Optical fiber cutting device and method based on ultra-short pulse lasers
An ultra-short pulse laser and cutting device technology, which is applied in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of secondary damage to the optical fiber end face, inability to cut the optical fiber obliquely, and difficulty in obtaining the optical fiber end face, etc. The effect of deformation, simple device structure and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The present embodiment takes cutting quartz SMF-28 optical fiber as example, specifically as follows:
[0039] Original material: Silica fiber SMF-28;
[0040] Ultrashort pulse laser: 50fs, 800nm, 1000Hz;
[0041] The detailed description of SMF-28 fiber vertical cutting is as follows:
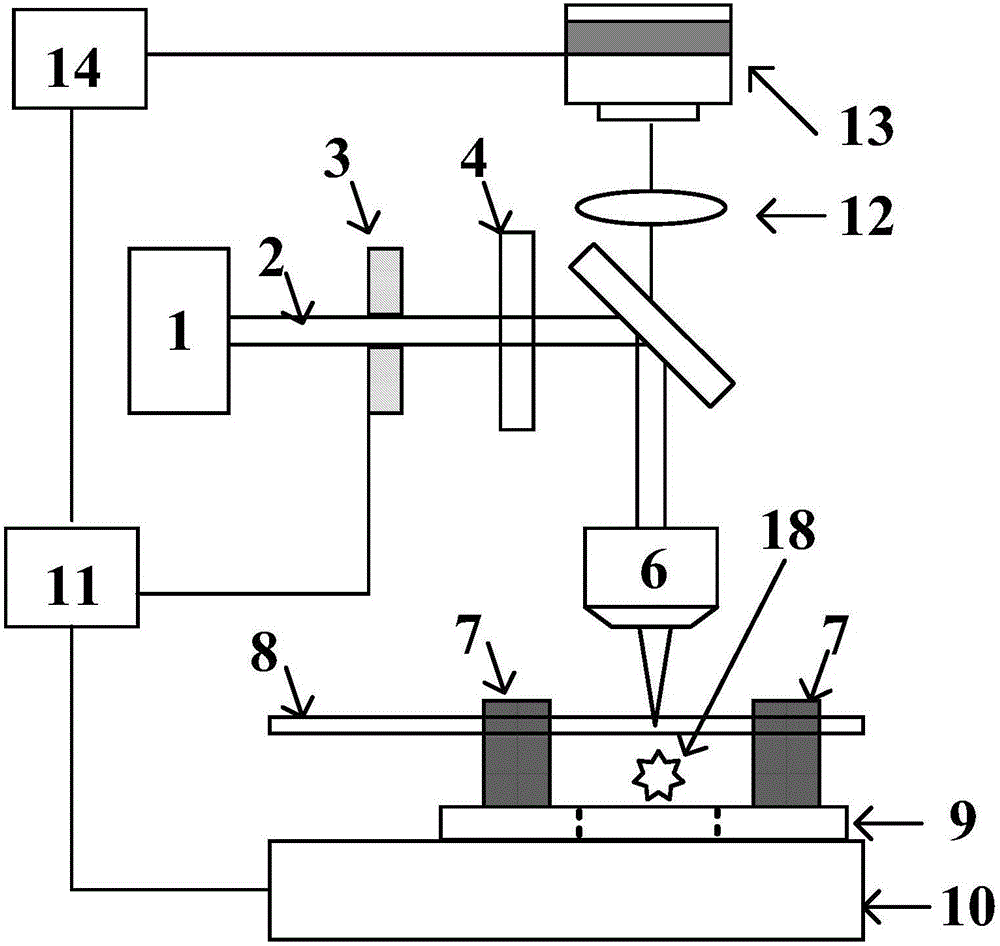
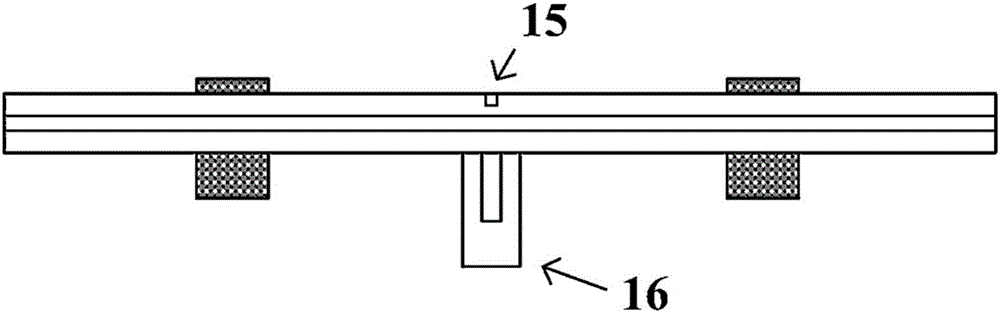
[0042] (1) Fix the optical fiber 8 on the electric translation platform 10, and fix it with a V-shaped optical fiber magnetic clamp 7;
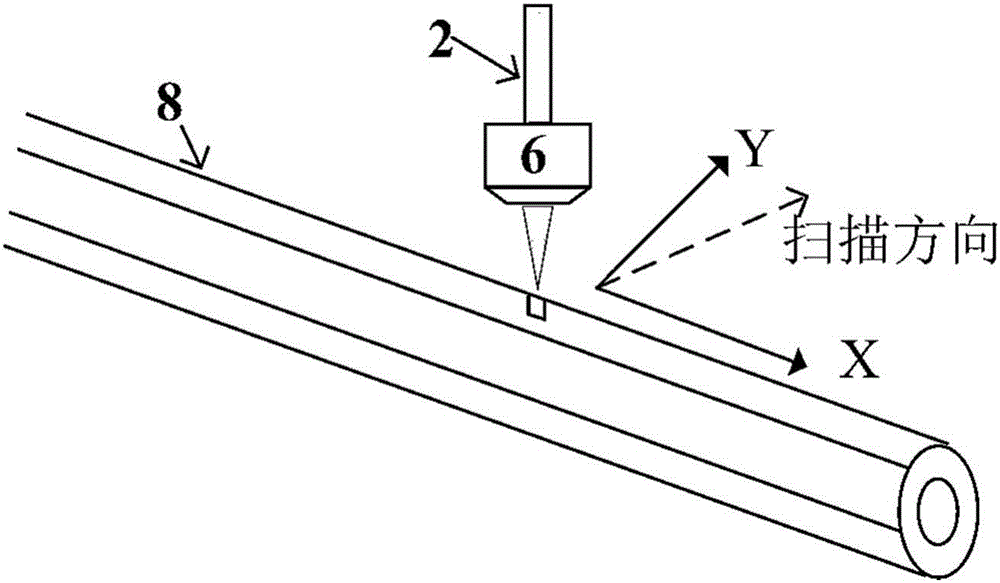
[0043] (2) Select a microscopic objective lens 6 with 20× and a numerical aperture of 0.45, and under the auxiliary observation of the imaging lens 12 and the CCD detector 13, move the starting point of the optical fiber groove position to the focus position of the femtosecond laser 2 through the microscopic objective lens 6 At , adjust the three-dimensional electric translation stage 10 so that the top end of the optical fiber 8 is clearly imaged in the imaging system, and the coordinate of this position on the laser transmission axis Z-axis is defi...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Original material: solid core photonic crystal fiber;
[0049] Ultrashort pulse laser: 50fs, 800nm, 1000Hz;
[0050] (1) For the fixing of the optical fiber, refer to the corresponding process of Embodiment 1.
[0051] (2) For the relative position adjustment method of the optical fiber 8 and the focus point of the laser 2 , refer to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
[0052] (3) Use the three-dimensional electric translation stage 10 to set the optical fiber 8 at a Z-axis position of 20 μm, and align the laser light to the starting point of the position to be grooved according to the scanning movement platform. The laser power was set at 2 mW, and the scanning speed was set at 100 μm / s. Open the optical shutter 3 to focus the femtosecond laser 2 on the optical fiber through the microscope objective lens. At the same time, the program controls the three-dimensional electric translation stage to drive the optical fiber to move along the axial direction...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Original material: hollow-core photonic crystal fiber;
[0057] Ultrashort pulse laser: 50fs, 800nm, 1000Hz;
[0058] (1) Fixing of the optical fiber 8 refers to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
[0059] (2) For the relative position adjustment method of the optical fiber 8 and the focus point of the laser 2 , refer to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
[0060] (3) Use the three-dimensional electric translation stage 10 to set the position of the optical fiber at the Z-axis to 20 μm, and align the laser with the starting point of the position to be grooved according to the scanning movement platform. The laser power was set to 1.5 mW, and the scanning speed was set to 100 μm / s. Open the optical shutter 3 to focus the femtosecond laser 2 on the optical fiber 8 through the microscopic objective lens 6. At the same time, the three-dimensional electric translation stage 10 is controlled by the program to drive the optical fiber 8 to move...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com