Prediction method for bat moth hatching rate
A technology of egg hatching rate and prediction method, applied in animal husbandry and other directions, can solve the problems of wasted space, wasted feed, different density, etc., and achieve the effect of saving breeding space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method for predicting the hatchability of bat moth eggs, comprising the steps of:
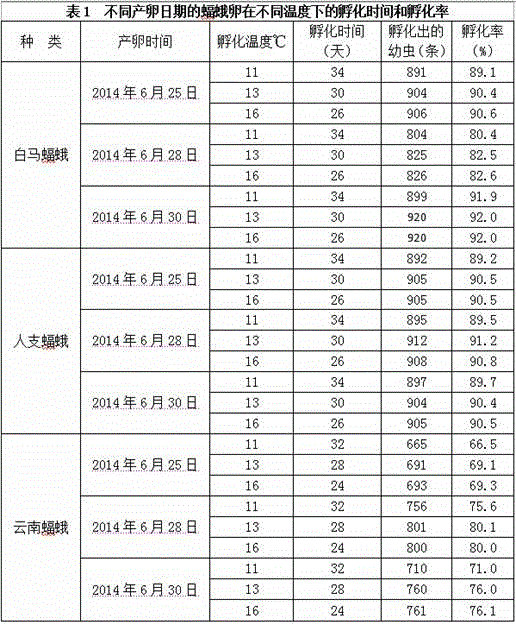
[0032] In step (1), the eggs of a certain oviposition date of the manta moth to be determined are washed with clean water, dried, and 200 eggs are sampled;
[0033] Step (2), select multiple petri dishes of the same size, the diameter of the petri dish is 8cm, spread filter paper on the bottom of the petri dish, and pour 500ml of cold boiled water into each petri dish;
[0034] Step (3), put the eggs sampled in step (1) into a petri dish for incubation, the incubation temperature is 11°C; after sampling, put the remaining eggs into other petri dishes at the same density for incubation, the hatching temperature is higher than that obtained by sampling The hatching temperature of the eggs is 2°C lower; if the hatching temperature is lower than the ambient temperature, it needs to be hatched in a refrigerated artificial climate box or a cold room.
[0035] Step (4), during the hatching p...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for predicting the hatchability of bat moth eggs, comprising the steps of:
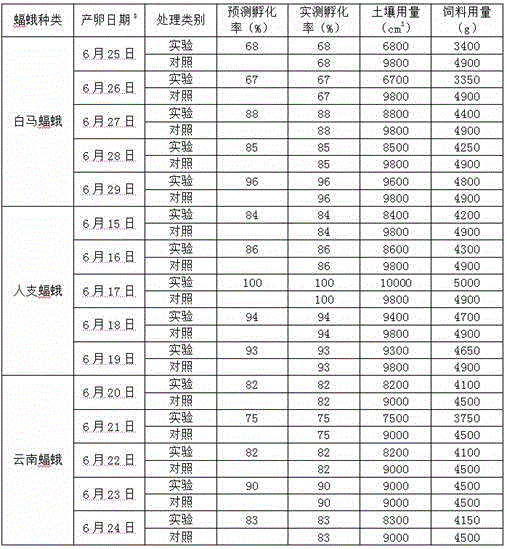
[0042] In step (1), the eggs of the bat moth to be determined on multiple oviposition dates are washed with water and dried, and 50-1000 eggs are sampled on each date;
[0043] Step (2), select multiple petri dishes of the same size, the diameter of the petri dish is 5cm, spread filter paper on the bottom of the petri dish, and pour 100ml of cold boiled water into each petri dish;
[0044] In step (3), the eggs sampled in step (1) were placed in different petri dishes for incubation according to the spawning date, and the eggs with the same spawning date were placed in the same petri dish for incubation, and the incubation temperature was 16°C; after sampling The remaining eggs are divided into dishes according to the same density according to the spawning date, and put into other petri dishes for incubation. The incubation temperature is 3°C lower than that of the eggs obtained by sam...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for predicting the hatchability of bat moth eggs, comprising the steps of:
[0052] In step (1), the eggs of multiple oviposition dates of the yunnanensis moth and the white horse moth to be determined are washed with clean water and dried, and 1000 eggs of each species are sampled for each date;
[0053] Step (2), select multiple petri dishes of the same size, the diameter of the petri dish is 10cm, spread filter paper on the bottom of the petri dish, and pour 1000ml of cold boiled water into each petri dish;
[0054] In step (3), the eggs sampled in step (1) are divided into plates according to the type and spawning date for incubation. Eggs of the same type and the same spawning date are placed in the same petri dish for incubation, and the incubation temperature is 17°C; after sampling, the remaining According to the same density, the eggs were divided into different dishes according to the type and date of spawning, and placed in other petri dishes for inc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com