Fermentation control process for Mut<s> type recombinant Pichia pastoris
A technology of Pichia pastoris and fermented liquid, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, measurement/inspection of microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., and can solve the problems of slow methanol utilization rate, easy drift and failure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
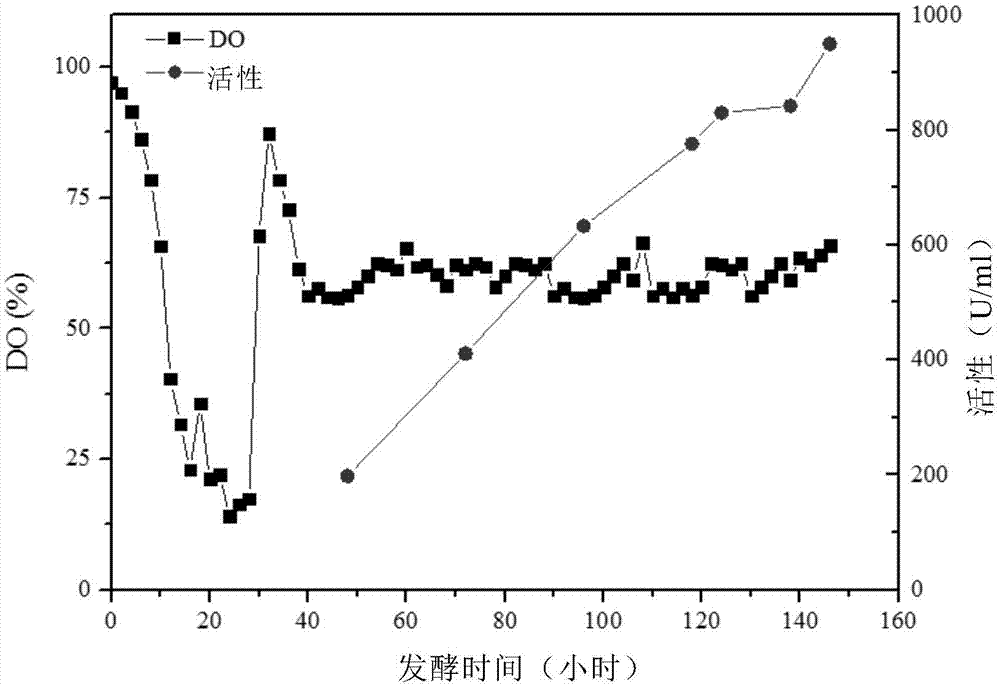
[0156] Embodiment 1 adopts a single DO control strategy.
[0157] Such as figure 1 As shown, the whole fermentation process is divided into three stages, 0-24h is the glycerol batch fermentation stage, DO is reduced from the initial 100% to 14.1%, 24-28h is the glycerol feeding stage, DO% is maintained at 15-20%, After the wet weight of the bacteria reaches 200g / L, pulse 1g / L methanol every 1h for 4 times, so that Pichia pastoris enters the methanol adaptation period. During the adaptation period, the DO is kept at about 70-80%, and the DO drops rapidly. to 61.5%, indicating that Pichia pastoris has been able to adapt to and utilize methanol well, and the methanol feeding stage is started. The feeding control of methanol is controlled by DO feedback, and the DO is maintained at 55-65% by adjusting the methanol feeding rate between until the end of fermentation.
[0158] The fermentation results of methanol flow rate controlled by DO feedback are as follows figure 1 As shown...
Embodiment 2
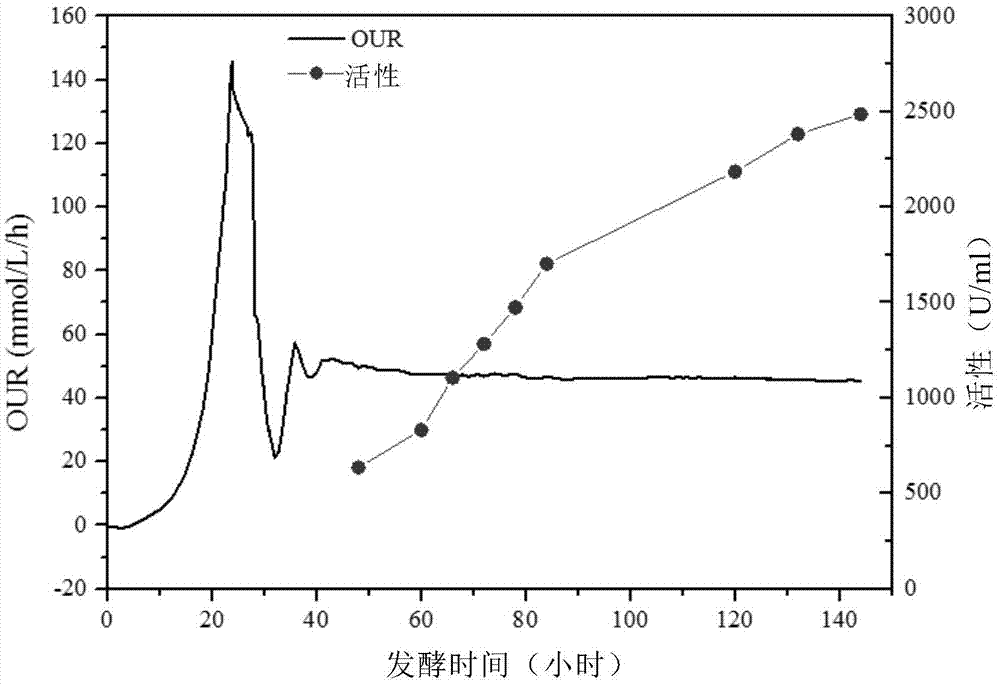
[0160] Embodiment 2 adopts the strategy of separate OUR control.
[0161] Such as figure 2 As shown, the whole fermentation process is divided into three stages, 0-24h is the glycerol batch fermentation stage, OUR rises from the initial 0mmol / L / h to 131.71mmol / L / h, 24-28h is the glycerol feeding stage, and OUR maintains At 117-131mmol / L / h, after the wet weight of the bacteria reaches 200g / L, pulse 1g / L of methanol every 1h for 4 times, so that Pichia pastoris enters the methanol adaptation period, and the OUR keeps decreasing during the adaptation period. The lowest dropped to 21.3mmol / L / h, and then began to rebound to 50mmol / L / h, and then OUR entered a plateau, indicating that Pichia pastoris has been able to adapt and utilize methanol well, and began to carry out the methanol feeding stage, methanol The feeding control of OUR is controlled by OUR feedback, and OUR is maintained between 45-50mmol / L / h by adjusting the methanol feeding rate until the end of fermentation.
[...
Embodiment 3
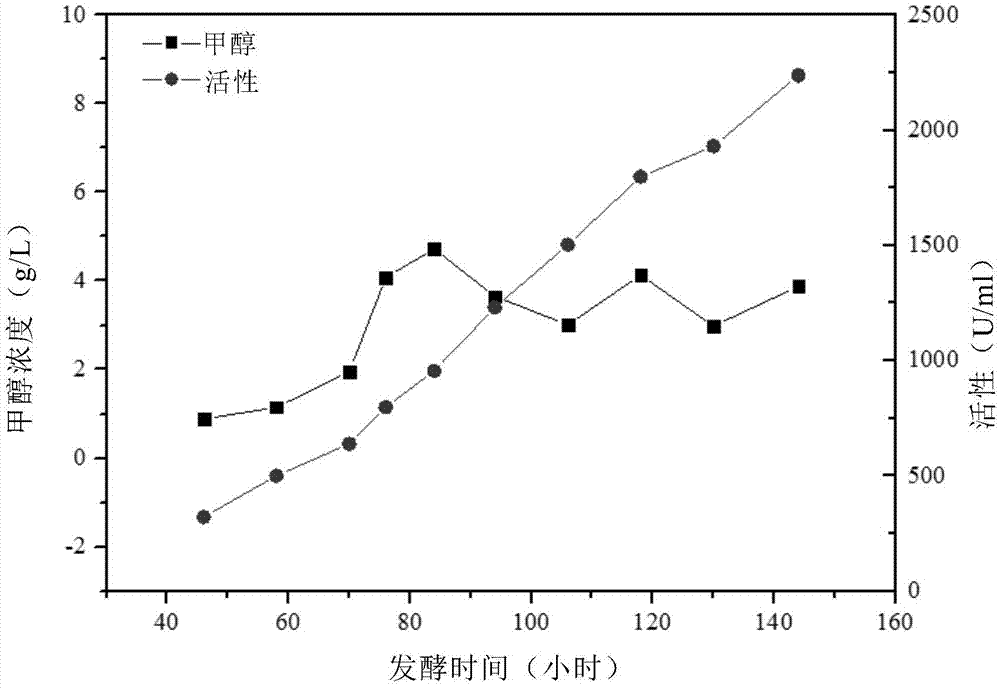
[0164] Embodiment 3 adopts the strategy of methanol concentration feedback control.
[0165] Such as image 3 As shown, the whole fermentation process is divided into three stages, 0-24h is glycerol batch fermentation stage, Pichia pastoris uses glycerol as carbon source, 24-28h is glycerol feed stage, Pichia pastoris still uses glycerol as carbon source, bacteria After the wet weight of the body reaches 200g / L, the Pichia pastoris enters the methanol adaptation period by pulse-filling 1g / L methanol every 1h for 4 times. Concentration feedback controls the concentration of methanol in the fermentation broth at 3-5g / L until the end of fermentation.
[0166] The final fermentation result of methanol flow rate controlled by methanol concentration feedback is as follows: image 3 As shown, it can be seen that the final yield is 2238U / ml.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com