General database transparent encryption system
A transparent encryption and database technology, applied in the fields of information security and database encryption, can solve the problem of not supporting general database types and general SQL statement types, and achieve the effect of reducing storage overhead, high versatility, and preventing data leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
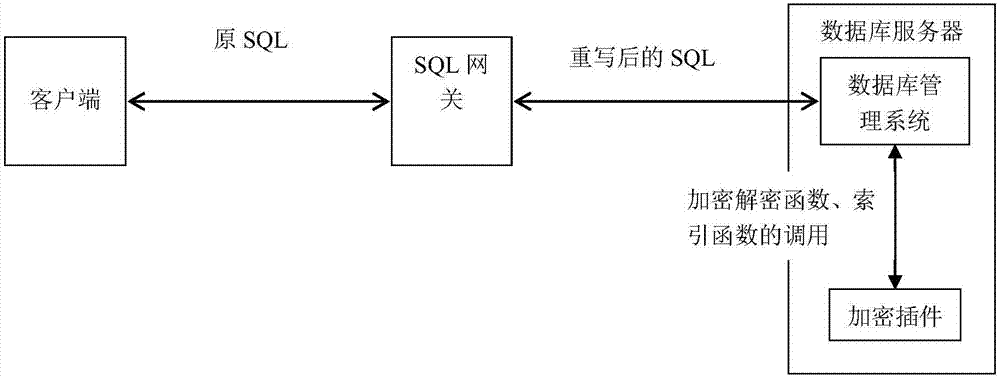
[0038] Such as figure 1 Shown is a structural schematic diagram of a general database transparent encryption system, which consists of figure 1 It can be seen that the database encryption system is composed of SQL gateway and encryption plug-in. The SQL gateway is located at the entrance of the database in the form of a proxy, accepts all access to the database, rewrites the access and forwards it to the database instance, and the database instance invokes the encryption plug-in according to the received request to realize transparent encryption and decryption of the database.
[0039] The specific steps for a SQL request to be processed are as follows:
[0040] Step (1) The client sends a SQL request;
[0041] Step (2) The SQL gateway receives the SQL request and rewrites it according to the SQL content;
[0042] Step (3) The SQL gateway sends the rewritten SQL request to the database instance;
[0043] Step (4) The database instance executes the received SQL request, and...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Taking the ORACLE database as an example, this embodiment describes in detail the encryption transformation process of the existing ORACLE data table by a general database transparent encryption system of the present invention.
[0048]Table 1 shows the original data table T1 before encryption in this embodiment. It includes two fields C1 and C2 and there are already some records. The field ROWID is a pseudo-column provided by the ORACLE system, and its value indicates the physical location of each record, and is also the unique identifier of the encrypted record. C1 is a character field, which is a non-sensitive field and does not need to be encrypted. C2 is a numeric field and is a field to be encrypted.
[0049] Table 1: T1
[0050] ROWID C1 C2 1 APPLE 1 2 BEE 2 3 CAT 3 4 DOG 4
[0051] First, for the table T1 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the field C2 is renamed to EC2, and the ciphertext encrypted by the origin...
Embodiment 3
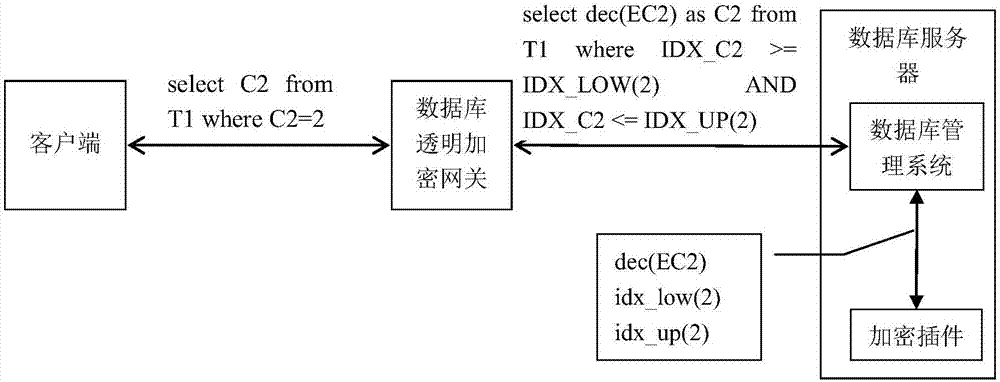
[0058] This embodiment elaborates in detail the specific processing of the SELECT request during the implementation of a general database transparent encryption system of the present invention.
[0059] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that for the SELECT request, the SQL gateway replaces the encrypted field before WHERE with a decryption function call, especially, replaces the encrypted field in the WHERE query condition or the encrypted field in the range query condition with the call of the order-preserving index function. For example, for an equivalence query:
[0060] SELECT C2 FROM T1 WHERE C2 = 2;
[0061] Rewritten on the SQL Gateway, this translates to:
[0062] SELECT DEC(EC2) AS C2 FROM T1 WHERE IDX_C2>=IDX_LOW(2)
[0063] AND IDX_C2<=IDX_UP(2);
[0064] The SQL gateway replaces the encrypted field C2 outside the query condition in the statement with the call of the decryption function DEC(). The parameter of this function call is the content of the correspond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com