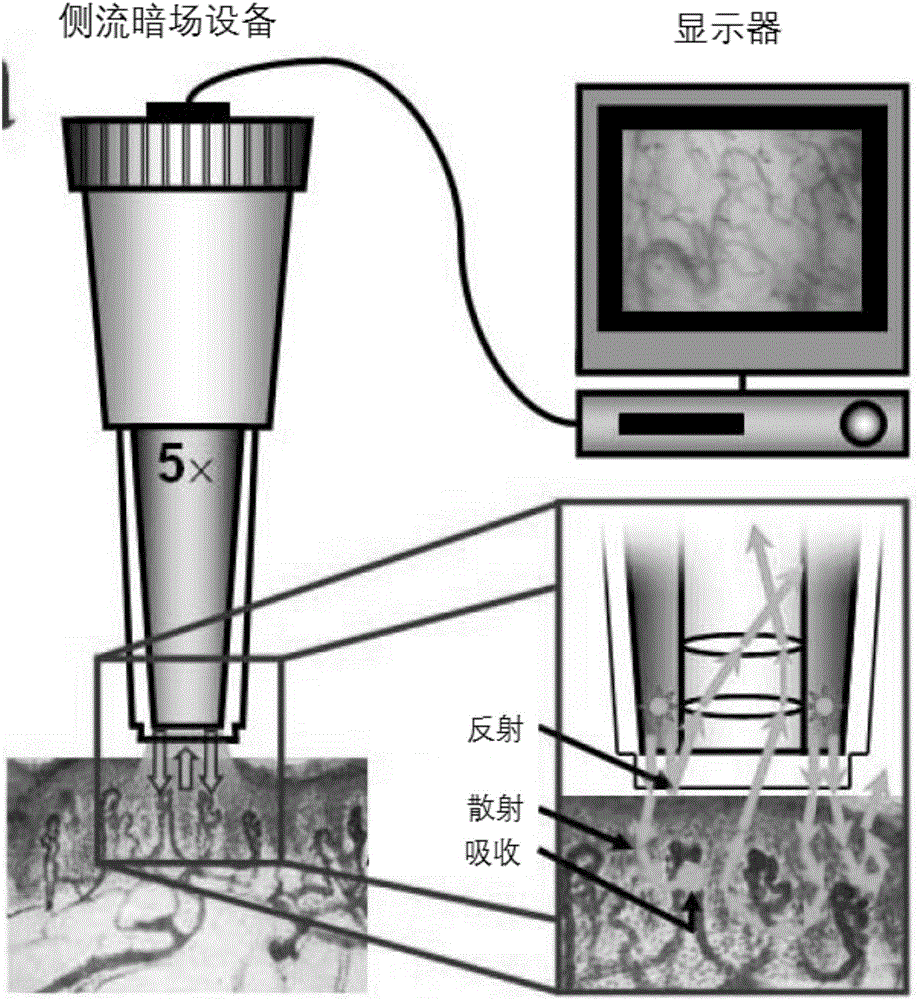
Three-dimensional imaging device for detecting human body microvascular ultramicrostructure
An ultrastructure and three-dimensional imaging technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems that two-dimensional imaging cannot meet the requirements, and two-dimensional imaging cannot obtain depth information, etc., and achieve the effect of improving clarity, simple and compact structure, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
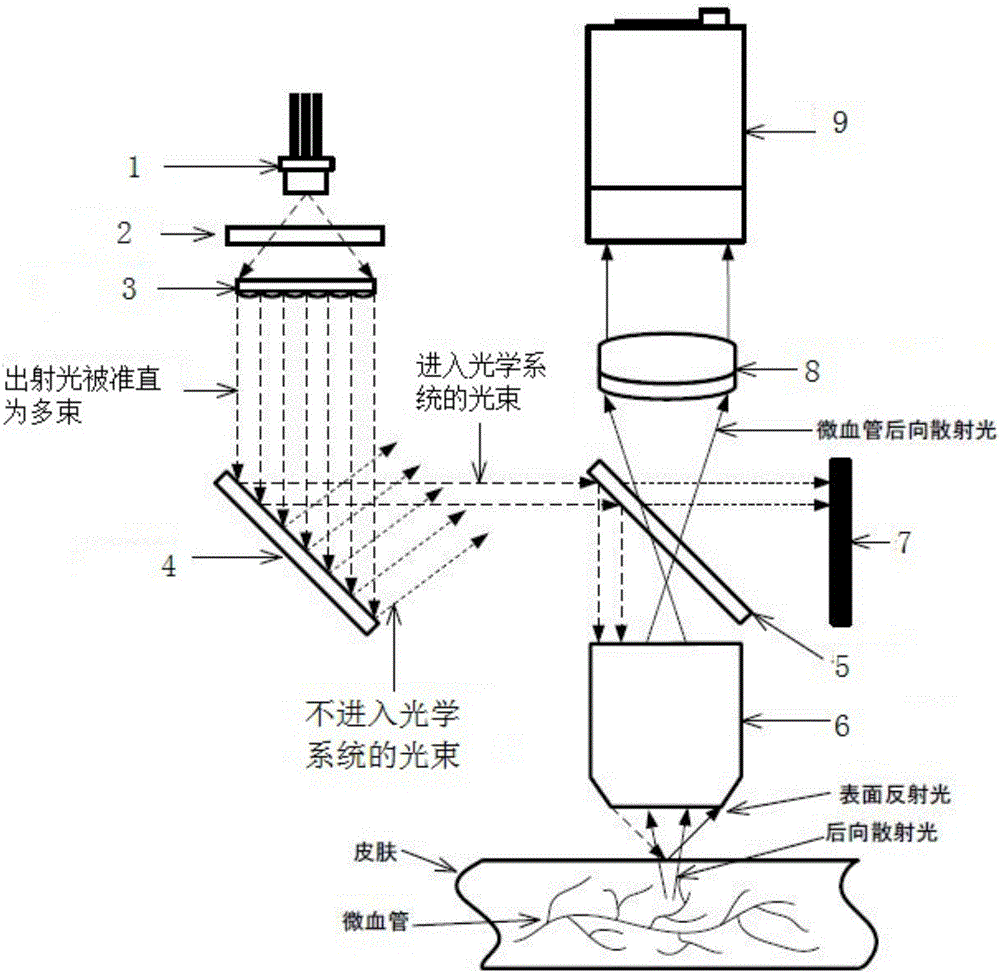
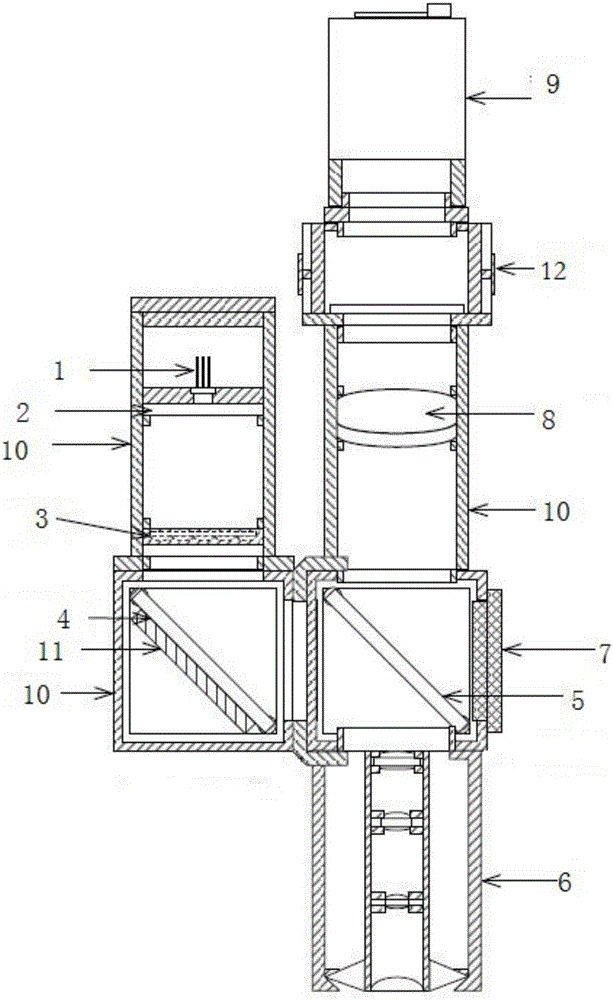
[0051] Such as Figure 2-3A three-dimensional imaging device for detecting the ultrastructure of human microvessels shown at least includes: a light source module for emitting multiple beams of collimated and parallel outgoing light; a light adjustment unit 2 for adjusting the outgoing light to circularly polarized light; The array reflective unit 4 for sequentially irradiating multiple beams of outgoing light into the dark field objective lens 6; the spectroscopic unit 5 for partially reflecting the light and partially transmitting it; Dark field objective lens 6; imaging unit 8 for imaging; imaging module 9 for presenting images.
[0052] Further, the imaging unit is used to focus light into the lens unit and receive the imaging light of the lens unit to make it clearly imaged on the imaging unit. The positions of the convex lenses can be interchanged, for example, a concave-convex lens and a biconvex lens are arranged in sequence along the direction of light source irradia...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Different from Example 1, as Figure 4-5 As shown, the dimming unit is arranged between the array transmission unit and the array reflection unit, that is, the outgoing light of the light source is collimated and divided into multiple beams, and then the beam is modulated into circularly polarized light. All the other are with embodiment 1.
[0073] In the method of using the three-dimensional imaging device to detect the microcirculation of the human body, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the outgoing light of the light source is collimated and divided into multiple beams, and then the beam is modulated into circularly polarized light before entering the optical system. All the other are with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0075] Different from Example 1, as Figure 6-7 As shown, the dimming unit is arranged between the array reflection unit and the spectroscopic unit, that is, the adjusted light beam that needs to enter the optical system is modulated into circularly polarized light before entering the optical system. All the other are with embodiment 1.
[0076] In the method of using the three-dimensional imaging device to detect the microcirculation of the human body, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the adjusted light beam that needs to enter the optical system is modulated into circularly polarized light before entering the optical system. All the other are with embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com