A method for preparing an oxide nanotube array layer on the surface of a zirconium-based amorphous alloy
A zirconium-based amorphous alloy and nanotube array technology, applied in the field of oxide nanotube arrays, can solve problems such as increasing the complexity of the processing process, and achieve the effects of uniform diameter distribution, wide application range and uniform structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
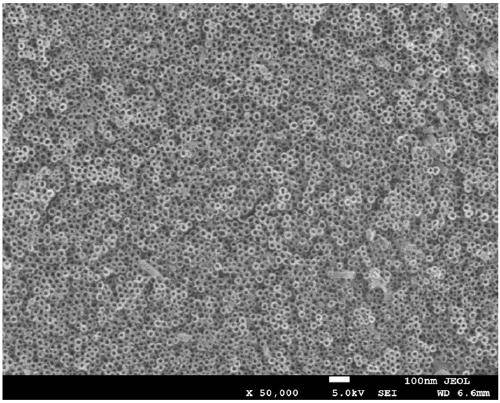
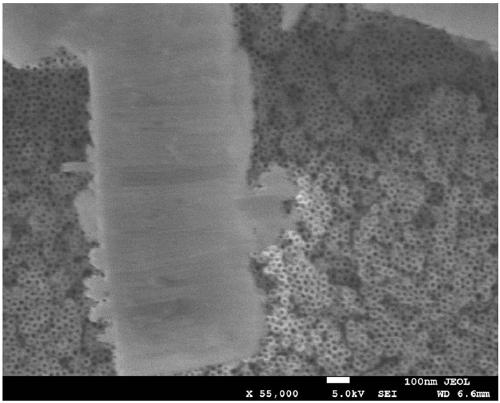
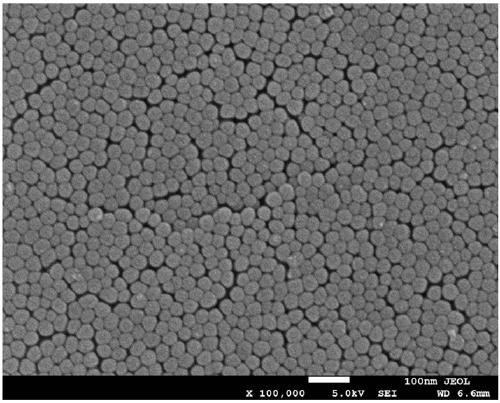
[0046] Embodiment 1: Utilize the anodic oxidation technology in Zr 56 Al 16 co 28 Fabrication of highly ordered nanotube arrays on the surface of bulk amorphous alloys
[0047] In this embodiment, the selected amorphous alloy composition is Zr 56 Al 16 co 28 , the preparation voltage is 20V. The diameter of the prepared nanotube is 15nm, and the thickness of the nanotube layer is 600nm. The preparation method of the nanotube array structure is as follows:
[0048] Step 1: Ingredients
[0049] Calculate the weight of each element related to it according to the required number of atoms. In the actual preparation process, convert the atomic amount of each element into mass weighing, which is a common knowledge in the field;
[0050] Step 2: Melting master alloy ingot
[0051] Put the raw materials weighed in step 1 into a vacuum induction melting furnace for melting, refining for 1 to 5 times to make the alloy uniform, and then take out the master alloy ingot;
[0052] ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2: Utilize the anodic oxidation technology in Zr 53 Al 16 co 23.25 Ag 7.75 Fabrication of highly ordered nanotube arrays on the surface of bulk amorphous alloys
[0060] In this embodiment, the selected amorphous alloy composition is Zr 53 Al 16 co 23.25 Ag 7.75 , the preparation method of the nanotube array structure is as follows:
[0061] Step 1: Ingredients
[0062] Calculate the weight of each element related to it according to the required number of atoms. In the actual preparation process, convert the atomic amount of each element into mass weighing, which is a common knowledge in the field;
[0063] Step 2: Melting master alloy ingot
[0064] Put the raw materials weighed in step 1 into a vacuum induction melting furnace for melting, refining for 1 to 5 times to make the alloy uniform, and then take out the master alloy ingot;
[0065] Melting conditions: when smelting raw materials, the vacuum degree in the vacuum induction melting furnace ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Embodiment 3: Utilize the anodic oxidation technology in Zr 56 Al 16。5 co 25 Nb 2.5 Fabrication of highly ordered nanotube arrays on the surface of bulk amorphous alloys
[0072]In this embodiment, the selected amorphous alloy composition is Zr 56 al 16.5 co 25 Nb 2.5 , the preparation method of the nanotube array structure is as follows:
[0073] Step 1: Ingredients
[0074] Calculate the weight of each element related to it according to the required number of atoms. In the actual preparation process, convert the atomic amount of each element into mass weighing, which is a common knowledge in the field;
[0075] Step 2: Melting master alloy ingot
[0076] Put the raw materials weighed in step 1 into a vacuum induction melting furnace for melting, refining for 1 to 5 times to make the alloy uniform, and then take out the master alloy ingot;
[0077] Melting conditions: when smelting raw materials, the vacuum degree in the vacuum induction melting furnace is > ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com