Testing method for coaxiality of flanges at two ends of pipeline valve
A detection method and coaxiality technology, applied in the detection field, can solve problems such as damage to the three-coordinate measuring machine platform, inability to guarantee coaxiality detection, unfavorable mass detection, etc., achieve good practicability and economy, and reduce labor Strength, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] In the following description, for purposes of explanation, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of one or more embodiments. It may be evident, however, that these embodiments may be practiced without these specific details.
[0017] Various embodiments according to the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
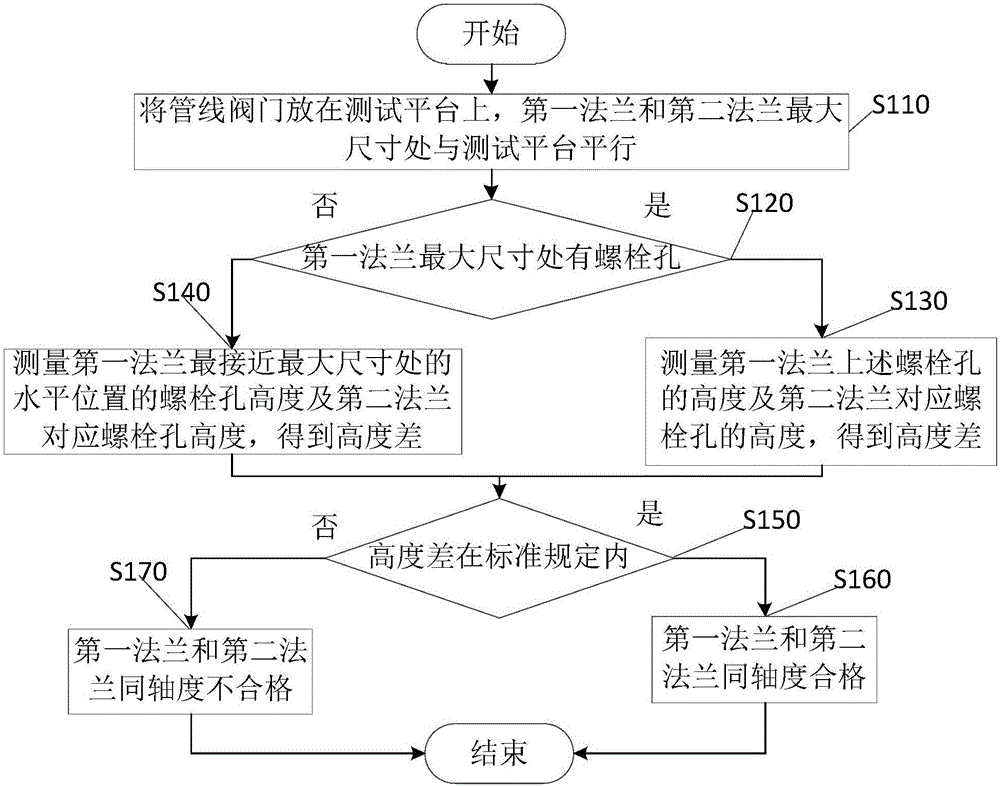
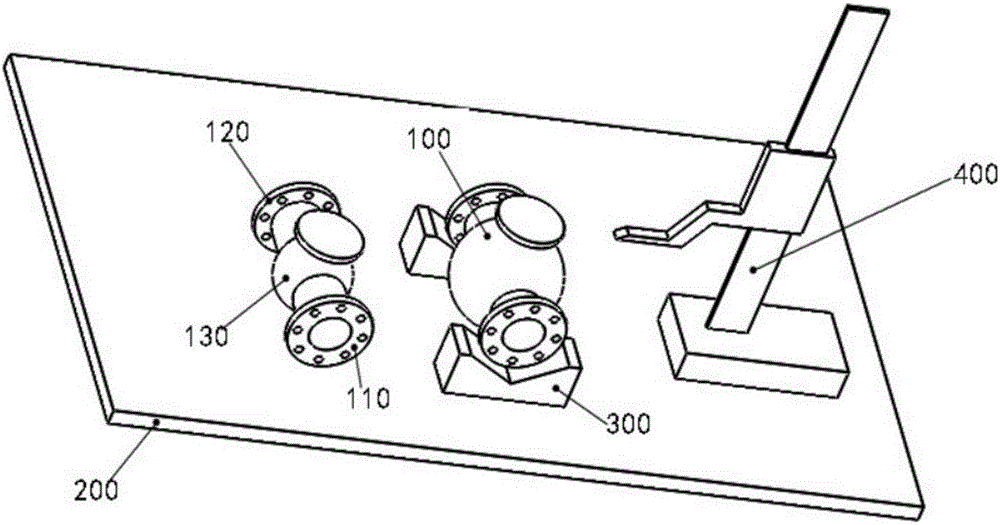
[0018] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the method for detecting the coaxiality of flanges at both ends of the pipeline valve of the present invention, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the method for detecting the coaxiality of flanges at both ends of the pipeline valve of the present invention, as figure 1 with 2 As shown, the method for detecting the coaxiality of flanges at both ends of the pipeline valve includes:
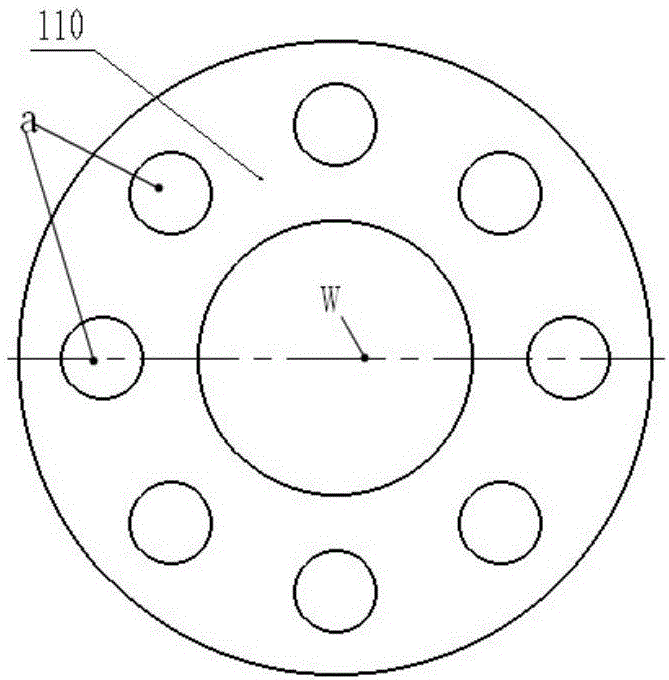
[0019] In step S110, the two ends of the pipeline valve 100 are symmetrically provided with a first flange 110 and a second flange 120,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com