Under-forest konjak annual plantation method
A planting method and an annual technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, forestry, plant cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of high disease incidence, poor quality of planting taro, and many bacteria, so as to resist the invasion of biological disasters and artificial agricultural operations Less, strong heat retention and moisturizing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
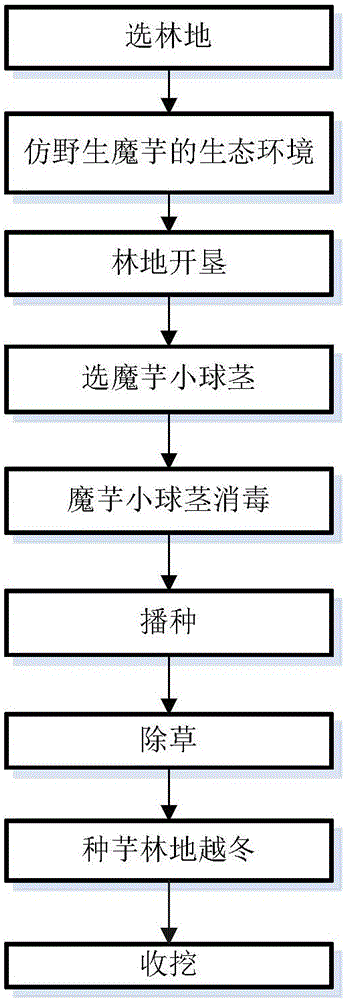
[0050] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of understory konjac seed taro 1 year planting method comprises the following steps:
[0051] ① Selection of forest land: Select the black locust forest that has been converted from farmland to forest, the age of the trees is more than 4 years, and the black locust forest is located in the area of 500-1000 meters above sea level.
[0052] ②Imitate the ecological environment of wild konjac: sparse forest or cut branches, so that the shade degree is 50%;
[0053] The illuminance meter is used to measure the light intensity. The shading degree of the black locust forest is 50%. In the first year of planting bulbs, the incidence of konjac under the forest is less than 5%. above.
[0054] ③Forest land reclamation: In spring, small-scale rotary tillage machinery is used to reclaim black locust forest land that has been converted from farmland to forest;
[0055] There is no need for soil disinfection in the black locust woodland. In fact, t...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of understory konjac seed taro 1 year planting method comprises the following steps:
[0067] ①Selection of forest land: Select chestnut forests that have been converted from farmland to forests. The trees are more than 4 years old, and the chestnut forests are located at an altitude of 500-1000 meters.
[0068] ②Imitate the ecological environment of wild konjac: sparse forest or cut branches, so that the shade degree is 40%;
[0069] Under the sunlight at 12-13 noon, observe the ratio of the sun scattered light under the forest to the open field. Accounting for 40% is enough. The method is simple and practical. In the first year of planting, the incidence of chestnut forests is less than 5%.
[0070] ③ Forest land reclamation: In the autumn and winter of the year before planting, 900-1275 kg / ha of konjac special fertilizer is applied, and small-scale rotary tillage machines are used in spring to reclaim the chestnut woodland that has be...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of understory konjac seed taro 1 year planting method comprises the following steps:
[0082] ①Selection of forest land: Select the Houbin trees that have been converted from farmland to forests. The trees are more than 4 years old, and the Houbin trees are located at an altitude of 500-1000 meters.
[0083] ②Imitate the ecological environment of wild konjac: sparse forest or cut branches, so that the shade degree is 30%;
[0084] Under the sunlight at 12-13 noon, observe the ratio of the sun scattered light under the forest to the open field. Accounting for 30% is enough. The method is simple and practical. In the first year of planting, the incidence rate under the forest is less than 5%, while the strong light and shade degree in the open field is less than 30%, and the incidence rate reaches 20%.
[0085] ③Forest land reclamation: in the autumn and winter of the year before sowing, 900-1275 kg / ha of konjac special fertilizer is appli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com