Method for optimizing laser radar detection atmospheric composition spectral line analysis
A technology of laser radar and component spectrum, which is applied in the directions of measuring devices, climate sustainability, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems that cannot meet the detection requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
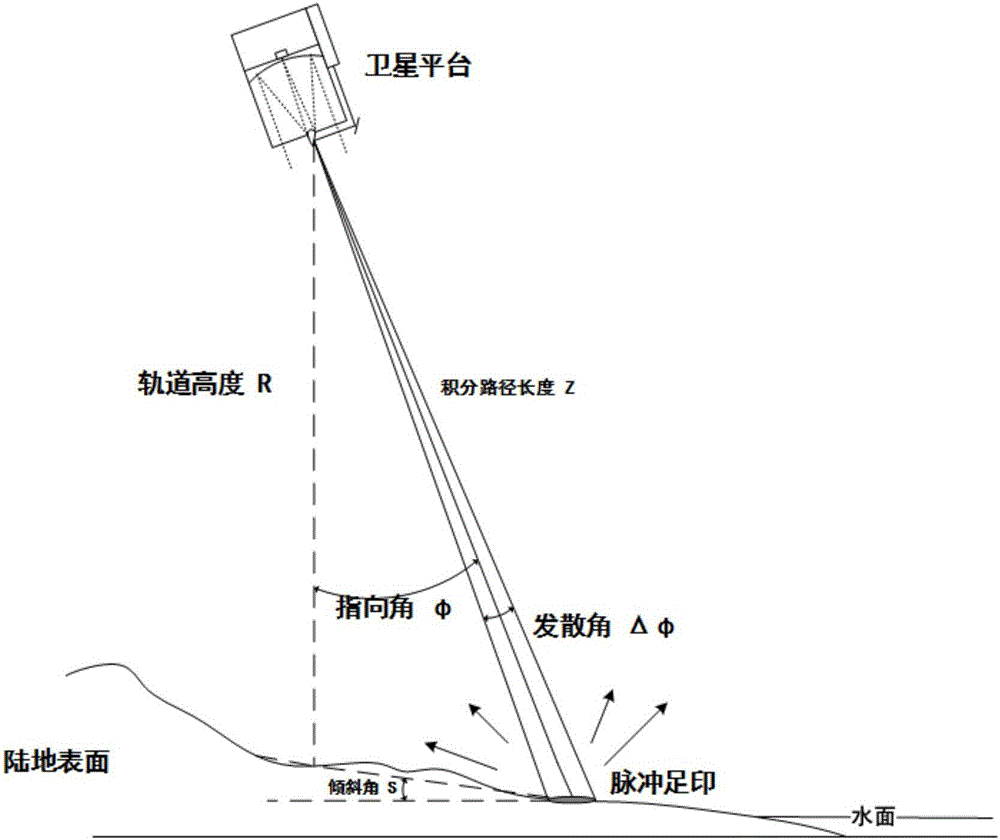
[0109] As shown in the figure, a method for optimizing laser radar detection atmospheric component spectral line analysis is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps:
[0110] Step 1, establish the IPDA lidar equation for hard target reflection
[0111] The integrated path differential absorption (IPDA, Integrated Path Differential Absorption) laser radar detection method is used to detect the backward reflection signal from the hard target. The echo signal received by the detector comes from the pulse echo signal reflected by the hard target, such as figure 1
[0112] , the specific IPDA lidar equation is as follows:
[0113]
[0114]
[0115]
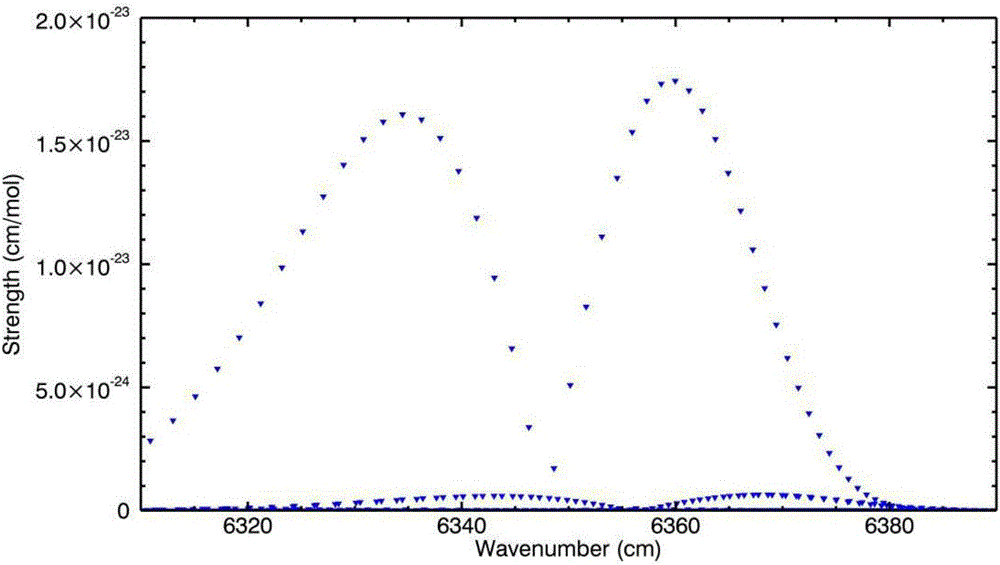
[0116] Equations (1) and (2) are based on the fact that the wavelength of each laser pulse is transmitted by CO 2 Optical depth due to absorption, used to calculate CO in the entire atmosphere 2 content. Receive the echo signal reflected by the ground surface through the detector,
[0117] Step 2, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com