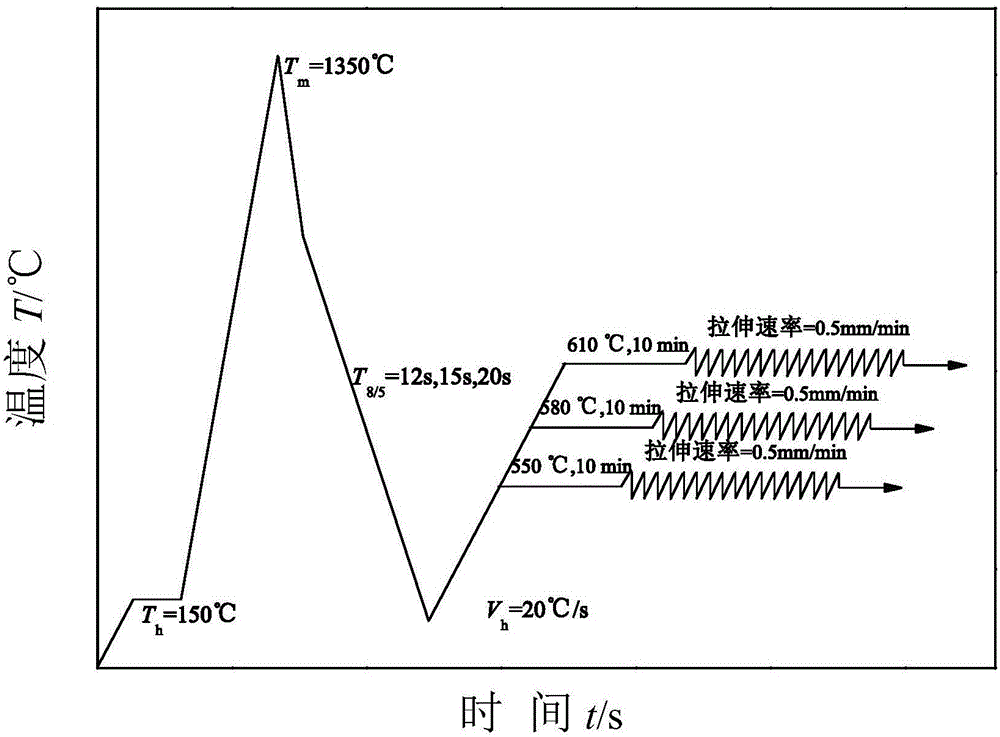
Steel for nuclear reactor pressure vessel and preparation method of steel
A technology for pressure vessels and nuclear reactors, applied in the field of steel for pressure vessels, can solve the problems of production, weight increase, shallow hardening depth on both sides, etc., and achieve the effect of improving structure uniformity and performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] The present invention provides the preparation method of the nuclear reactor pressure vessel steel that above-mentioned technical solution provides, comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Provide an alloy comprising the components defined in the above technical solution;
[0044] (2) heating the alloy, and performing first-stage forging in the recrystallization zone, the cumulative deformation of the first-stage forging is 200% to 350%;
[0045] (3) Carry out the second-stage forging in the non-recrystallized area and then air-cool to obtain a preheated steel ingot, the cumulative deformation of the second-stage forging is 50% to 150%:
[0046] (4) The preheated steel ingot obtained in the step (3) is subjected to conditioning treatment, the quenching temperature of the tempering treatment is 930-950°C, and the tempering temperature of the tempering treatment is 650-670°C.
[0047] In the present invention, the alloy comprising the components defined in the above ...
Embodiment 1
[0062] The molten steel is smelted in an electric furnace, refined outside the furnace and vacuum treated, and cast into steel ingots containing the components shown in Table 1. At the same time, non-metallic inclusions in steel are inspected: Class A 0.5, Class B 0.5, Class C 0.5, Class D 1.0.
[0063] Heating to 1250°C, the first-stage forging is carried out in the recrystallization zone, the initial forging temperature is 1220°C, the final forging temperature is 1000°C, the cumulative deformation of the first-stage forging is 350%, and then the temperature is lowered to 870°C for the second stage Two-stage forging with a cumulative deformation of 50%. After the forging is completed, the thickness of the forged piece obtained by air cooling is 20mm.
[0064] Quenching and tempering treatment: raise the temperature to 940°C for 60 minutes of heat preservation treatment to complete the water cooling to complete the quenching process, then heat to 660°C for 80 minutes and then...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The molten steel is smelted in an electric furnace, refined outside the furnace and vacuum treated, and cast into steel ingots containing the components shown in Table 3. At the same time, non-metallic inclusions in steel are inspected: Class A 0.5, Class B 0.5, Class C 0.5, Class D 1.0.
[0076] Heating to 1200°C, the first-stage forging is carried out in the recrystallization zone, the initial forging temperature is 1220°C, the final forging temperature is 1000°C, the cumulative deformation of the first-stage forging is 200%, and then the temperature is lowered to 870°C for the second stage For two-stage forging, the cumulative deformation is 100%. After the forging is completed, the thickness of the forged piece obtained by air cooling is 20mm.
[0077] Quenching and tempering treatment: raise the temperature to 960°C for 60 minutes of heat preservation treatment to complete the water cooling to complete the quenching process, then heat to 650°C for 80 minutes and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com