Fibre optic cable with tuned transverse sensitivity
A cable and optical fiber technology, applied in the field of optical fiber cable and its manufacturing, can solve the problems of cover, insensitivity of incident pressure wave, identification and detection of backscattered signal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
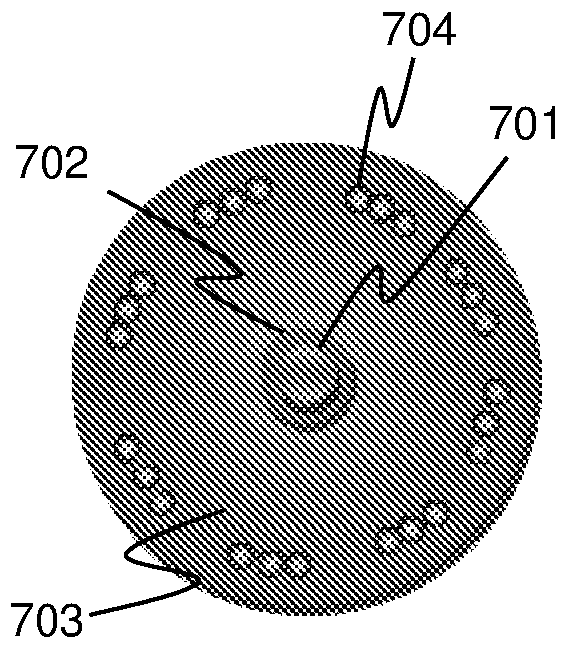
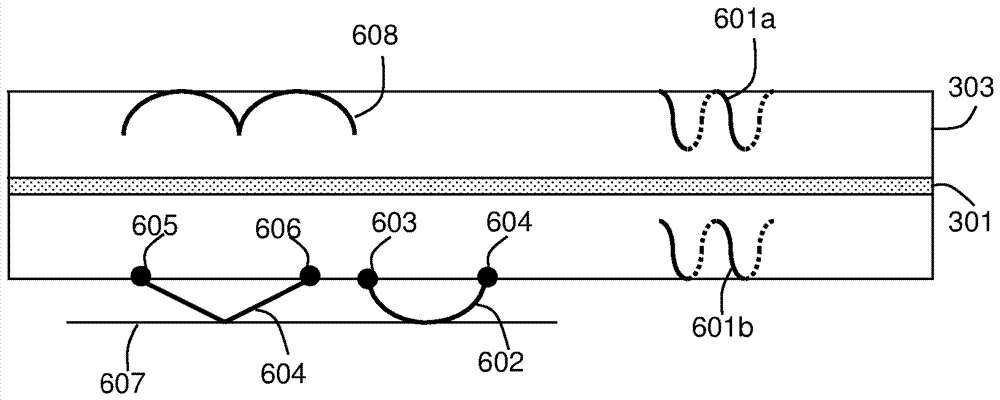
[0052] Embodiments of the present invention relate to a fiber optic cable suitable for use in fiber optic sensing, such as distributed acoustic sensing (DAS), with a desired or tuned sensitivity to transverse strain. Some embodiments relate to fiber optic cables suitable for distributed fiber optic sensing that have relatively good sensitivity to transverse strain (eg, improved transverse sensitivity compared to conventional fiber optic cables). Other embodiments relate to fiber optic cables suitable for distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) that are substantially insensitive to transverse strain.
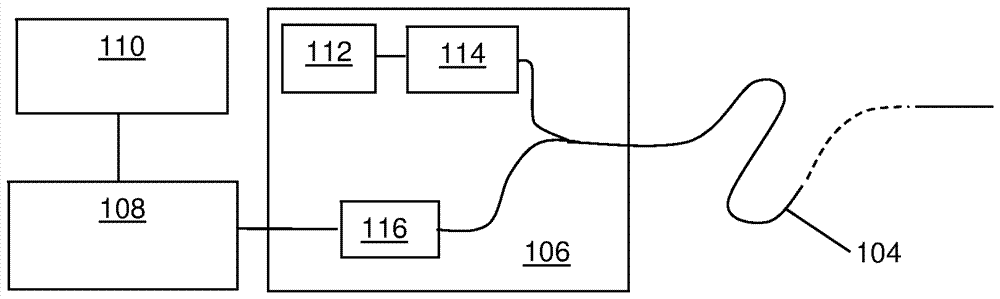
[0053] figure 1Schematic showing the distributed fiber optic sensing setup. A length of sensing fiber optic 104 is removably connected to an interrogator 106 at one end. The output from the interrogator 106 is passed to a signal processor 108 which may be co-located with the interrogator or which may be remote from the interrogator, and optionally to a user interface which in practi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com