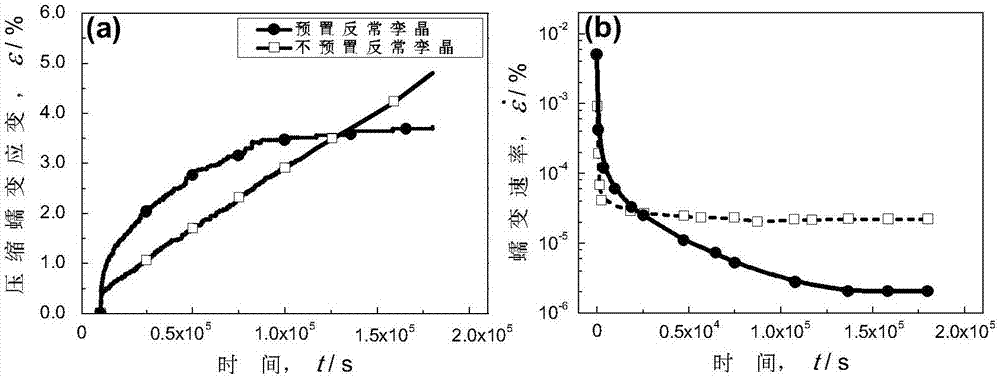
Method for improving high-temperature creep resistance of rare-earth-containing magnesium alloy by virtue of anomalous twin crystals
A technology of creep resistance and rare earth magnesium, which is applied in the field of high temperature creep resistance, can solve the problems of increased production cost, increased alloy density, and aggravated rare earth elements, etc., and achieves low environmental protection cost, improved creep resistance, and applicable materials wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The raw material used in this embodiment is as-cast Mg-6Gd-3Y-1Zn-0.4Zr magnesium alloy. The average grain size of the as-cast state is about 70 μm. The orientation of the grains is analyzed based on the electron backscattering technique, and the loading direction is selected according to the result of the orientation distribution. At 300℃, pre-compress the test piece along the direction of the angle 20~70° with the normal direction of the base surface, and the compression rate is 0.003s -1 , The amount of strain is about 0.005 to 0.05.
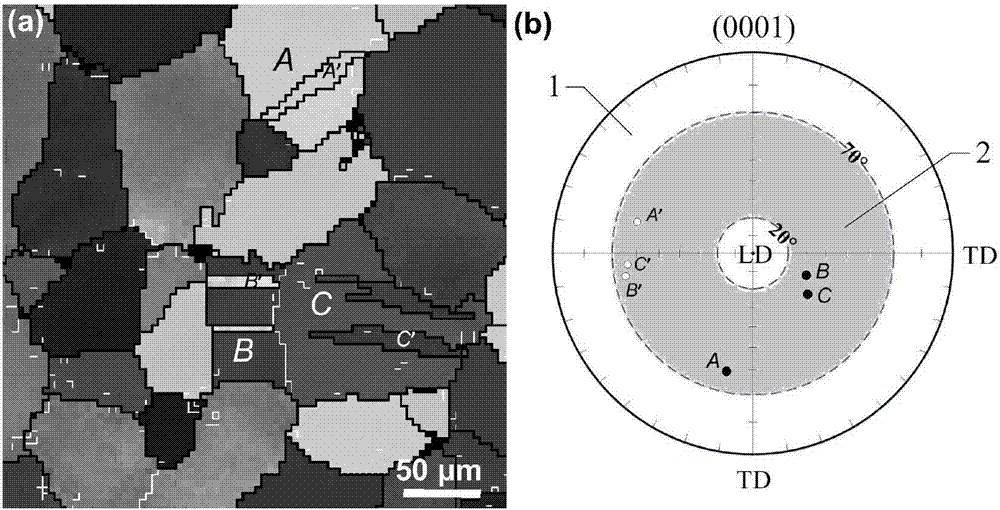
[0026] The distribution map of the tissue orientation of the specimen after compression is as follows figure 1 As shown in (a), the (0001) basal pole distribution map of the twin crystal grain matrix A, B, C and their corresponding twins A’, B’, C’ figure 1 (b) made. will figure 1 (b) The area is divided, where LD (Loading Direction) is the loading direction, TD (Transverse Direction) is 90° transverse to the loading direction. When comp...
Embodiment 2
[0029] In this embodiment, the raw material used is Mg-6Gd-3Y-0.4Zr hot-rolled sheet. After homogenization annealing at 500℃ for 2h, the average grain size is about 100μm. At 30℃, 0.03s -1 The test piece is pre-stretched in the direction of the angle between the lower edge and the normal direction of the base surface at 20-70°, and the strain is about 0.01-0.03.
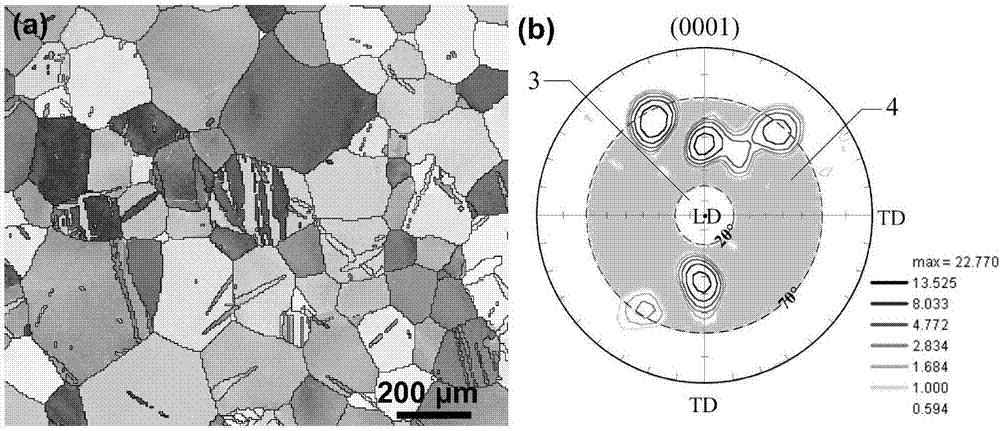
[0030] Analyze the grain orientation of the tensile specimen based on the electron backscattering technique, and obtain the orientation distribution image 3 (a), draw the (0001) basal plane pole figure containing the twin crystal grain matrix and divide its area. When stretched along the loading direction, 3 is the normal twin zone and 4 is the abnormal twin zone, such as image 3 (b) Shown. From image 3 (b) It can be seen that the angle between the loading direction and the normal direction of the (0001) basal plane of these grains is mainly concentrated at 20-70°, which meets the 15-75° abnormal twinning criterion. ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] In this embodiment, the raw material used is Mg-2Y magnesium alloy hot-rolled sheet, and after homogenization annealing at 450° C. for 2 hours, the average grain size is about 120 μm. It is pre-cured repeatedly at 150°C. Due to the particularity of the repeated bending deformation method, the tissues on both sides of the neutral layer will be subjected to loads in two opposite directions during the repeated bending process. The appropriate bending method should be selected to ensure that the base surface of the grain is 15-60° with the loading direction, and the cumulative strain is about 0.002 to 0.04.
[0034] Orientation distribution of tissue after pre-deformation treatment Figure 5 (a) Analyze the (0001) basal pole figure containing twin crystal grains Figure 5 (b) make and divide areas, Figure 5 In (b) 5 is the normal twin zone corresponding to stretching or compression along the loading direction during repeated bending, and 6 is the abnormal twin zone. by Figu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com