Multi-level structure fabric for radome and its weaving method
A multi-level, radome technology, applied in the field of fabric weaving, can solve the problems of unfavorable resin matrix fiber infiltration, lower mechanical properties of composite materials, lower fiber strength utilization, etc., and achieve low cost, low porosity, and small yarn bending Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Multi-Layered Plain Weave Fabric
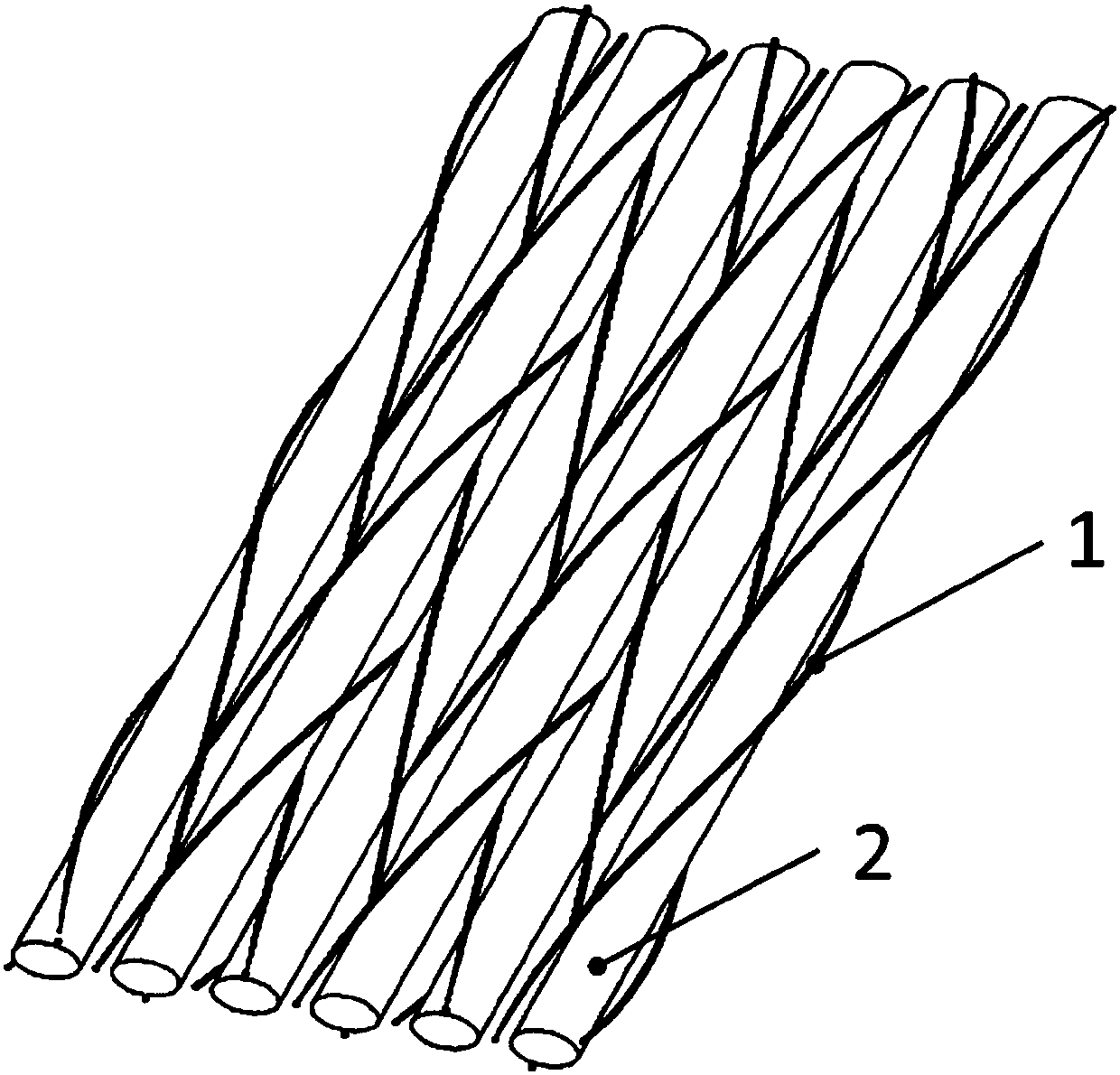
[0029] Multi-ply plain weave (see Figure 4 ) includes a warp sub-fabric 4 and a weft sub-fabric 5; the sub-fabric is a two-dimensional three-way weaving structure formed by axial yarns 2 parallel and straightly arranged and bound by weaving yarns 1.
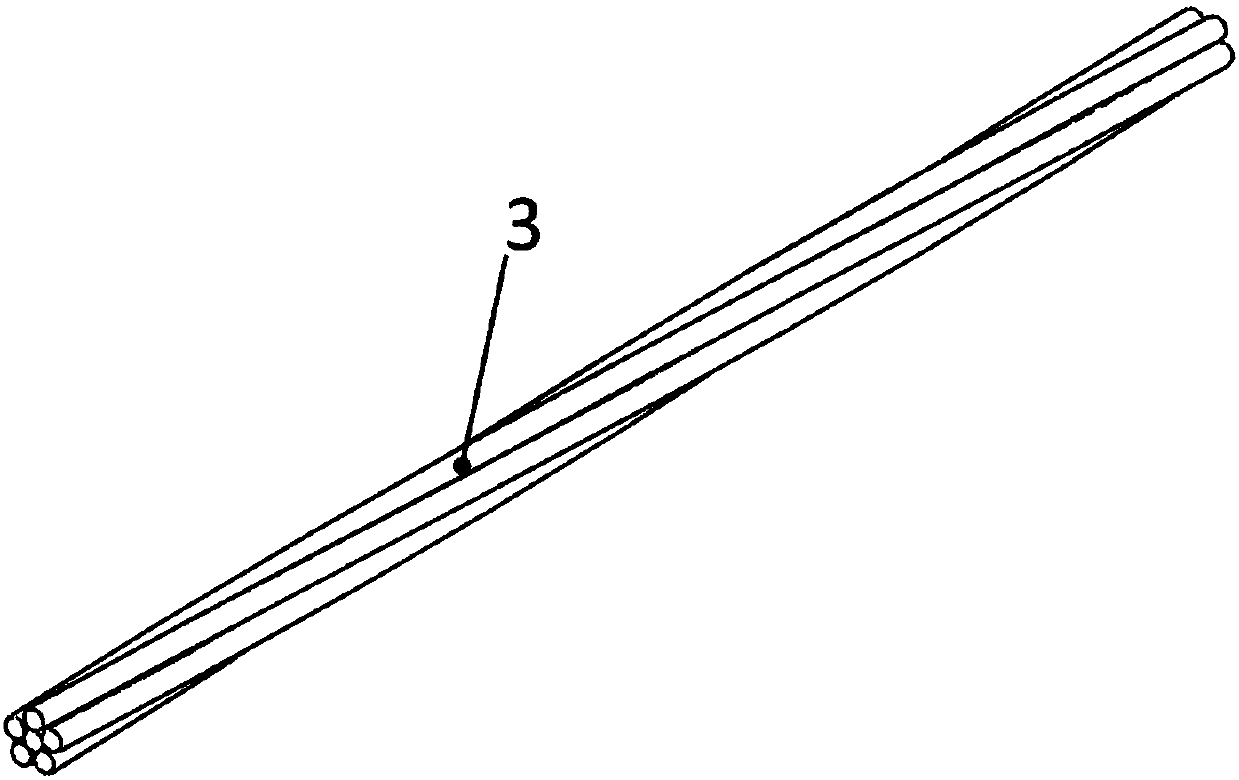
[0030] (1) Selection of yarns: 27Tex quartz yarn is selected for braiding yarn 1, and 190Tex quartz yarn is selected for axial yarn 2. The fineness of the axial yarn 2 is 7.04 times that of the weaving yarn 1;
[0031] (2) Weaving of the sub-fabric: both the warp sub-fabric 4 and the weft sub-fabric 5 select 13 weaving yarns 1 and 6 axial yarns 2, and adopt a two-dimensional three-way belt weaving process. Line 1 bundles parallel and straight axial yarns 2 to form a sub-fabric, the width of the sub-fabric is 4.0 mm, and the thickness is 0.3 mm;
[0032] (3) Weaving of the fabric: the warp density is 22 threads / 10cm, the weft density is 22 threads / 10cm, and the warp sub-fabr...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Multi-level layered fabric
[0035] Multilayer laminated fabric (see Figure 5 ) includes a warp sub-fabric 4 and a weft sub-fabric 5; the sub-fabric is a two-dimensional three-way weaving structure formed by axial yarns 2 parallel and straightly arranged and bound by weaving yarns 1.
[0036] (1) Selection of yarn: 27Tex quartz yarn is selected for weaving yarn 1, and 190Tex quartz yarn is selected for axial yarn 2. The fineness of the axial yarn 2 is 7.04 times that of the weaving yarn 1;
[0037] (2) Weaving of the sub-fabric: the warp direction sub-fabric 4 selects 13 weaving yarns 1 and 6 axial yarns 2, and adopts a two-dimensional three-way belt weaving process to weave into a flat strip-shaped sub-fabric. 4.0mm and a thickness of 0.3mm; the weft sub-fabric 5 selects 25 weaving yarns and 12 axial yarns, and adopts a two-dimensional three-way belt weaving process to weave a flat strip-shaped sub-fabric with a width of 8.1mm, thickness 0.3mm;
[0038]...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Multi-level Orthogonal Three-way Fabric
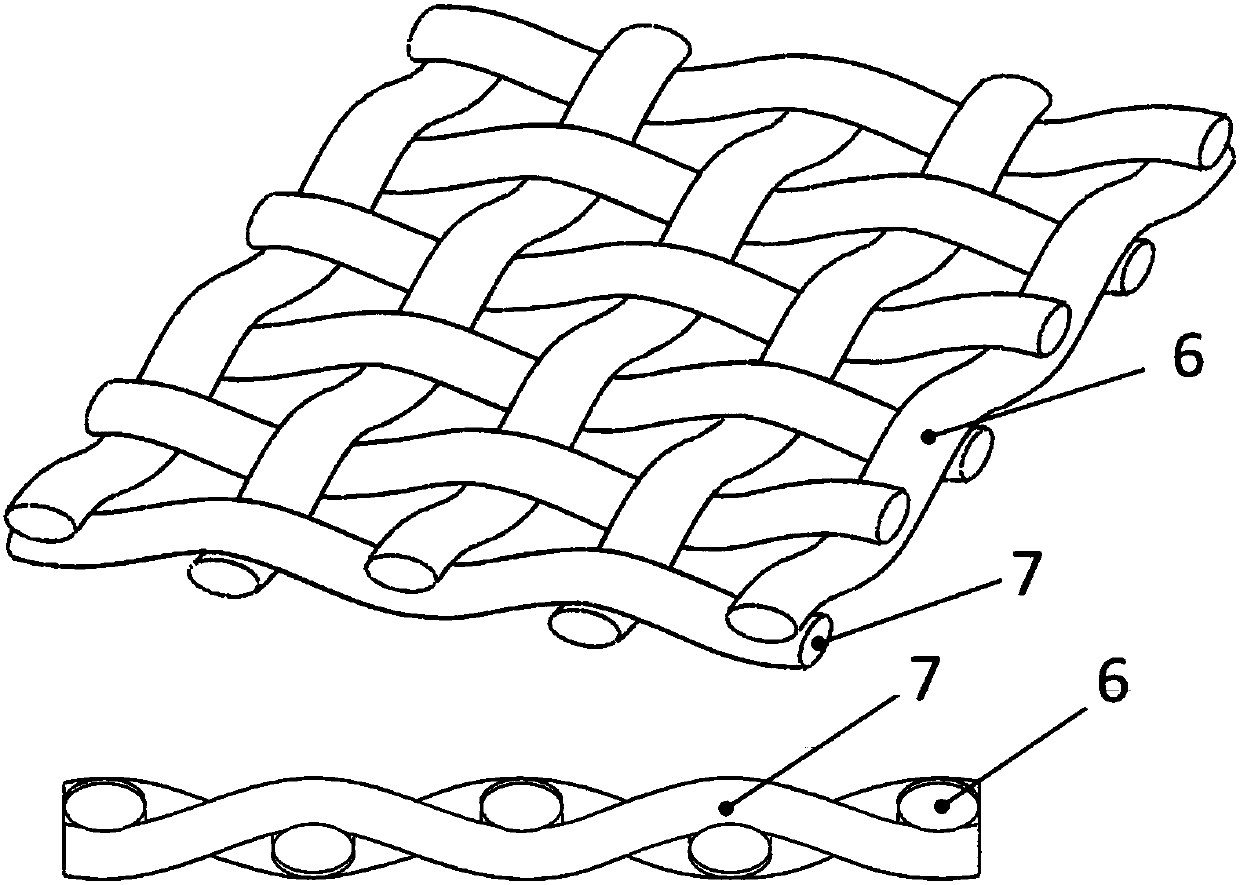
[0040] Multilayer Orthogonal Triaxial Fabric (see Image 6 ) includes a warp sub-fabric 4, a weft sub-fabric 5 and a normal yarn 8; the sub-fabric is a two-dimensional three-dimensional weaving structure formed by axial yarns 2 being parallel and straightly arranged and bound by a weaving yarn 1 .
[0041] (1) Selection of yarns: weaving yarn 1 selects 27Tex quartz yarn, axial yarn 2 selects 380Tex quartz yarn, and normal direction yarn 8 selects 190Tex quartz yarn. The fineness of the axial yarn 2 is 14.08 times that of the weaving yarn 1.
[0042] (2) Weaving of the sub-fabric: both the warp sub-fabric 4 and the weft sub-fabric 5 select 37 weaving yarns 1 and 18 axial yarns 2, and are woven by a two-dimensional three-way belt weaving process Flat strip-shaped sub-fabric, object width 13.5mm, thickness 0.5mm;
[0043] (3) Fabric weaving: the warp density is 7 threads / 10cm, and the weft density is 7 threads / 10cm. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com