Artificial surface plasmon-based polarization sensor
A polarization sensor, localized surface plasmon technology, applied in the direction of electromagnetic field characteristics, etc., to achieve the effect of easy manufacturing, lower operating frequency, and a wide range of product applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
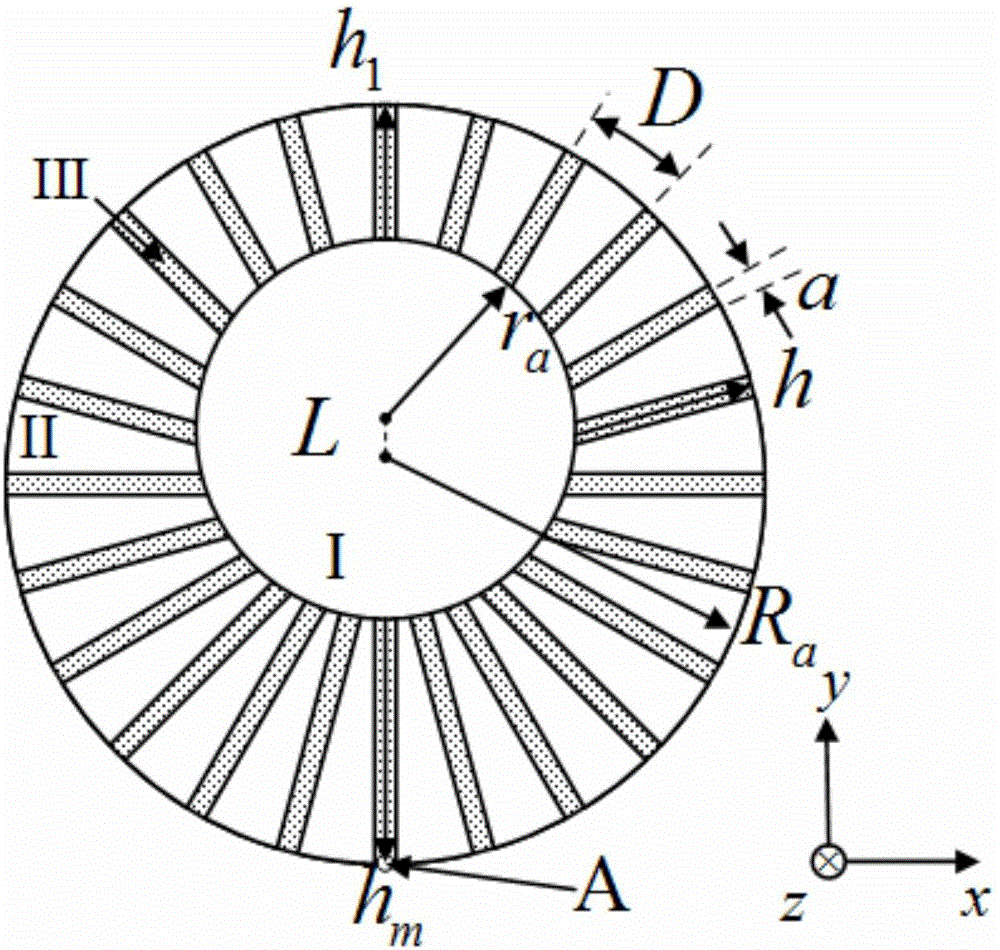
[0019] like figure 1 As shown, the basic structure of the sensor is a metal sheet with a thickness of 0.018 mm. The shape of the metal sheet is circular, and the thickness direction is defined as the z direction. A solid metal cylinder of equal height is distributed inside the metal sheet, and fan-shaped grooves with different depths (h) are evenly distributed along the outer circumferential direction of the metal sheet, and the grooves are filled with dielectric materials. Since the center of the inner cylinder does not coincide with the center of the entire structure, there is a distance L, resulting in unequal depths of the grooves. Along the direction from top to bottom, the depth of the groove gradually increases. Regions I and II in the figure are metal material parts, and region III is a groove part filled with dielectric materials. The radius of the outer cylinder is R a , the radius of the inner cylinder is r a , the shallowest and deepest groove depths are h 1 a...
Embodiment 2
[0021] as figure 1 The sensor shown is an example, the radius r a = 3 mm, R a = 10 mm, the radii of the shallowest and deepest grooves are h 1 = 5 mm, h m = 9 mm, the distance between the center of the entire structure and the center of the inner cylinder is L= 2 mm. The resonant frequencies of different groove depths are also different. The dielectric constant of the filling dielectric material is equal to 1, and a medium with a uniform dielectric constant can enhance the penetration of electromagnetic waves in the structure. The number of grooves is set to N=120.
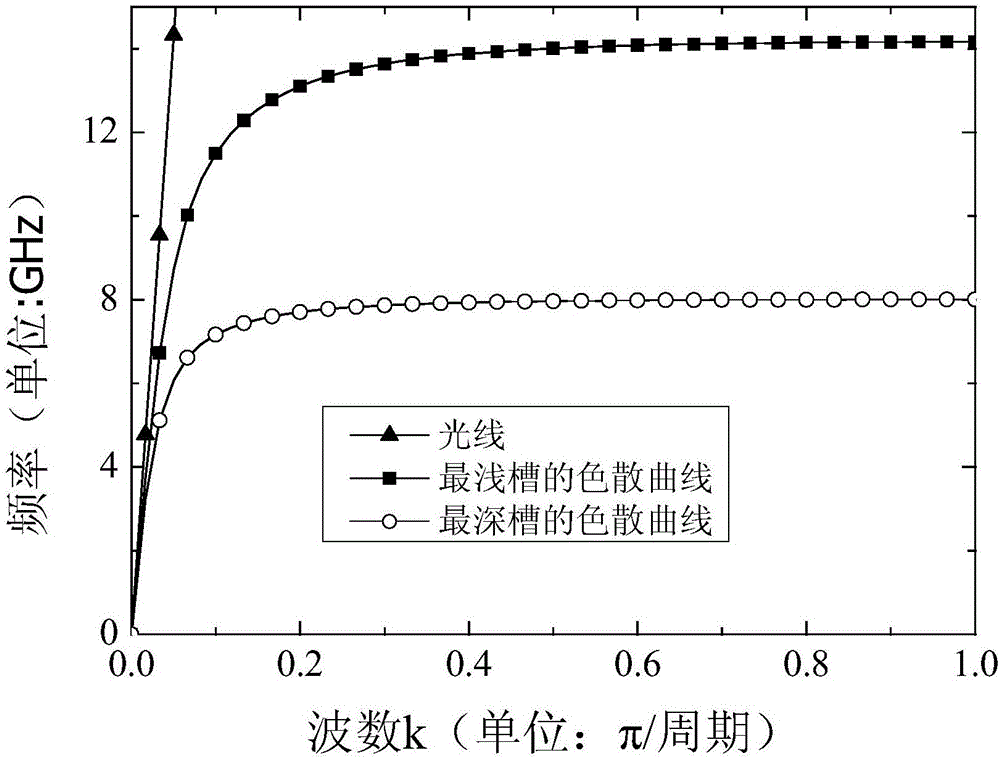
[0022] According to the second embodiment, for a single periodic structure with different groove depths, electromagnetic simulation software can be used to obtain the following figure 2 In the dispersion curve shown, the two curves correspond to the dispersion curves of the deepest groove and the shallowest groove respectively. It can be found that they are both located on the right side of the light, indic...
Embodiment 3
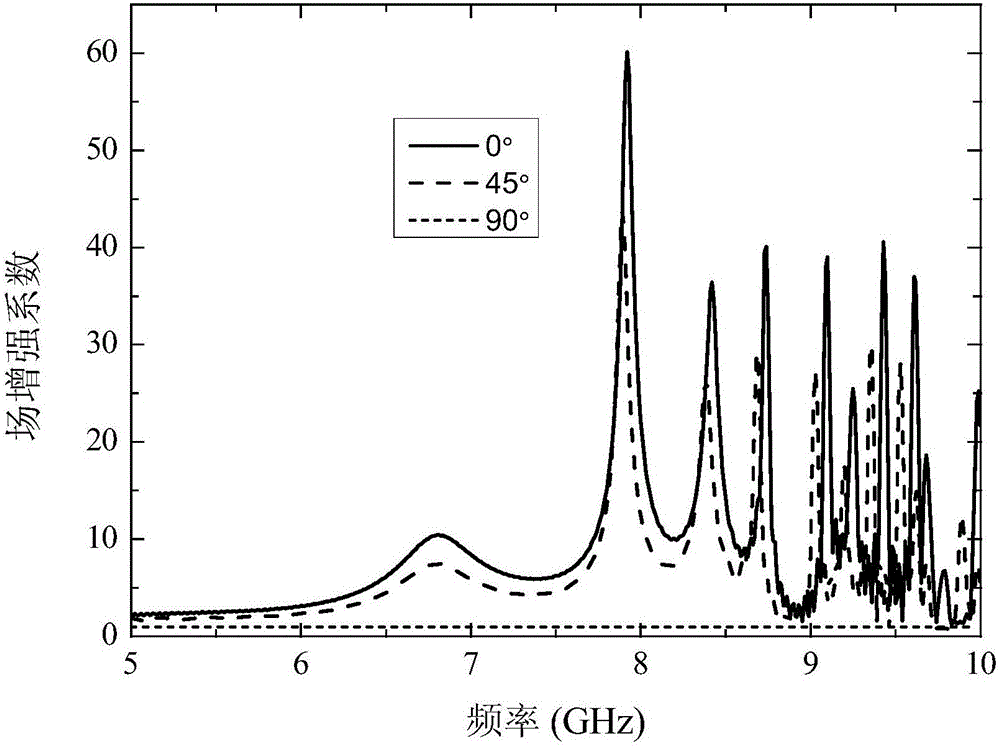
[0024] According to Embodiment 1, it is defined that the plane wave is incident along the +y direction to the -y direction, the wave vector is defined as the y direction, the electric field and the magnetic field are both in the xz plane, and the angle between the electric field component and the x axis is defined as θ, in A probe is set at position A at the bottom of the sensor structure 0.5 mm above the z direction. The probe can detect the electric field strength. The frequency band of the incident plane wave is 5 GHz to 10 GHz, and the electric field strength of the incident wave is 1 V / m. The ratio of the electric field strength detected by the probe to the electric field strength of the incident wave is defined as the field enhancement coefficient, image 3 It can be found that the field enhancement coefficient varies significantly with the angle θ in the entire frequency band, and the field enhancement gradually weakens with the increase of the angle θ. For the case whe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com