Control system for suppressing torque ripples of brushless direct current motor and torque ripple suppression method for control system
A brushed DC motor and motor controller technology, applied in torque ripple control, control system, electronic commutation motor control, etc. The effect of speed of response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
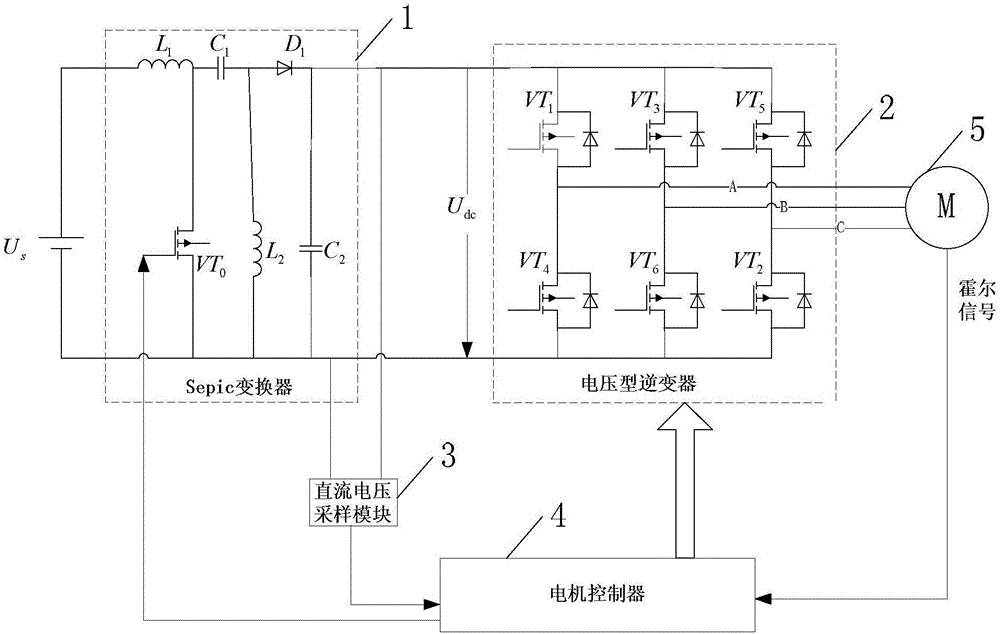
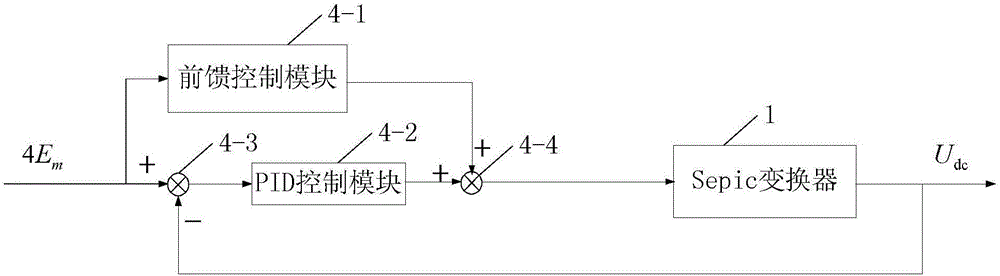
[0050] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, a brushless DC motor torque ripple suppression control system described in this embodiment includes a DC power supply U s , Sepic converter 1, voltage type inverter 2, DC voltage sampling module 3 and motor controller 4;
[0051] DC power supply U s The anode of the positive pole is connected to the positive pole input terminal of the Sepic converter 1, and the DC power supply U s The negative pole of is connected to the negative pole input terminal of Sepic converter 1;
[0052] The output end of the Sepic converter 1 is connected to the input end of the voltage type inverter 2, and the output end of the voltage type inverter 2 is connected to the three-phase winding of the controlled brushless DC motor 5;
[0053] The DC voltage sampling module 3 is used to collect the DC voltage output by the Sepic converter 1, and sends the collected DC voltage signal to the motor controller 4;
[0054] Col...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0056] Specific implementation mode two: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the brushless DC motor torque ripple suppression control system described in the first embodiment is that the Sepic converter 1 includes an inductor L 1 , inductance L 2 , capacitance C 1 , capacitance C 2 , Diode D 1 and MOSFET tube VT 0 ;
[0057] Inductance L 1 One end of the DC power supply U s the positive connection of the
[0058] Inductance L 1 The other end of the capacitor C 1 One end and the MOSFET tube VT 0 the source connection,
[0059] Capacitance C 1 The other end of the inductor L is simultaneously 2 one end of the diode D 1 the anode connection,
[0060] Diode D 1 The cathode and capacitance C 2 One end of the diode D is connected 1 The negative electrode of is used as an output end of Sepic converter 1;
[0061] DC power supply U s The negative pole of the MOSFET tube VT at the same time 0 The drain, inductance L 2 ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0062] Specific implementation mode three: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the brushless DC motor torque ripple suppression control system described in Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the voltage-type inverter 2 is a three-phase voltage-type bridge Inverter, three-phase voltage type bridge inverter including 6 switching tubes VT 1 to VT 6 , and 6 switching tubes VT 1 to VT 6 Both are MOSFET tubes,
[0063] Among them, the upper bridge arm of the three-phase voltage type bridge inverter is the switching tube VT 1 , VT 3 , VT 5 , the lower bridge arm is the switching tube VT 4 , VT 6 , VT 2 ;
[0064] A diode is connected in antiparallel between the drain and source of each MOSFET,
[0065] Switch tube VT 1 to VT 6 The gates of each are used to receive the control signal output by the motor controller 4.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com