Preparation method of super-strong washable polyester fabric moisture absorption and sweat releasing finishing agent
A moisture-wicking, polyester fabric technology, applied in the field of preparation of moisture-wicking finishing agents, can solve the problems of poor washability, to overcome poor washability, antistatic and decontamination, good hydrophilicity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
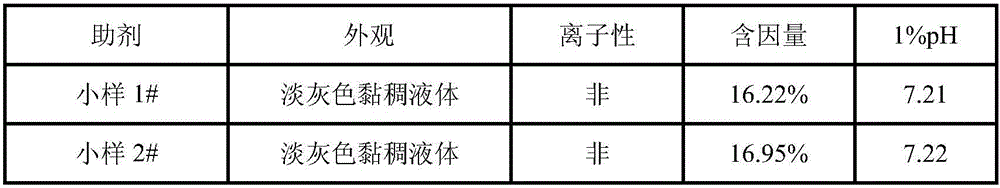
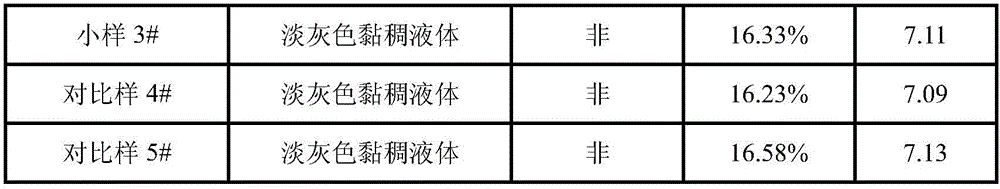
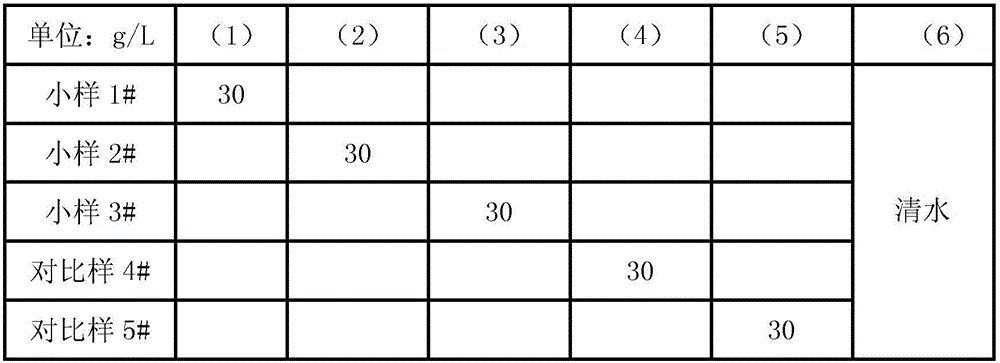
[0018] The polyethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol were subjected to dehydration reaction respectively, and the temperature was controlled at 100-105° C. for vacuum dehydration for 1 hour. After the dehydration is completed, weigh 150g of polyethylene glycol, 42g of ethylene glycol, 0.06g of antimony trioxide and 0.15g of calcium acetate in a reaction vessel equipped with a thermometer and a nitrogen tube, stir for 10min, and add 56g of terephthalic acid di For methyl ester, the temperature was raised slowly under the protection of nitrogen. When the temperature rose to 160°C, the temperature was controlled at 160-170°C for 1 hour.
[0019] After the transesterification is completed, continue to heat up to 180°C, control the temperature at 180-190°C for 30 minutes, then raise the temperature to 200°C, control the temperature at 200-210°C for 30 minutes, continue to heat up to 220°C, add 45g of polypropylene glycol and 135g of polyethylene Diol, heat up to 260°C, control t...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The polyethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol were subjected to dehydration reaction respectively, and the temperature was controlled at 100-105° C. for vacuum dehydration for 1 hour. After the dehydration is completed, weigh 145g of polyethylene glycol, 50g of ethylene glycol, 0.08g of antimony trioxide and 0.17g of magnesium acetate in a reaction vessel equipped with a thermometer and a nitrogen tube, stir for 10min, and add 61g of terephthalic acid di For methyl ester, the temperature was raised slowly under the protection of nitrogen. When the temperature rose to 160°C, the temperature was controlled at 160-170°C for 1 hour.
[0023] After the transesterification is completed, continue to heat up to 180°C, control the temperature at 180-190°C for 30 minutes, then raise the temperature to 200°C, control the temperature at 200-210°C for 30 minutes, continue to heat up to 220°C, add 49g of polypropylene glycol and 136g of polyethylene Diol, heat up to 260°C, control...
Embodiment 3
[0026] The polyethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol were subjected to dehydration reaction respectively, and the temperature was controlled at 100-105° C. for vacuum dehydration for 1 hour. After the dehydration is completed, weigh 158g of polyethylene glycol, 45g of ethylene glycol, 0.06g of antimony trioxide and 0.2g of zinc acetate in a reaction vessel equipped with a thermometer and a nitrogen tube, stir for 10min, and add 65g of terephthalic acid di For methyl ester, the temperature was raised slowly under the protection of nitrogen. When the temperature rose to 160°C, the temperature was controlled at 160-170°C for 1 hour.
[0027] After transesterification, continue to heat up to 180°C, control the temperature at 180-190°C for 30 minutes, then raise the temperature to 200°C, control the temperature at 200-210°C for 30 minutes, continue to heat up to 220°C, add 43g of polypropylene glycol and 125g of polyethylene Diol, heat up to 260°C, control the temperature at 260...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com