Incidence matrix-based distribution network traveling wave fault localization method
A correlation matrix, traveling wave fault technology, applied in fault location, fault detection by conductor type, measurement of electricity, etc., can solve problems such as bad data identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
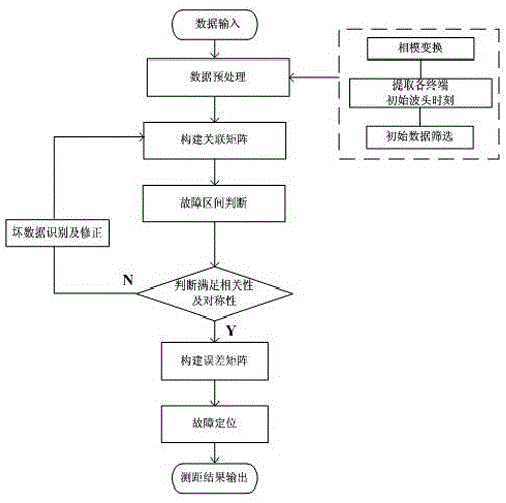
[0054] Embodiment 1: as attached figure 1 , 2 As shown, the distribution network traveling wave fault location method based on the correlation matrix includes the following steps:
[0055] The first step is to input data and perform data preprocessing, including (1) phase-mode transformation. Due to the coupling of transient traveling waves in the transmission process of transmission lines, in order to reduce the influence of phase-to-phase coupling, Clark transformation is used to transform the three-phase voltage to obtain α , β, and 0 moduli, select α modulus for analysis; (2) find the initial moment of fault, use wavelet transform to detect the sudden change point of transient voltage signal, and use it as the initial fault moment of each measurement node; (3) screen abnormal nodes, according to The measured initial fault time and amplitude screen the nodes to exclude obviously abnormal nodes;
[0056] The second step is to construct an association matrix. Each backbone ...
Embodiment 2
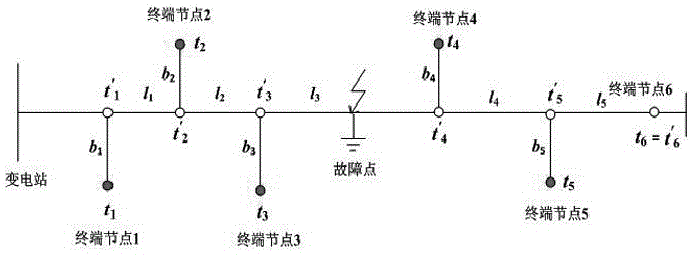
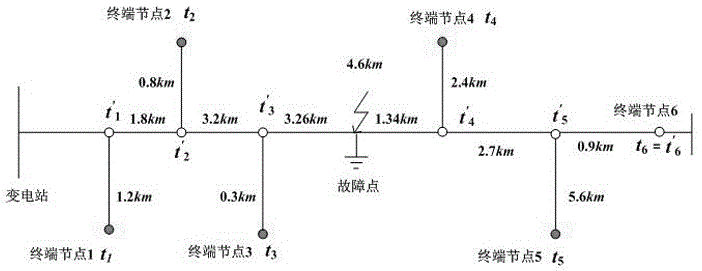
[0092] Embodiment 2: as attached image 3 As shown, the simulation model was built based on the actual 10kV distribution network line, in which the main line length is 11.4km, and positioning terminal devices are installed at the end of the line and the ends of five main branch lines. The sampling rate is 1.25MHz. The transmission line model refers to The actual line is built, and the fault point is at the distance t' from the main line 3 at 3.26km. The fault location calculation follows the following steps:
[0093] Step 1: Phase-mode transformation extracts the α modulus for analysis, and extracts the initial fault moment of each terminal node through wavelet transformation [t 1 , t 2 , t 3 , t 4 , t 5 , t 6 ] and filter the data;
[0094] Step 2: Calculate the backbone node time [t' according to the initial failure time of the actual terminal node 1 , t' 2 , t' 3 , t' 4 , t' 5 , t'6 ]=[87076.8, 87070.5, 87059.4, 87052.8, 87063, 87065.2];
[0095] Step 3: Const...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com