Mounting structure and method for producing mounting structure
A structure and assembly surface technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, printed circuit manufacturing, printed circuit assembly of electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as unclear connection reliability of solder joints
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
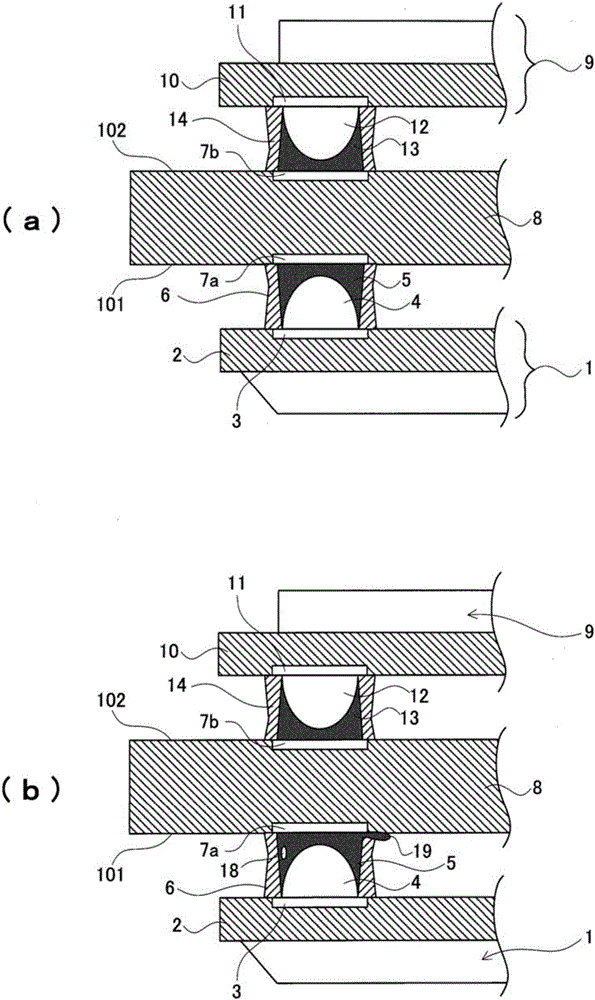
[0037] The assembled structure of Embodiment 1 is as image 3 shown.
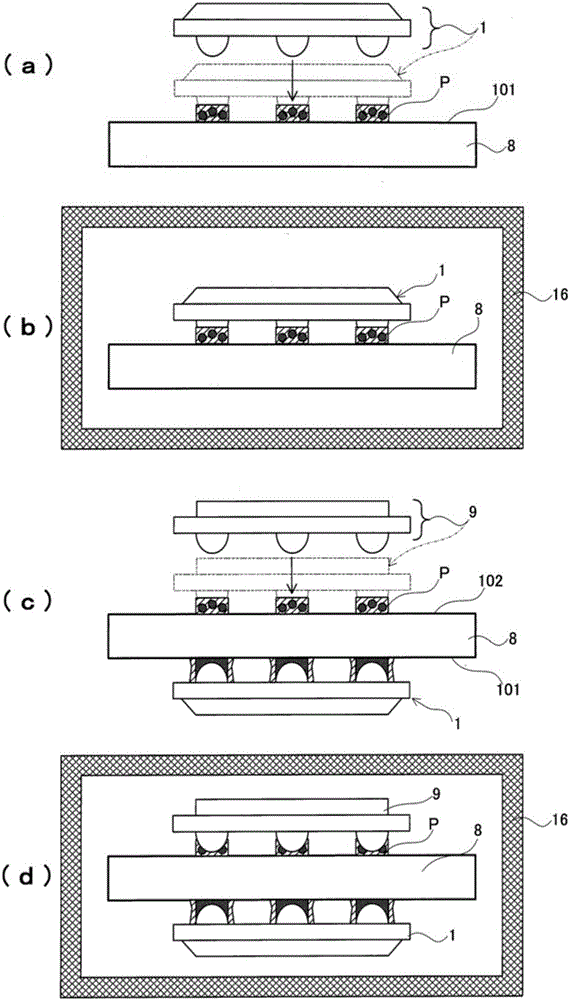
[0038] In this assembled structure, the components and the like of the solder paste used are selected. Thus only by implementing figure 1 (a)~ figure 1The same process described in (d) can produce a good assembled structure.
[0039] To explain, to express the existing example figure 1 (a)~ figure 1 (d), figure 2 (a), figure 2 (b) The same parts are described with the same symbols.
[0040] In this assembly structure, the semiconductor element 1 as the first assembly component is solder-assembled on the primary assembly surface 101 of the circuit board 8 as the component to be assembled, and the semiconductor element 1 as the second assembly component is solder-assembled on the secondary assembly surface 102 of the circuit substrate 8. The semiconductor element 9 is formed.
[0041] Hemispherical bumps 4 are formed on the electrodes 3 formed on the substrate 2 of the semiconductor element 1 . Th...
Embodiment approach 2
[0052] Figure 4 The assembly structure of Embodiment 2 is shown.
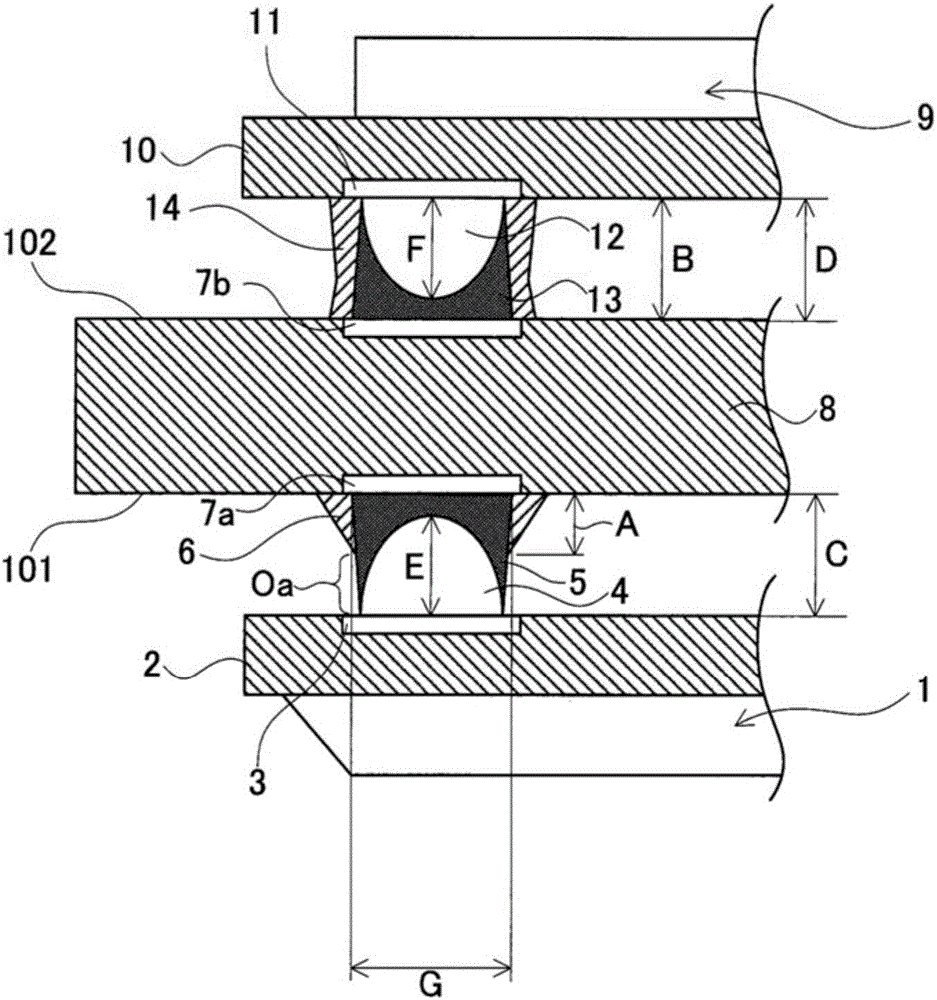
[0053] exist image 3 In the illustrated first embodiment, the vertices of the bumps 4 of the semiconductor element 1 do not directly contact the electrodes 7 a of the primary mounting surface 101 of the circuit board 8 . In addition, cured solder 5 is interposed between the apex of the bump 4 and the electrode 7 a. On the other hand, in the second embodiment, the apexes of the bumps 4 of the semiconductor element 1 are directly in contact with the electrodes 7 a of the primary mounting surface 101 of the circuit board 8 . Other than that, it is the same as Embodiment 1.
[0054] ie, with image 3 In the same way as in the case of , the solder 5 and half of the entire surface of the bump 4 are not covered with the reinforcing resin 6 . An exposed portion Oa exposing a part of the solder 5 is formed. with Embodiment 1 image 3 The difference is that the apex of the bump 4 is in contact with the electrode...
Embodiment approach 3
[0058] Figure 5 The assembly structure of Embodiment 3 is shown.
[0059] exist image 3 In the assembly structure according to Embodiment 1 shown, the semispherical bump 4 is formed on the electrode 3 of the semiconductor element 1 . But when Figure 5 In the assembled structure of the semiconductor device 1, spherical bumps 41 are used on the electrodes 3 of the semiconductor element 1. Only this point is different from image 3 different. Other than that, it is the same as Embodiment 1. That is, the apex of the reinforcing resin 6 does not come into contact with the bump 41, and the exposed portion Oa where a part of the solder 5 is exposed is not in contact with the bump 41. image 3 The situation is similarly formed. The composition of the bump 41 is the same as that of the bump 4 .
[0060] Therefore, the ratio of the gap width C between the circuit substrate 8 and the substrate 2 image 3 The gap in the situation is much larger. Therefore, the strength is weak...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com