Regional power grid T line fault range-finding system based on generalized measurement
A technology of fault distance measurement and regional power grid, which is applied in radio wave measurement system, fault detection according to conductor type, satellite radio beacon positioning system, etc. It can solve the problem that current and voltage sensors are easily affected by saturation and the difficulty of installing current transformers , unable to achieve precise positioning and other problems, to achieve the effect of convenient daily maintenance, high reliability and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
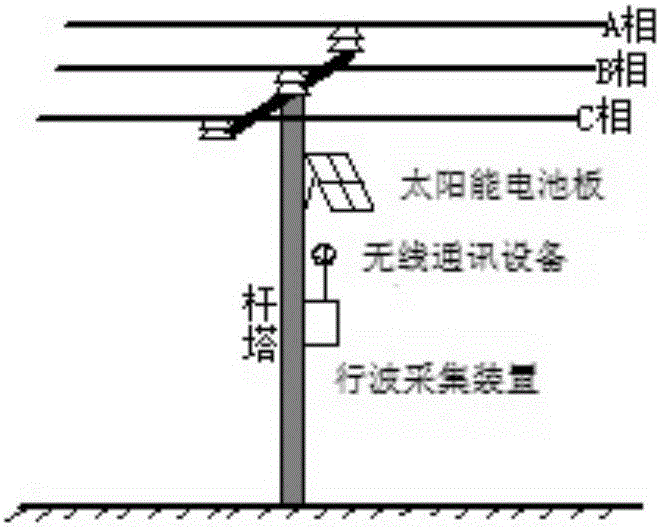
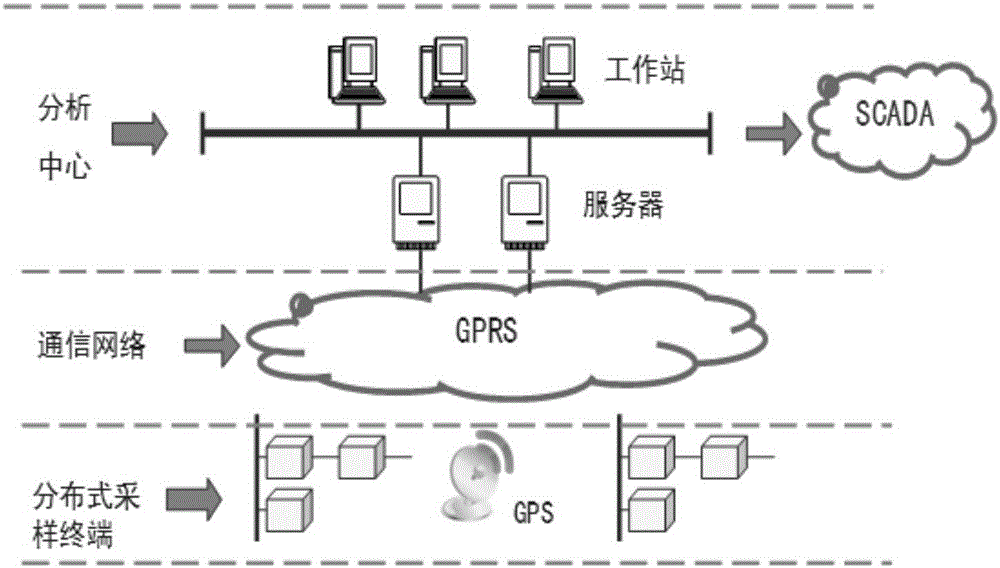
[0032] Traveling wave acquisition and ranging principle
[0033] Traveling wave ranging theory
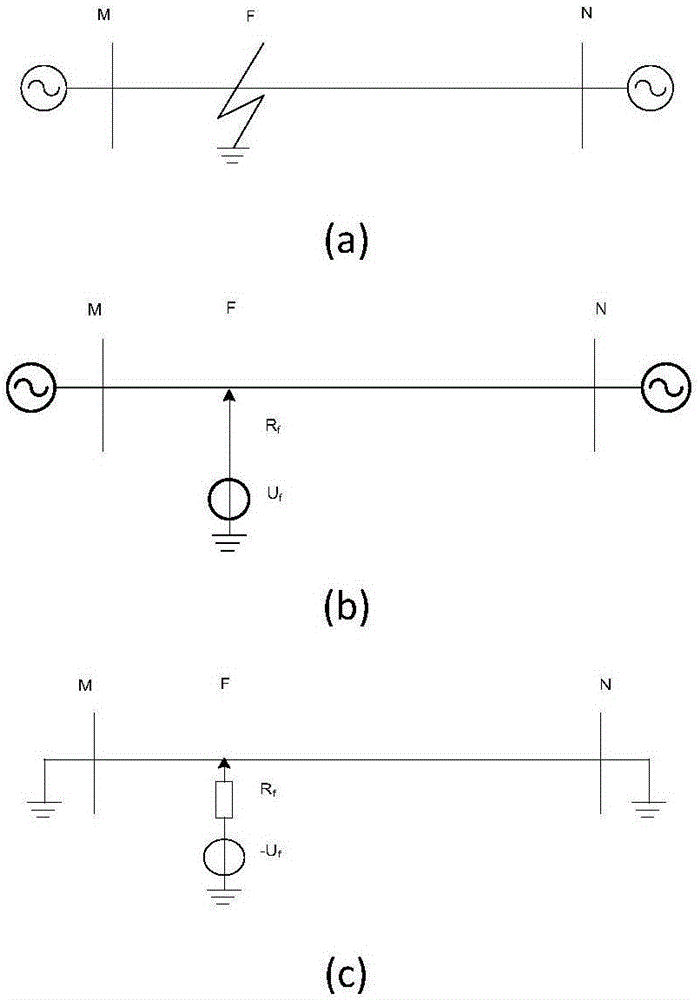
[0034] When a fault occurs on a transmission line, the superposition principle can be used to figure 1 As shown in (a), it can be equivalently divided into non-fault state figure 1 (b) Shown and fault attached state figure 1 (c) shown.
[0035] figure 1 (b) The non-fault state refers to the normal operation state before the fault, and the equivalent voltage source U f The value is the normal voltage when there is no fault at the fault point; the additional state of the fault occurs after the fault, and is equal to the value of the voltage in the non-fault state, and the direction is opposite, and its additional equivalent voltage source is -U f . Fault-attached states are independent of non-faulted states, but are affected by how the system operates. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com