Preparation method of polyacrylonitrile based heat stabilized fiber
A polyacrylonitrile-based heat and heat stabilization technology, which is applied in the fields of fiber chemical characteristics, chemical post-treatment of synthetic polymer artificial filaments, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient polycondensation reaction and affecting the performance of carbon fibers, etc. Achieve the effects of reducing structural defects, improving compactness, and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
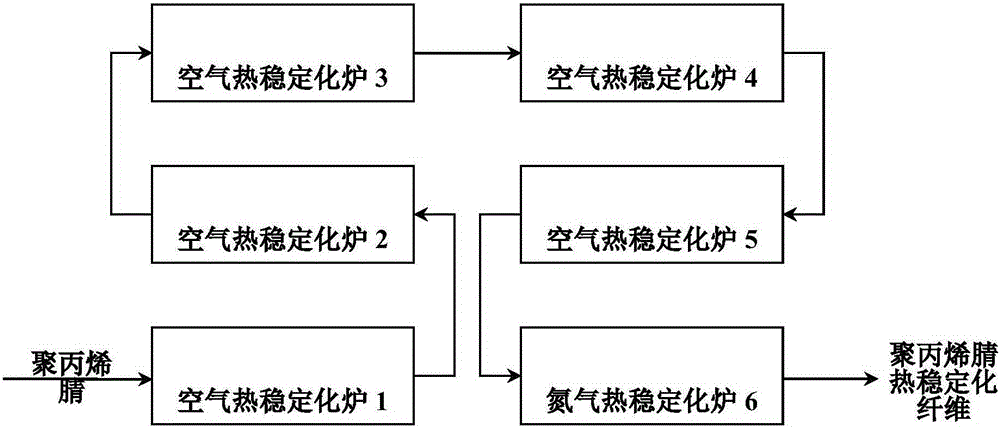
[0014] First, the polyacrylonitrile precursors are sequentially heat-treated in three air thermal stabilization furnaces at 230°C, 250°C, and 270°C. The constant temperature zone of each air heat stabilization furnace is the same length, and the total heat treatment time is 60min. The total draft of the five air heat stabilization furnaces is 6%. Then, the obtained fiber is heat-treated in a nitrogen stabilization furnace at a temperature of 270° C., the stabilization furnace time is 12 minutes, and the draft is -2% to obtain a polyacrylonitrile thermally stabilized fiber.
[0015] The obtained thermally stabilized fiber is subjected to low-temperature carbonization and high-temperature carbonization treatments. The low temperature carbonization temperature is 350-700°C, the heat treatment time is 3 minutes, and the draft is 3%; the high temperature carbonization temperature is 1350°C, the heat treatment time is 3 minutes, and the draft is -3.5%. The results of the mechanical p...
Embodiment 2
[0017] First, the polyacrylonitrile precursors are sequentially heat-treated in five air thermal stabilization furnaces at 190°C, 218°C, 240°C, 260°C, and 270°C. The constant temperature zone of each air heat stabilization furnace is the same length, and the total heat treatment time is 60min. The total draft of the five air heat stabilization furnaces is 6%. Then, the obtained fiber is heat-treated in a nitrogen stabilization furnace at a temperature of 270° C., the stabilization furnace time is 12 minutes, and the draft is -2% to obtain a polyacrylonitrile thermally stabilized fiber.
[0018] The obtained thermally stabilized fiber is subjected to low-temperature carbonization and high-temperature carbonization treatments. The low temperature carbonization temperature is 350-700°C, the heat treatment time is 3 minutes, and the draft is 3%; the high temperature carbonization temperature is 1350°C, the heat treatment time is 3 minutes, and the draft is -3.5%. The results of the...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Firstly, the polyacrylonitrile precursor is heat-treated in five air thermal stabilization furnaces in sequence at 200°C, 215°C, 230°C, 255°C, and 265°C. The constant temperature zone of each air heat stabilization furnace is the same length, and the total heat treatment time is 60min. The total draft of the five air heat stabilization furnaces is 6%. Then, the obtained fiber is heat-treated in a nitrogen stabilization furnace at a temperature of 265° C., the stabilization furnace time is 12 minutes, and the draft is -2% to obtain a polyacrylonitrile thermally stabilized fiber.
[0021] The obtained thermally stabilized fiber is subjected to low-temperature carbonization and high-temperature carbonization treatments. The low temperature carbonization temperature is 350-700°C, the heat treatment time is 3 minutes, and the draft is 3%; the high temperature carbonization temperature is 1350°C, the heat treatment time is 3 minutes, and the draft is -3.5%. The results of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com