Monte Carlo-based equivalence reliability assessing method
A reliability, equivalent network technology, applied in data processing applications, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problem that the voltage and power support of the external network cannot be correctly reflected, the calculation accuracy of the reliability evaluation index is difficult to guarantee, and the power of the tie line cannot be reflected. Changes and other problems, to achieve the effect of small error, accurate reliability evaluation, and improved calculation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
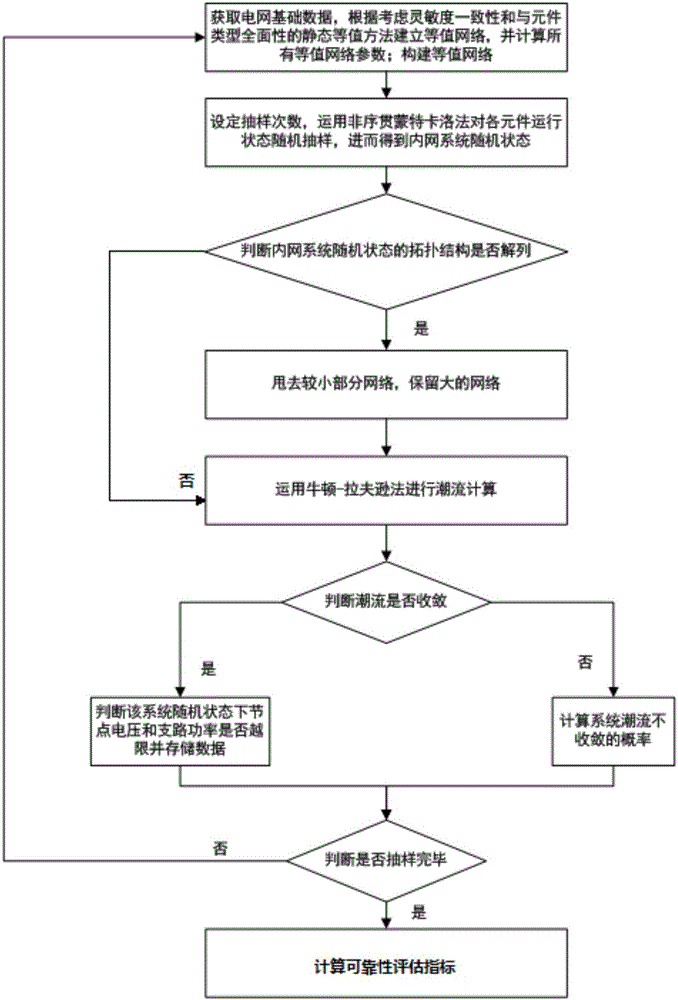
[0040] As shown in the figure, a Monte Carlo-based equivalent reliability evaluation method provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] S1: Obtain the basic data of the power grid, establish an equivalent network according to the static equivalent method that considers sensitivity consistency and comprehensiveness with component types, and calculate all equivalent network parameters; construct an equivalent network;
[0042] S2: Set the number of sampling times, use the non-sequential Monte Carlo method to randomly sample the operating status of each component, and then obtain the random status of the intranet system;
[0043] S3: Determine whether the topological structure of the random state of the intranet system is disassembled, and if so, discard the smaller part of the network and retain the larger network;
[0044] S4: If not, go to the next step S5;
[0045] S5: Use the Newton-Raphson method for power flow calculation;
[0046] S6: Judging whet...
Embodiment 2
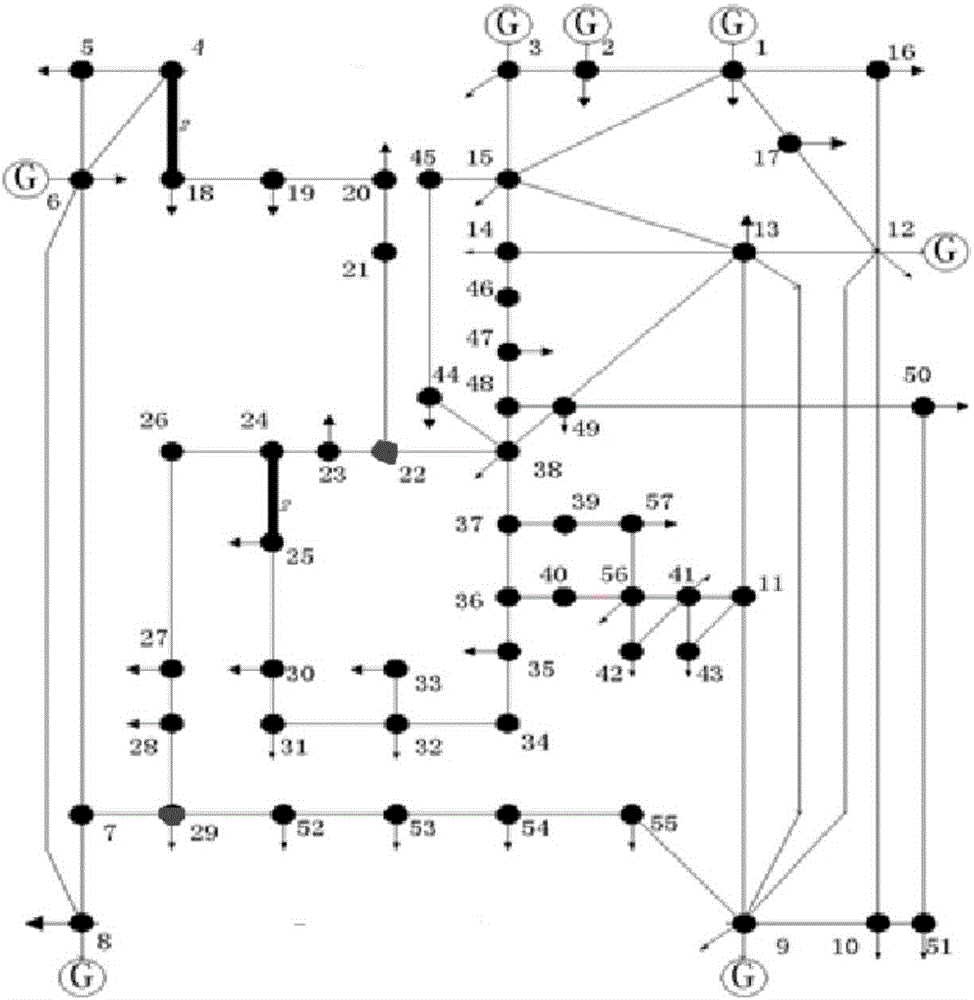
[0064] The Monte Carlo-based equivalent reliability evaluation method provided in this embodiment. First, the basic data of the entire network needs to be input, including the parameters and connection relationships of system components, the division of internal and external networks, and the availability of each component. Build an equivalence network according to a static equivalence method that considers sensitivity consistency and comprehensiveness with component types, and calculates all equivalence network parameters. Use the non-sequential Monte Carlo method, which is suitable for reliability evaluation of large-scale systems and high-order fault conditions, to simulate the operation of components and the magnitude of load fluctuations, and obtain the random state of the intranet system, and then analyze whether there is splitting and power flow in the network topology. Calculate and judge whether the branch power flow or node voltage exceeds the limit. Finally, the re...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The Monte Carlo-based equivalent reliability evaluation method provided in this embodiment, the specific method steps are as follows:
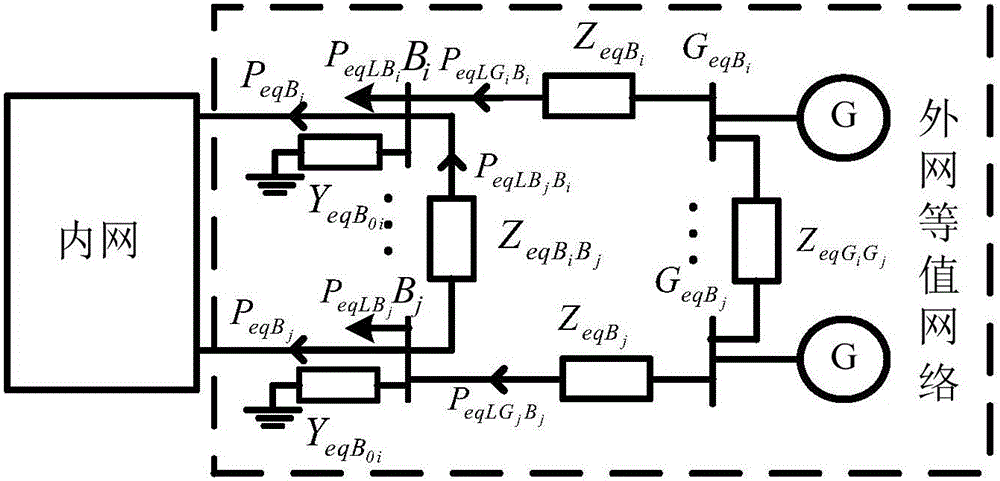
[0076] Input basic data: input the basic data of the interconnected grid, including the parameters of the primary equipment of the whole network (that is, the impedance of all lines, the susceptance to the ground and its transmission power constraints, the impedance of the transformer, the admittance to the ground, the transformation ratio and its transmission power Constraints, ground admittance of all nodes and connected load power, generator output and its output constraints, etc.) and topology (that is, the grid partition and the connection relationship of each node in the grid).
[0077] The Internet network nodes before equivalence are divided into three parts, which are the external network node set E, the border node set B and the internal network node set I. According to the division of internal and external networks, the numbe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com