Unfrozen-water content calculating method based on frozen soil heat-conduction coefficient
A technology of thermal conductivity and calculation method, which is applied in the field of calculation of unfrozen water content based on the thermal conductivity of frozen soil, can solve the problems of easy loss of heat, difference in accuracy, and difficulty in guaranteeing the accuracy of test specific heat, etc., and achieves convenient calculation of temperature field. convenient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
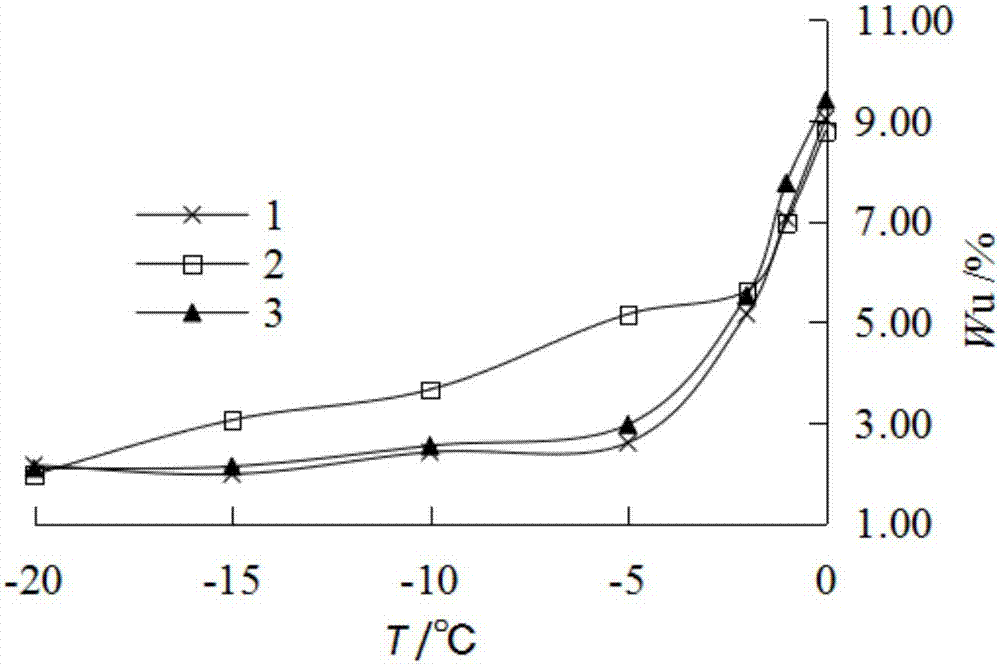
[0027] The calculation method of the unfrozen water content based on the thermal conductivity of frozen soil of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0028] The principle of the calculation method of unfrozen water content based on the thermal conductivity of frozen soil of the present invention: Based on the three-phase composition of saturated frozen soil, the calculation method of thermal conductivity is deduced according to the geometric average method, and on this basis, a method based on the thermal conductivity of frozen soil is proposed. Calculation method of unfrozen water content.
[0029] The method for calculating unfrozen water content based on the thermal conductivity of frozen soil provided by the present invention includes the following steps:
[0030] 1) Determine the dry density as ρ d The thermal conductivity λ of the saturated frozen soil sample at negative temperature is measured after drying the saturated frozen s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com