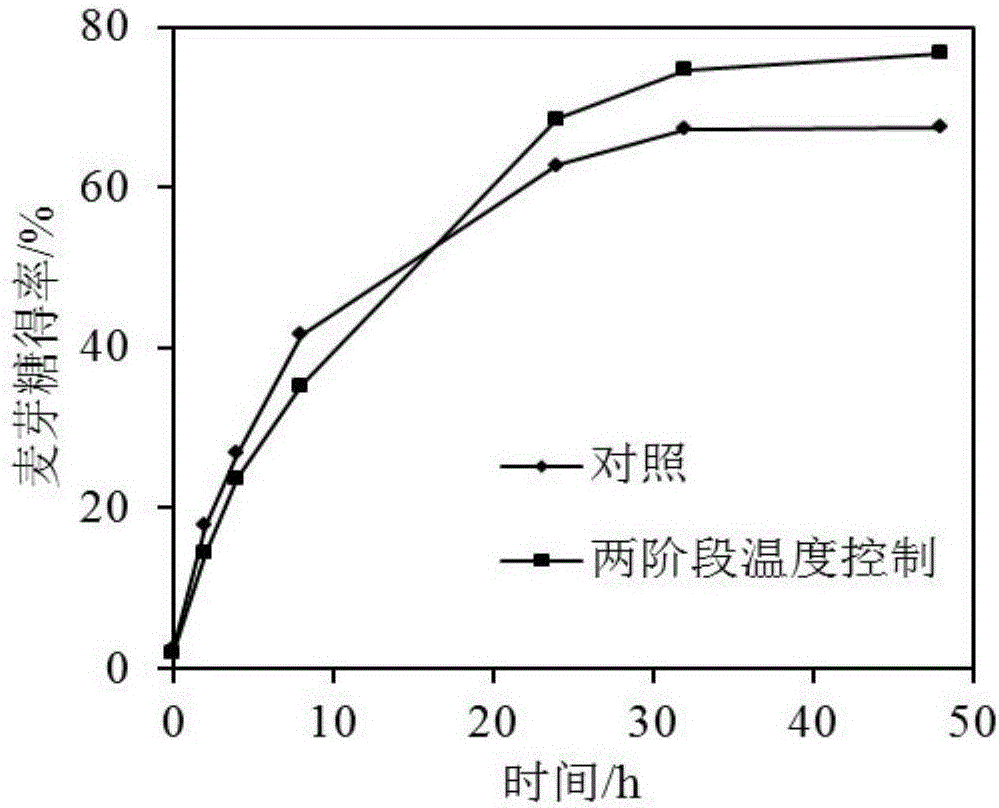
[0029] Example 3 The effect of two-stage temperature control on the yield of maltose, a substrate of 30% (w / w) saccharification of complex enzymes.
[0030] After starch milk with an initial concentration of 30% (w / w) was liquefied by high-temperature-resistant α-amylase, the DE value of the starch liquefaction product was controlled to be 15, the pH was adjusted to 5.0, the temperature was 50°C, and 50 U / g of starch was added. β-amylase starts saccharification and timing; after saccharification for 8 hours, add 4 ASPU / g starch pullulanase, adjust the temperature to 60°C, and continue saccharification for 40 hours. After regular sampling and dilution, the maltose content was detected by HPLC, and the yield was calculated. The temperature was kept at 60°C, and the two enzymes were added simultaneously as a control. The result is as figure 2 As shown, when the substrate concentration is 30%, relative to constant temperature saccharification, two-stage temperature control can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com