Rotor structure of magnetic levitation ultra high speed permanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor and rotor structure technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic attraction or thrust holding device, etc., can solve the problem of weakening the effective magnetic field of permanent magnets and the bearing capacity of magnetic bearings Large size, high volume and weight, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the critical speed of the first-order bending, increasing the linear speed, and reducing the weight of the rotor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
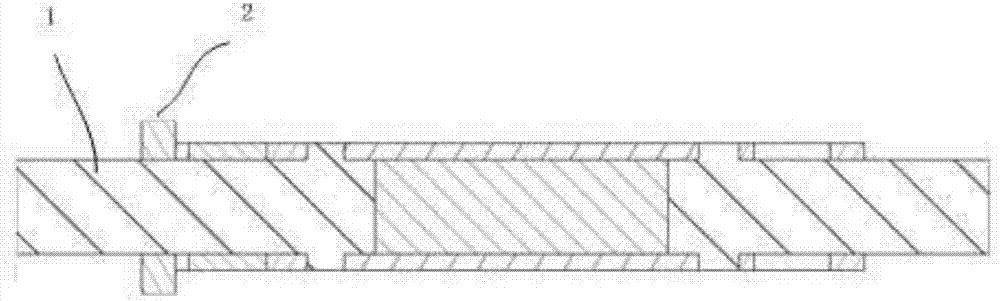
[0026] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment discloses a rotor structure of a maglev ultra-high-speed permanent magnet motor, which is a classic three-section shaft structure as a whole. The thrust disc and the left shaft are combined into one, which is the thrust disc shaft 1, which is made of high yield strength magnetic metal material, and the corresponding part of the thrust disc must be a solid structure, which can reduce the maximum centrifugal stress by half, and the thrust disc shaft 1 The part in contact with the permanent magnet 3 must be a hollow structure, which can reduce the short-circuit effect on the magnetic field of the permanent magnet 3 . The rest of the thrust disc shaft 1 can be made into a hollow structure to reduce the weight of the shaft 4 . The first magnetic bearing assembly 5 of the radial magnetic bearing on the right side of the thrust disk shaft 1 is a ring structure, usually made of silicon steel sheets to reduce eddy current loss. The fi...
Embodiment 2
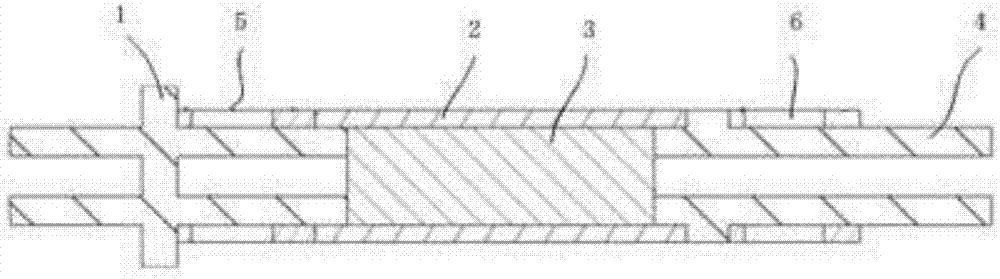
[0033] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment discloses a rotor structure of a maglev ultra-high-speed permanent magnet motor. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the shaft 4 in this embodiment is made of magnetically conductive material, and the shaft 4 is in contact with the permanent magnet 3 The part of the permanent magnet 3 is a hollow structure, and the end away from the permanent magnet 3 adopts a closed structure. The shaft 4 is the shaft extension end, which needs to be connected with the load. In some practical occasions, it is better to use a solid shaft, and it can also have the advantages of a hollow structure to reduce the mass.
[0034] In addition, the sheath 2 is made of carbon fiber composite material, because the thermal expansion coefficient of carbon fiber composite material is basically 0, which cannot be assembled by heating, and can only be assembled by cooling.
Embodiment 3
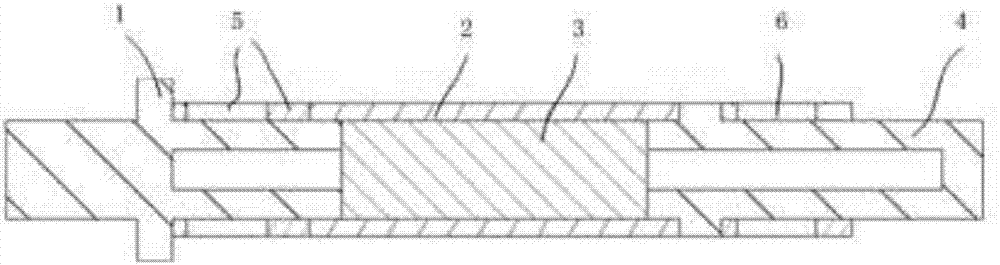
[0036] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment discloses a rotor structure of a magnetic levitation ultra-high-speed permanent magnet motor. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the shaft 4 in this embodiment is made of non-magnetic material, and its whole is a solid structure. The shaft 4 is made of non-magnetic material, which can make the magnetic flux leakage of the permanent magnet smaller.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com