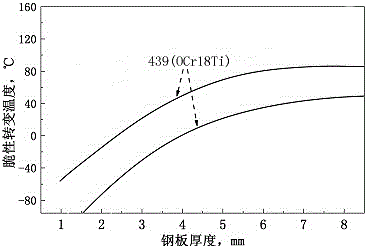
Medium-chromium molybdenum-free ferritic stainless steel extremely low in brittle transition temperature and preparation method thereof
A technology of brittle transition temperature and stainless steel, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of thick plate brittle transition temperature control and improvement, high brittle transition temperature, low brittle transition temperature, etc., to promote sustainable development, reduce life cycle cost, improve Effects on service life and safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Smelt in a vacuum induction melting furnace according to the set composition, and cast into a slab; the composition of the slab contains C0.005%, N 0.015%, Si 0%, Mn 0%, P 0.03%, S 0.007% by mass percentage, O 0.005%, Cr 18%, Nb 0.18%, Ti0.05%, Ni 0.4%, Al 0.2%, Cu 0.3%, the balance is iron and unavoidable impurities;
[0037] Heat the slab to 1000°C, keep it warm for 150min, and then hot-roll in multiple passes, the rolling start temperature is 950°C, the reduction in each pass is 30-50%, the final rolling temperature is 650°C, and the cumulative reduction is 96% , to obtain hot-rolled plate;
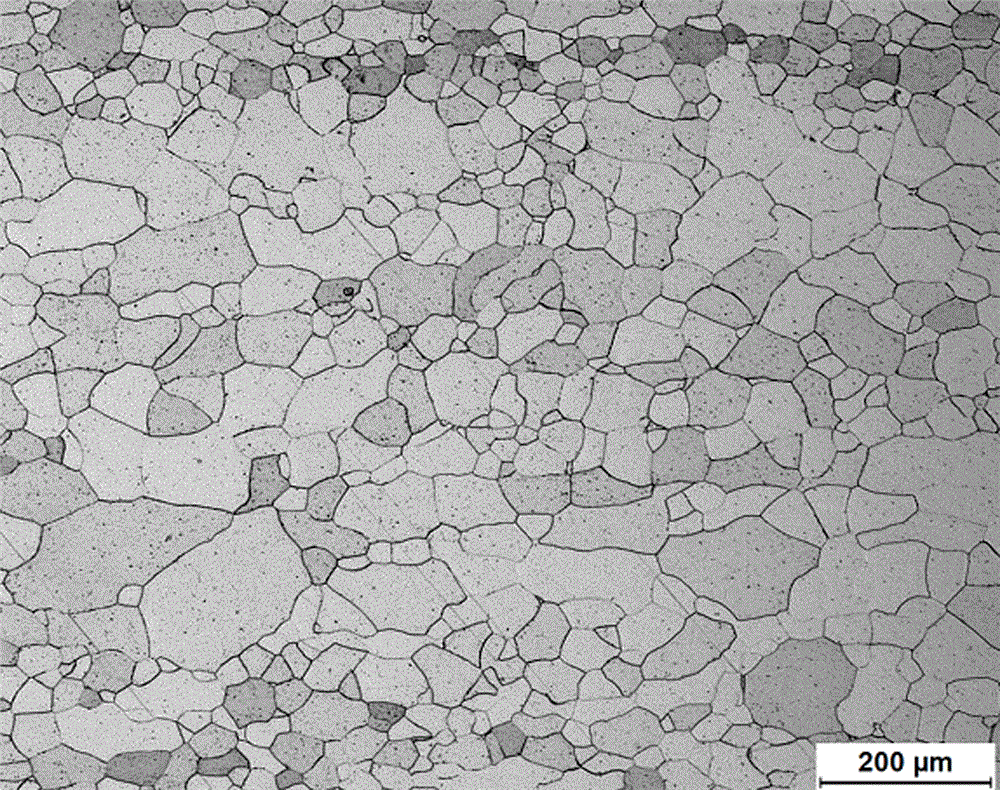
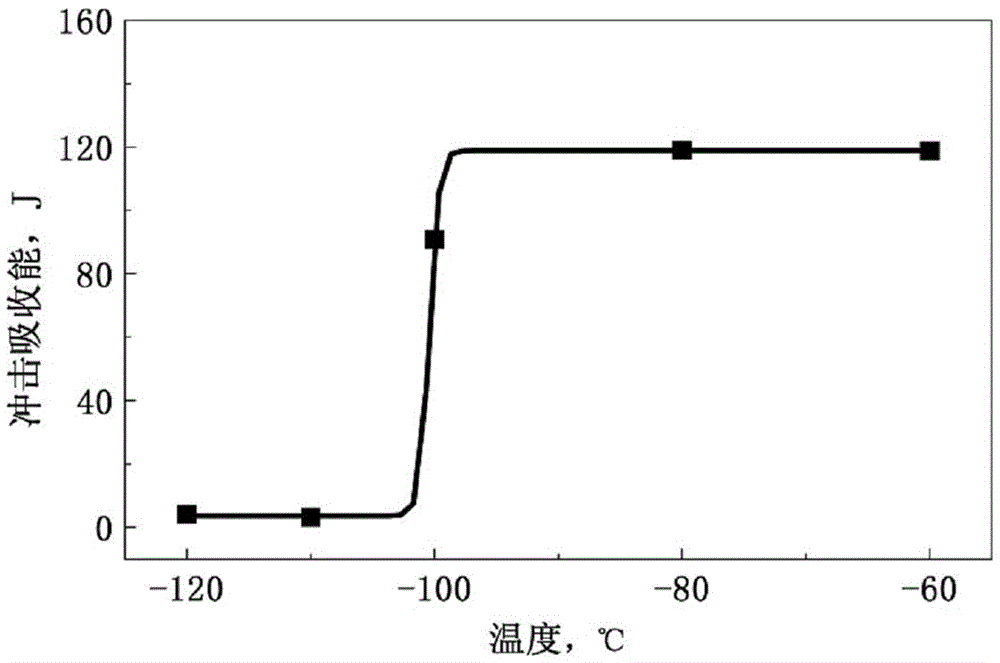
[0038] Heat the hot-rolled plate to 850°C and hold it for 8 minutes to make it fully recrystallized to complete the hot-rolled annealing, and obtain a medium-chromium-molybdenum-free ferritic stainless steel with a thickness of 8mm and a microstructure such as figure 2 shown. After the Charpy impact test, the impact absorbed energy-temperature curve of the medium-chromium-mol...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Smelted in a vacuum induction melting furnace according to the set composition, and poured into a slab; the composition of the slab contains C0.009%, N 0.011%, Si 0.3%, Mn 0.1%, P 0.02%, S 0.005% by mass percentage, O 0.003%, Cr 20%, Nb 0.13%, Ti0.08%, Ni 0.3%, Al 0.18%, Cu 0.4%, the balance is iron and unavoidable impurities;
[0041] Heat the slab to 1100°C, keep it warm for 90 minutes, and then hot-roll for multiple passes. The rolling start temperature is 1050°C, the reduction in each pass is 30-50%, the final rolling temperature is 700°C, and the cumulative reduction is 97%. , to obtain hot-rolled plate;
[0042] Heat the hot-rolled plate to 900°C and hold it for 7 minutes to make it fully recrystallized to complete the hot-rolled annealing, and obtain a medium-chromium-molybdenum-free ferritic stainless steel with a thickness of 6mm. The impact absorption energy-temperature curve is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the brittle transition temperature is -115°C, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Smelt in a vacuum induction melting furnace according to the set composition, and cast into a slab; the composition of the slab contains C0.015%, N 0.005%, Si 0.5%, Mn 0.2%, P 0.01%, S 0.006% by mass percentage, O 0.002%, Cr 22%, Nb 0.08%, Ti0.1%, Ni 0.2%, Al 0.1%, Cu 0.5%, the balance is iron and unavoidable impurities;
[0045] Heat the slab to 1200°C, keep it warm for 60 minutes, and then hot-roll for multiple passes. The rolling start temperature is 1100°C, the reduction in each pass is 30-50%, the final rolling temperature is 750°C, and the cumulative reduction is 98%. , to obtain hot-rolled plate;
[0046] Heat the hot-rolled plate to 950°C and keep it warm for 6 minutes to make it fully recrystallized to complete the hot-rolled annealing, and obtain a medium-chromium-molybdenum-free ferritic stainless steel with a thickness of 5.5mm. The impact absorption energy-temperature curve is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the brittle transition temperature is -120°C, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com