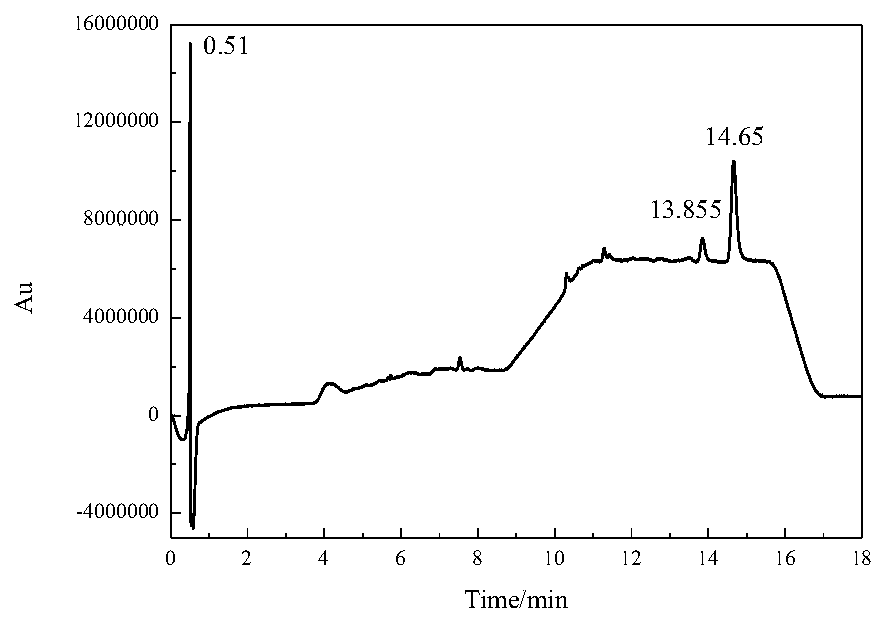
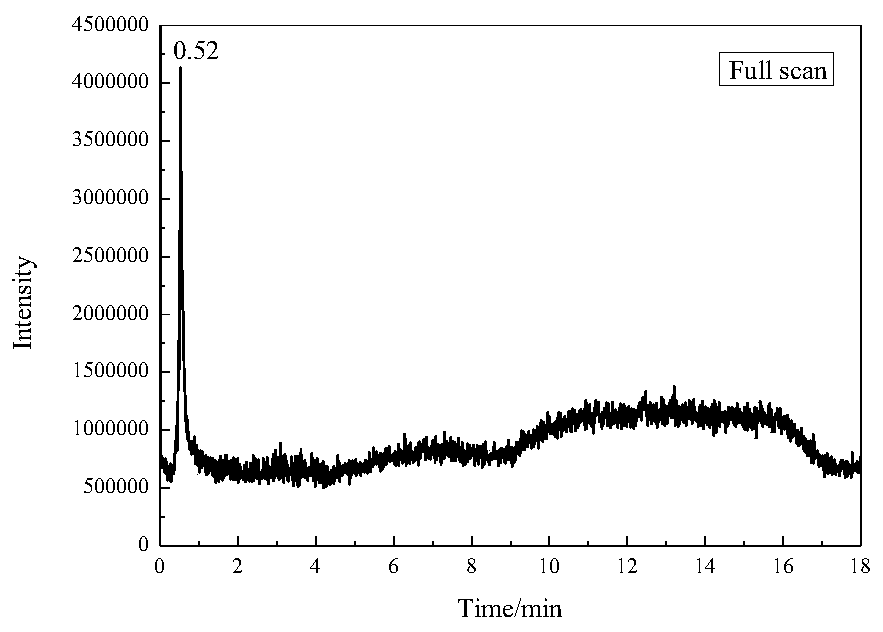
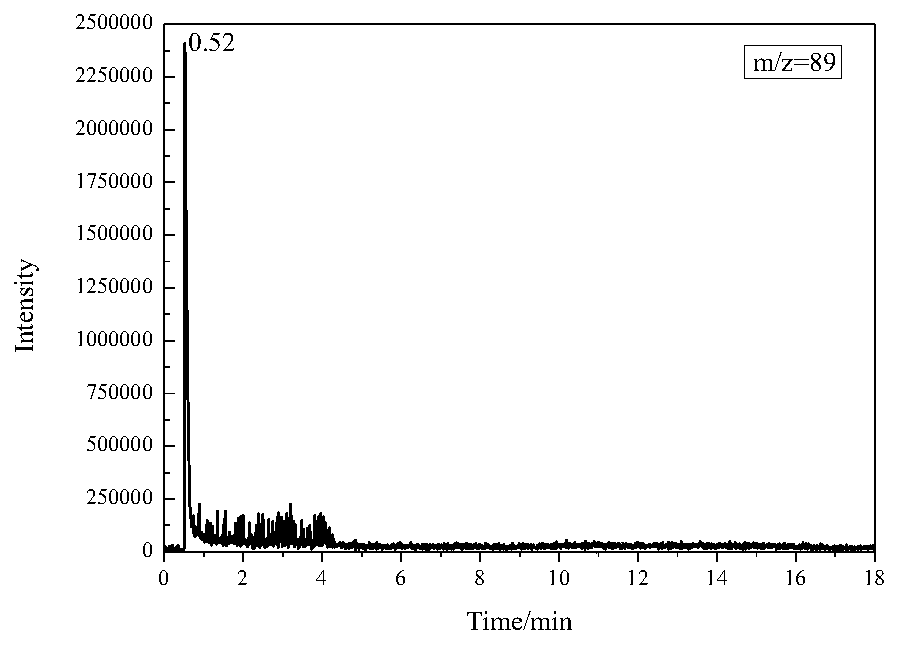
A method for identification of yellow rice wine residues in ancient wine-bodied porous ceramic materials
A technology of porous ceramics and identification methods, applied in the identification field of ancient yellow rice wine residues, can solve the problems of different absorption and residue levels of residues, affecting residue analysis, difficulty in knowing residues are absorbed, etc., and achieves extraction conditions that are easy to control , the complete and feasible effect of the method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] (1) Weigh 0.01 g of clay pot fragments and air-dry them at room temperature. Grind it into a powder with an agate mortar and add it to a round bottom flask;
[0050] (2) Next, add the prepared ethanol-water (volume ratio 15:85) solution into the round-bottomed flask, shake it to fully soak it. With a condenser, extract in an ultrasonic water bath at 85°C for 90 minutes;
[0051] (3) After the extraction, cool down to room temperature, and centrifuge the extract for 10-16 minutes. Take the supernatant and store it at 4-6°C;
[0052] (4) Inject the extract into an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer for detection.
Embodiment 2
[0054] (1) Weigh 0.01 g of clay pot fragments and air-dry them at room temperature. Grind it into a powder with an agate mortar and add it to a round bottom flask;
[0055] (2) Next, add the prepared ethanol-water (volume ratio 10:90) solution into the round-bottomed flask, shake it to make it fully saturated. With a condenser, extract in an ultrasonic water bath at 45°C for 90 minutes;
[0056] (3) After the extraction, cool down to room temperature, and centrifuge the extract for 10-16 minutes. Take the supernatant and store it at 4-6°C;
[0057] (4) The extract was detected by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Embodiment example 1
[0060] Liquid chromatography detection conditions: the mobile phase is KH2PO4-phosphate buffer solution with pH=2.85, the flow rate is 0.8mL / min, and the column temperature is 30°C;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com