A multiplex fluorescent gene detection method for rapidly distinguishing ect, mad, mcmv, poly
A multiple fluorescence, rapid technology, applied in the direction of microbial determination/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing detection cost, less sample consumption, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0035] Construction of example 1 murine pox virus, mouse adenovirus, mouse cytomegalovirus and mouse polyomavirus plasmid
[0036] Use the kit TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit to extract the DNA of ECT, MAD, MCMV and POLY viruses respectively, and perform PCR amplification with the above corresponding primers respectively. The amplification primers are:
[0037] ECT primer E1: 5'-TACGGTGTATATGGCTACTCA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1);
[0038] ECT primer E2: 5'-ACTGCTGCTTCCTATACTCG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2);
[0039] MAD primer A1: 5'-AGACTCACACTGCGTATAGTCC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3);
[0040] MAD primer A2: 5'-CCAGAACTCGGTTATTCCCCA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4);
[0041] MCMV Primer C1: 5'-GCCCTCTTCATCCCTTACCT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5);
[0042] MCMV primer C2: 5'-GACCTCCATGTCCTTCATGC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6).
[0043] POLY primer P1: 5'-CCATGCTCCCTTCTATGCGAT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 7);
[0044] POLY primer P2: 5'-TCAGTCAGCCATAGATGCAA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 8).
[0045] The 5' ends of primers E1, A1, C1 and P1 are also added with a tag sequence through th...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Establishment of multiple fluorescent gene detection methods for mousepox virus, mouse adenovirus, mouse cytomegalovirus and mouse polyomavirus:
[0070] 1) Plasmid PCR amplification
[0071] Singleplex, triplex, and quadruple PCR amplification with primers that specifically amplify mousepox virus, mouse adenovirus, mouse cytomegalovirus, and mouse polyomavirus.
[0072] Preparation of upstream primer mixture: mix E1, A1, C1 and P1 at a ratio of 1:1:1:1; preparation of downstream primer mixture: mix E2, A2, C2 and P2 at a ratio of 1:1:1:1 ratio to mix. The specific regions of the above four viruses were amplified by using four specific templates, triple templates, and quadruple templates. The preparation of the triple template: mixing the three plasmids in a ratio of 1:1:1; the preparation of the quadruple template: mixing the four plasmids in a ratio of 1:1:1:1. The PCR amplification system and procedure were the same as in Example 1.
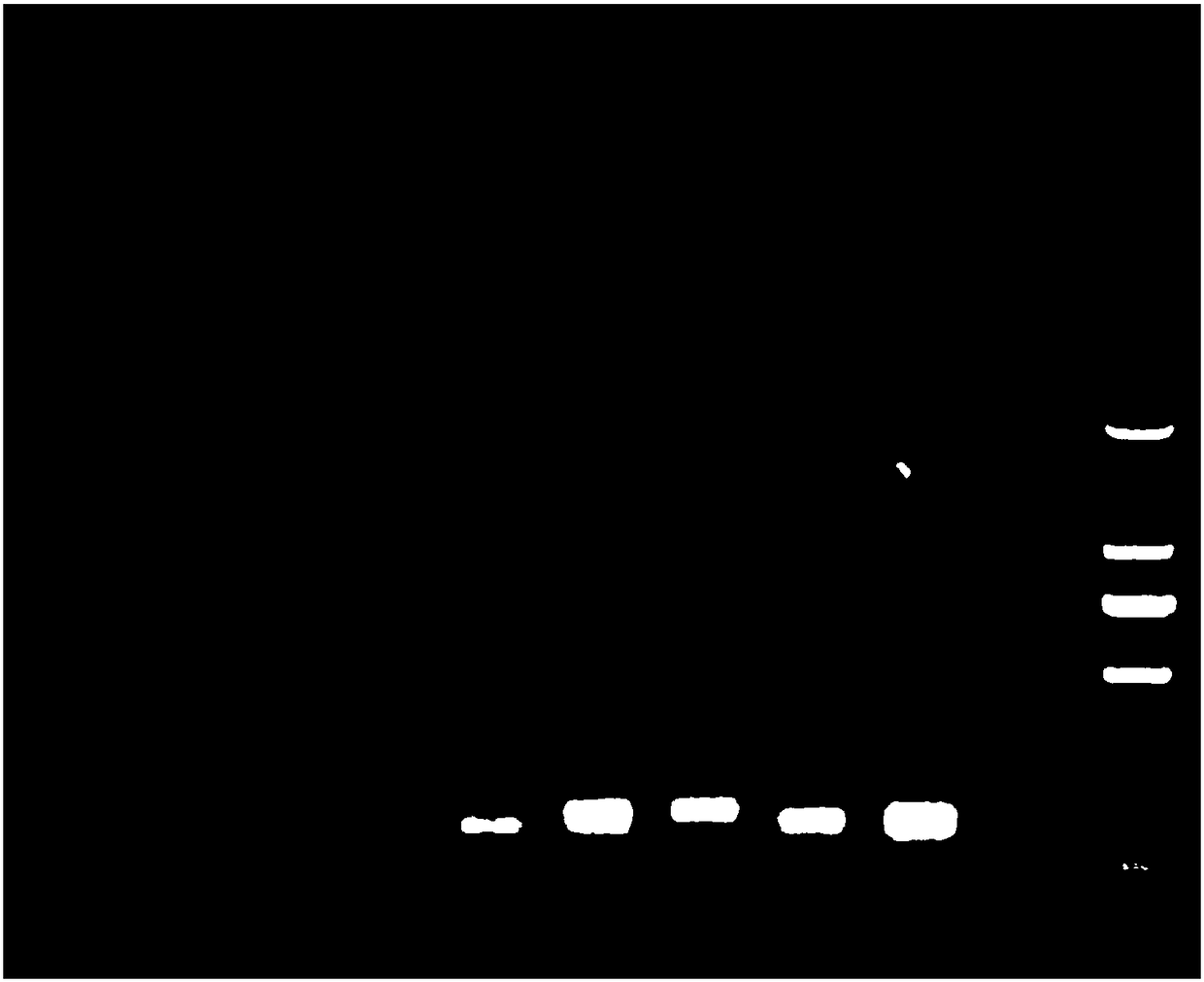
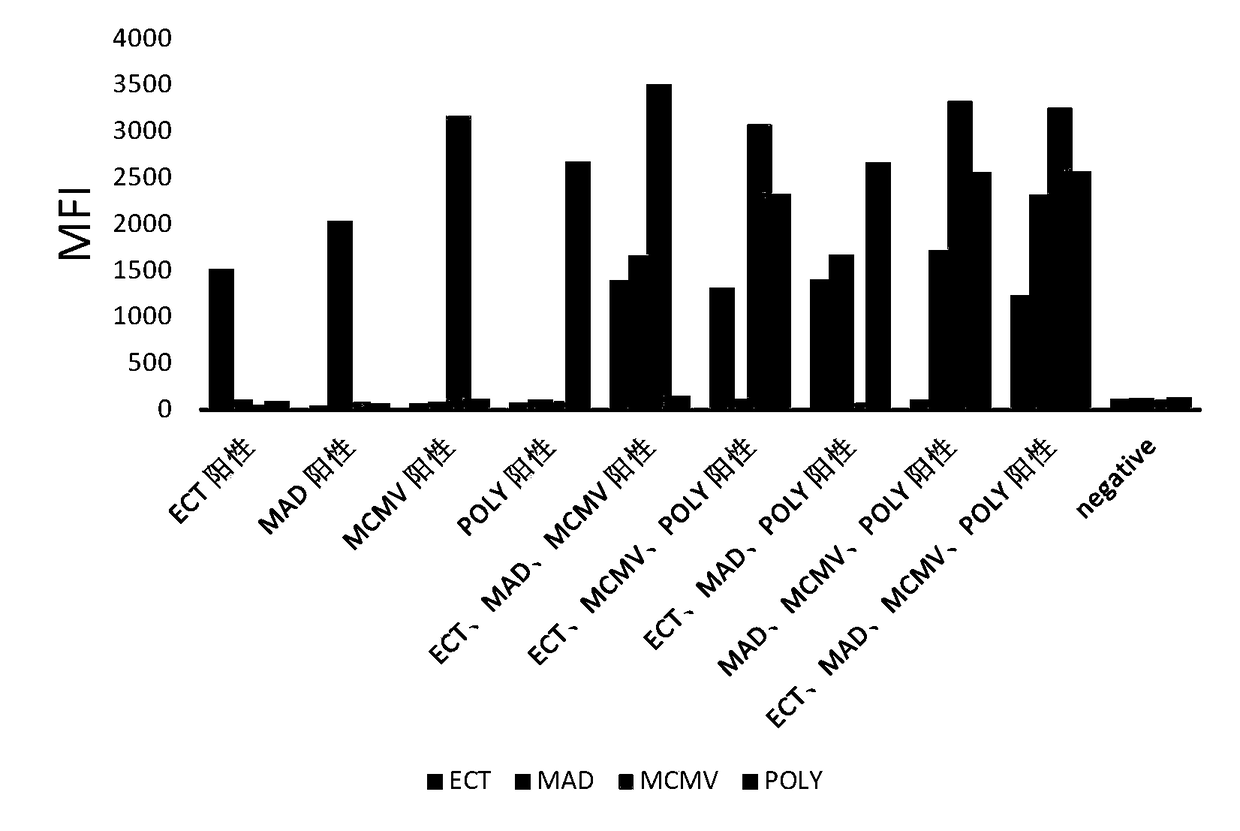
[0073] PCR produc...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Embodiment 3: Multiple fluorescent gene detection sensitivity experiment of ECT, MAD, MCMV, POLY
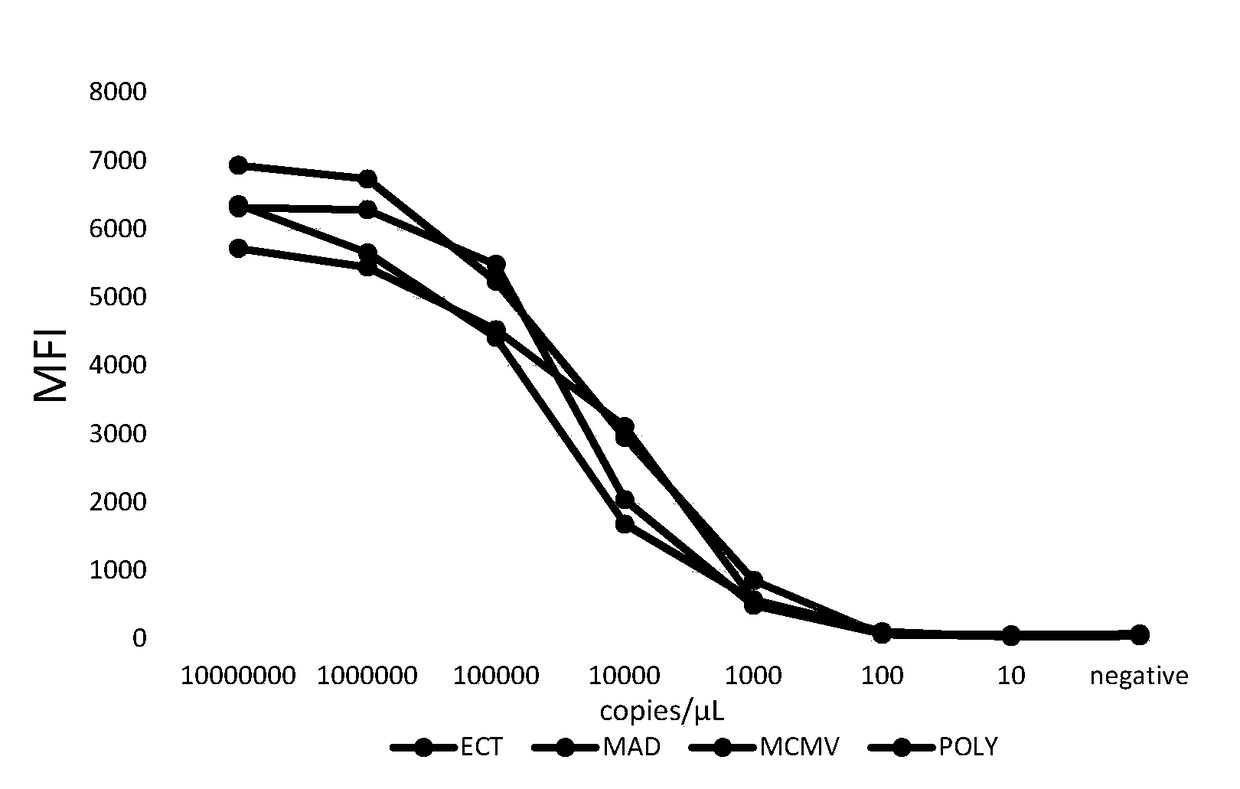
[0085] The prepared plasmid was quantified, diluted by 10-fold dilution method to 10 copies / μL, and detected by the multiple fluorescent gene detection method established above. The sensitivity test results of multiple fluorescent gene detection of ECT, MAD, MCMV and POLY are as follows: image 3 As shown, the experimental results show that the sensitivity of ECT, MAD, MCMV, and POLY is high, and the detection limit is 1000copies / μL.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com