A method of using a biochip for shear force experiments
A biochip and shear force technology, applied in the field of biochips used for shear force experiments, can solve problems such as lack of cell culture biochips, reduce experimental time and errors, ensure reliability, and achieve micro-observation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
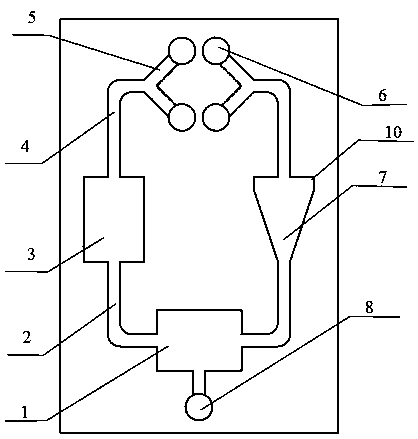
[0019] Attached below Figure 1-4 The present invention will be further described. A method for using a biochip for shear force experiment, the operation steps are as follows.
[0020] The first step is to select the chip size according to the cell shear force experiment.
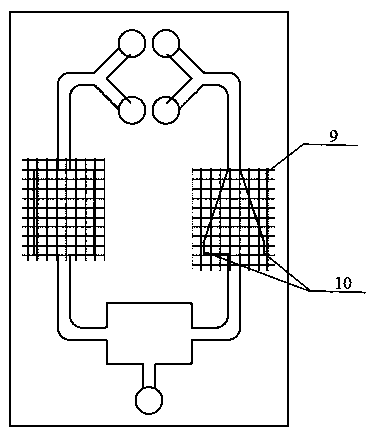
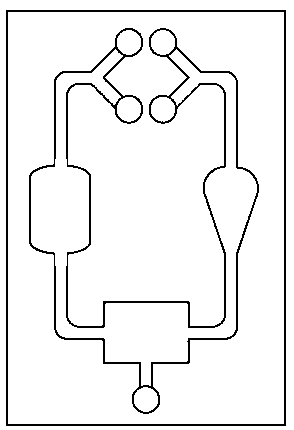
[0021] In the second step, the shape and size of the rectangular culture area 3 and the conical culture area 7 of the selected chip, as well as the dimensions of all channels, are input into the computer, and CAD software is used for drawing; then the drawing data is imported into the fluid simulation software, and the calculated Fluid flow network of 1 rectangular culture zone 3 and 1 conical culture zone 7 at experimental fluid flow rates.
[0022] In the third step, the above-selected chips are used to divide the experimental cells into the experimental group and the control group to cultivate the experimental cells. Stem cells and nutrient solution are injected into pairs from the injection holes 6 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com